Summary:
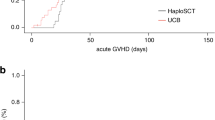
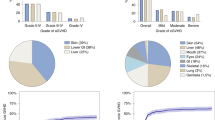
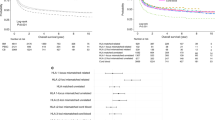
HLA disparity is a major risk factor for graft rejection and GVHD. We report a patient with CML (accelerated phase) who underwent allogeneic SCT from a mismatched unrelated donor and developed acute GVHD. With immunosuppression, GVHD symptoms improved but graft rejection occurred. After a second conditioning regimen, the patient received a second graft from a haploidentical related donor. Engraftment occurred, but the patient died from GVHD and pulmonary aspergillosis. Chimeric analysis revealed that all leukocytes were of donor 2 origin apart from CD3+ T cells, which were 100% donor 1 type. Thus, in spite of intensified immunosuppression and successful transplantation of a second graft, T cells from the first donor persisted and induced severe acute GVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Storb R, Prentice RL, Thomas ED et al Factors associated with graft rejection after HLA-identical marrow transplantation for aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 1983; 55: 573–585.
Uharek L, Glass B, Gaska T et al. Influence of donor lymphocytes on the incidence of primary graft failure after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a murine model. Br J Haematol 1994; 88: 79–87.
Martin PJ, Hansen JA, Buckner CD et al. Effects of in vitro depletion of T cells in HLA-identical allogeneic marrow grafts. Blood 1985; 66: 664–672.
Martin PJ . Donor CD8 cells prevent allogeneic marrow graft rejection in mice: potential implications for marrow transplantation in humans. J Exp Med 1993; 178: 703–712.
Beatty PG, Clift RA, Mickelson EM et al. Marrow transplantation from related donors other than HLA-identical siblings. N Engl J Med 1985; 313: 765–771.
Einsele H, Ehninger G, Hebart H et al. Polymerase chain reaction monitoring reduces the incidence of cytomegalovirus disease and the duration and side effects of antiviral therapy after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1995; 86: 2815–2820.
Einsele H, Hebart H, Kauffmann-Schneider C et al. Risk factors for treatment failures in patients receiving PCR-based preemptive therapy for CMV infection. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 757–763.
Bader P, Stoll K, Huber S et al. Characterization of lineage-specific chimaerism in patients with acute leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation before and after relapse. Br J Haematol 2000; 108: 761–768.
McGlave P, Bartsch G, Anasetti C et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia: initial experience of the National Marrow Donor Program. Blood 1993; 81: 543–550.
Goldman JM, Druker BJ . Chronic myeloid leukemia: current treatment options. Blood 2001; 98:2039–2042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiesmann, A., Bader, P., Bamberg, M. et al. Severe acute graft-versus-host disease after T-cell depleted allogeneic stem cell graft from a second donor caused by persisting T-cells from the first donor. Bone Marrow Transplant 32, 511–513 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704170
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704170
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Second allo-SCT from a different donor can improve severe steroid-resistant gut GVHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)
-
Autologous/syngeneic stem cell transplantation to treat refractory GvHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2004)