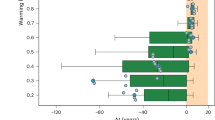
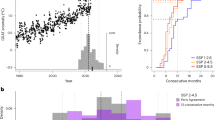
Abstract
THE thermal conductivity of powdered plaster of Paris was reported in 1896 by Lees and Chorlton1. Their value of 0.00261 gm. cal./sec./deg C./cm. has since been incorporated into the literature of heat transfer, primarily through the medium of the “International Critical Tables”. So recently as 1950, text-books have continued to report this value. Unfortunately, the decimal point in the original paper and subsequent copies has been misplaced. Lees and Chorlton should have reported a value of 0.000261 gm. cal./sec./deg. C./cm.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lees, C. H., and Chorlton, J. D., Phil. Mag., 41, 495 (1896).
Ingersoll, L. R., Zobel, O. J., and Ingersoll, A. C., “Heat Conduction” (Univ. Wisconsin Press, 1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BROWN, W. Thermal Properties of Plaster of Paris in the Powdered Form. Nature 179, 1187 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1038/1791187a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1791187a0