Abstract
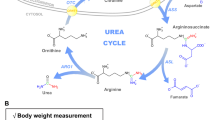
THE major pathway of histidine breakdown is to glutamic acid, and this occurs via two relatively stable intermediate compounds, urocanic acid and formimino-glutamic acid. A competent folic-acid coenzyme is required to accept the formimino-group in the last stage of this pathway. When there is impaired, folic-acid function formimino-glutamic acid accumulates and is excreted in the urine. This has been widely used as a test of folic-acid deficiency in man1, the urinary excretion of formimino-glutamic acid being measured after an oral dose of 15 g of histidine hydrochloride. The urinary excretion of formiminoglutamic acid after oral doses of histidine may be accompanied by the excretion of urocanic acid2. The purpose of this communication is to direct attention to the importance of urocanic acid in the urine of patients with megaloblastic anæmia and other disease states following oral doses of 15 g of histidine hydrochloride.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luhby, A. L., Cooperman, J. M., and Teller, D. N., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. N.Y., 101, 351 (1958).
Bennett, Myra C., and Chanarin, I., Lancet, ii, 1095 (1961).
Chanarin, I., and Bennett, Myra C., Brit. Med. J., i, 27 (1962).
Baldridge, R. C., J. Biol. Chem., 231, 207 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BENNETT, M., CHANARIN, I. Urinary Excretion of Urocanic Acid and Formimino-glutamic Acid. Nature 196, 271–272 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/196271a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/196271a0