Summary:
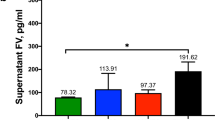
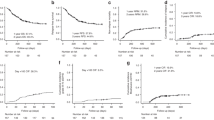
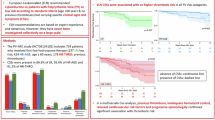
The hypercoagulable state caused by the use of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) has been cited in anecdotal reports. Since tissue factor (TF) is the main initiator of the coagulation cascade, we examined if rhG-CSF had an inductive effect on the TF-dependent pathway in 18 healthy donors receiving rhG-CSF (10 μg/kg/day × 5 days) for peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization. After rhG-CSF, there were increases both in TF antigen (TF:Ag) (P=0.01) and TF procoagulant activity (TF:PCA) (P=0.06) plasma levels and in TF:Ag cytofluorimetric expression on CD33 (+) cells (P=0.04). Mean activities of FVIII and vWF also increased significantly. Thrombin time was slightly prolonged (P=0.06) due to significant increases in plasma D-dimer levels. In addition, while FIX activity remained stable, there were marked reductions in mean plasma FX and FII activities and a slight decrease in FVII activity that resulted in a significant prolongation of prothrombin time within normal ranges. In conclusion, the administration of rhG-CSF led to a ‘prothrombotic state’ via stimulation of TF and increased endothelial markers, such as F VIII and vWF. In the light of these findings, the use of rhG-CSF for stem cell mobilization should be undertaken cautiously in healthy donors with underlying thrombotic risk factors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderlini P, Körbling M, Dale D et al. Allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: consideration for donors. Blood 1997; 90: 903–908.
Anderlini P, Rizzo JD, Nugent ML et al. Peripheral blood stem cell donation: an analysis from the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry (IBMTR) and European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplant (EBMT) databases. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 689–692.
Conti JA, Scher HI . Acute arterial thrombosis after escalated-dose methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin and cisplatin chemotherapy with recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Cancer 1992; 70: 2699–2702.
Barbui T, Finazzi G, Grassi A, Marchioli R . Thrombosis in cancer patients treated with hematopoietic growth factors – a meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost 1996; 75: 368–371.
Schimoda K, Okamura S, Harada N et al. Identification of a functional receptor for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on platelets. J Clin Invest 1993; 9: 1310–1313.
Kanaji T, Okamura T, Nagafuji K et al. Megakaryocytes produce the receptor for granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Blood 1995; 85: 3359–3360, (Letter).
Kawachi Y, Watanabe A, Uchida T et al. Acute arterial thrombosis due to platelet aggregation in patient receiving granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 413–416.
Rappaport SI, Rao LVM . The tissue factor pathway: how it has become a ‘Prima Ballerina’. Thromb Haemost 1995; 74: 7–17.
Nemerson Y, Giesen PLA . Some thoughts about localization and expression of tissue factor. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 1998; 9: 45–47.
Rao LVM, Pendurthi UR . Tissue factor on cells. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 1998; 9: 27–35.
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Evangelista V et al. Neutrophil activation and haemostatic changes in healthy donors receiving granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1999; 93: 2506–2514.
Kuroiwa M, Okamura T, Kanaji T et al. Effects of granulocyte colony stimulating factor on the hemostatic system in healthy volunteers. Int J Hematol 1996; 63: 311–316.
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Oldani E et al. Changes of hemostatic parameters in healthy donors administered rhG-CSF for allogeneic blood progenitor cells (PBPC) collection. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 72a (Abstr.).
Nemerson, Y . Tissue factor in neutrophils. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: 802.
Bussolino F, Wang JM, Paola D et al. Granulocyte- and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factors induce human endothelial cells to migrate and proliferate. Nature 1989; 337: 471–472.
Blann AD, Taberner DA . A reliable marker for endothelial cell dysfunction: does it exist? Br J Haematol 1995; 90: 244–252.
LeBlanc R, Roy J, Demers C et al. Prospective study of rhG-CSF effects on hemostasis in allogeneic blood stem cell donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 991–996.
Dahlback B . Resistance to activated protein C, the Arg506 to Gln mutation in the factor V gene, and venous thrombosis. Functional tests and DNA-based assays, pros and cons. Thromb Haemost 1995; 73: 739–742.
Ozcan M . Changes in the natural anticoagulants following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Turk J Haematol 2000; 17: 138–142.
Lee KH, Lee JH, Choi SJ et al. Randomized comparison of two different schedules of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 24: 591–599.
Lindemann A, Herrmann F, Oster W et al. Hematologic effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor in patients with malignancy. Blood 1989; 8: 2644–2651.
Morrison AE, Green RHA, Watson D et al. Hematological and immunological changes in sibling allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cell donors. Blood 1997; 90: 391b (Abstr.).
Østerud B . The high responder phenomenon: enhancement of LPS induced tissue factor activity in monocytes by platelets and granulocytes. Platelets 1995; 6: 119–125.
Bach RR, Moldow CF . Mechanism of tissue factor activation on HL-60 cells. Blood 1997; 89: 3270–3276.
Albrecht S, Kotzsch M, Siegert G et al. Detection of circulating tissue factor and factor VII in a normal population. Thromb Haemost 1996; 75: 772–777.
Fukuda C, Iijima K, Nakamura K . Measuring tissue factor (factor III) activity in plasma. Clin Chem 1989; 35: 1890–1897.
Hidekazu T, Nakamura S, Higure A . Neutrophils express tissue factor in a monkey model of sepsis. Surgery 2000; 127: 209–216.
sterud B, Rao LVM, Olsen JO . Induction of tissue factor expression in whole blood: lack of evidence for the presence of tissue factor expression in granulocytes. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: 861–867.
Morton CT, Solovey A, Dandelet L . Enhanced expression of tissue factor (TF) by circulating endothelial cells following bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: 173a (Abstr.).
Ozcan M, Morton CT, Solovey A et al. Whole blood tissue factor procoagulant activity remains during severe aplasia following bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Thromb Haemost 2001; 85: 250–255.
Ozcan M, Beksac M . Is there a relationship between rhG-CSF response to conditioning regimen and engraftment after bone marrow transplantation? Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 533–535.
Kjalke M, Sorensen O, Niels B et al. Tissue factor expression by rabbit and human neutrophils. Thromb Haemost 1999; 94: 761 (Abstr.).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Ankara University Research Fund (99-09-00-006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topcuoglu, P., Arat, M., Dalva, K. et al. Administration of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor for allogeneic hematopoietic cell collection may induce the tissue factor-dependent pathway in healthy donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 33, 171–176 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704341
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704341
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Deep vein thrombosis: a less noticed complication in hematologic malignancies and immunologic disorders
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2020)
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) increases histone-complexed DNA plasma levels in healthy volunteers
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2017)
-
PBSC collection from family donors in Japan: a prospective survey
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Drug-Induced Thrombosis: An Update
Drug Safety (2013)
-
A novel perspective on stem cell homing and mobilization: review on bioactive lipids as potent chemoattractants and cationic peptides as underappreciated modulators of responsiveness to SDF-1 gradients
Leukemia (2012)