Abstract
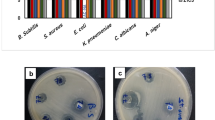
A SPECIFIC reaction has been found between complexes of the zinc group metals and the bacterial virus, T 2 r +. Zinc ions (M/100) do not inactivate T 2 r +, but if a variety of metal-complexing agents are added to a solution containing zinc nitrate and T 2 r +, the virus is rapidly and irreversibly inactivated. Identical reactions occur with cadmium ions. Mercuric mercury inactivates T 2 as the free ion as well as when present as a complex ion. Cyanide complexes of all three metals and iodide complexes of cadmium and mercuric mercury inactivate the virus. Inactivation also occurs when a number of amino-acids (such as M/100 glycine or glutamic acid) and pure proteins (such as trypsin or chymotrypsin at 2 mgm./ml.) are used as metal-complexing agents. Versene complexes of zinc, cadmium or mercuric mercury do not affect the virus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lanni, F., and Lanni, Y. T., Cold Spring Harbor Symp., 18, 159 (1953).
Hershey, A. D., and Chase, M., J. Gen. Physiol., 36, 39 (1952).
Barrington, L. F., and Kozloff, L. M., Science, 120, 110 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOZLOFF, L., HENDERSON, K. Action of Complexes of the Zinc Group Metals on the Tail Protein of Bacteriophage T 2 r + . Nature 176, 1169–1171 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1038/1761169b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1761169b0
This article is cited by
-
Photoaktivierbare Antiviruswirkung von Porphyrinen
Zeitschrift für Hygiene und Infektionskrankheiten (1957)