Abstract
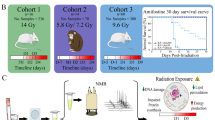
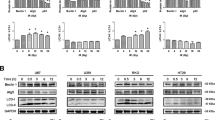
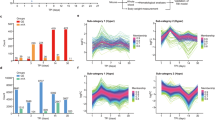
IT has been shown previously that the rate of formation of deoxyribonucleio acid is depressed by a sublethal dose of X-rays. Both the incorporation of phosphorus-321–5 and that of carbon-14 6,7 was found to be reduced about 50 per cent. The rate of incorporation of carbon-14 into the purines of ribonucleic acid is reduced as well7, though to a smaller extent than its incorporation into the purines of deoxyribonucleic acid. These blocking effects are presumably due to in-activation of enzymes involved in the synthesis of the deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid compounds. One or a few days after irradiation, the incorporation of carbon-14 into purines of deoxyribonucleic acid has nearly returned to the rate for the non-irradiated controls. This suggests that a partial reactivation has occurred. The early metabolic changes produced by irradiation are not confined to interference with nucleic acid synthesis. We find that irradiation interferes with glucose metabolism as well.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Euler, H., and Hevesy, G., Kungl. Danske Videnskab., Selskab. Biol. Med., 17, No. 8 (1942).
cf. Hevesy, G., “Radioactive Indicators” (Interscience Pub., New York, 1948).
Holmes, B., Brit. J. Radiol., 20, 450 (1947); 22, 487 (1949).
Holmes, B., Proc. Ciba Foundation (in the press).
Kelly, L. S., and Jones, H. B., Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 74, 493 (1950).
Hevesy, G., Nature, 163, 869 (1948).
Abrams, R., Archiv. Biochem., 30, 90 (1951).
Feller, D. D., Strisower, E. H., and Chaikoff, I. L., J. Biol. Chem., 187, 571 (1950).
Lourau, M., and Lartigue, O., Experientia, 6, 25 (1950).
Lourau, M., and Lartigue, O., C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 230, 1426 (1950).
Lourau, M., and Lartigue, O., C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 232, 1144 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HEVESY, G., FORSSBERG, A. Effect of Irradiation by X-Rays on the Exhalation of Carbon Dioxide by the Mouse. Nature 168, 692 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/168692a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/168692a0