Abstract
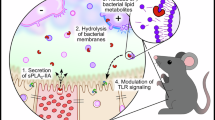
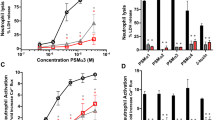
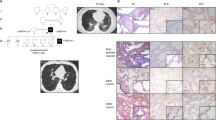
IT was previously reported1 that toxin from an αβ strain (B.S.M. 24) of Staphylococcus pyogenes contained a phospholipase which hydrolysed phosphatidyl inositol and lysophosphatidyl inositol.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Magnusson, B. J., Doery, H. M., and Gulasekharam, J., Nature, 196, 270 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DOERY, H., MAGNUSSON, B., CHEYNE, I. et al. A Phospholipase in Staphylococcal Toxin which hydrolyses Sphingomyelin. Nature 198, 1091–1092 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/1981091a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1981091a0
This article is cited by
-
Immunopathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus pulmonary infection
Seminars in Immunopathology (2012)
-
Removal of phospho-head groups of membrane lipids immobilizes voltage sensors of K+ channels
Nature (2008)