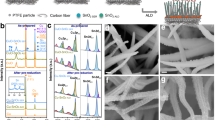
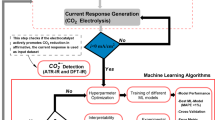
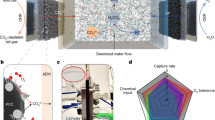
Abstract
WE have recently analysed a sample of medical oxygen by mass spectrometry, and found that the level of carbon monoxide, approximately 1 per cent, far exceeded the toxic level for humans. Subsequent investigation of the literature disclosed that this phenomenon is to be expected because of the interaction of oxygen with carbon impurities in the hot tungsten filament of the mass spectrometer electron gun1–3. In a mass spectrometer, used for general analysis of organic compounds, there is the additional possibility that carbide is formed on the tungsten surface which may then react with oxygen in the system. Carbides of rhenium have the advantage of being less stable than those of tungsten and this has led to the widespread use of rhenium filaments. Even with a rhenium filament, however, significant quantities of carbon monoxide are produced in oxygen analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singleton, J. H., J. Chem. Phys., 45, 2819 (1966).
Schlier, R. E., J. Appl. Phys., 29, 1162 (1958).
Becker, J. A., Becker, E. J., and Brandes, R. G., J. Appl. Phys., 32, 411 (1961).
Brion, C. E., Anal. Chem., 38, 1941 (1966).
Brion, C. E., and Hall, L. D., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 88, 3661 (1966).
Beynon, J. H., Fontaine, A. E., Turner, D. W., and Williams, A. E., J. Sci. Instrum., 44, 283 (1967).
Brion, C. E., Anal. Chem., 37, 1706 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BRION, C., STEWART, W. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Oxygen. Nature 217, 946 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/217946a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/217946a0