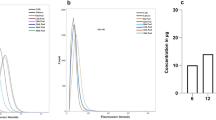
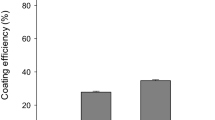
Abstract
THE importance of vitamin A (retinol) for normal growth and development of vertebrates is well established1 but its mechanism(s) of action, except in vision, remains obscure. Retinol can influence differentiation of epithelial cells2 and is required for normal development of the testis and for maintenance of pregnancy3, suggesting a regulatory role resembling that of certain hormones in some aspects of its activity. The action of many steroid hormones is apparently mediated through specific cellular binding proteins4. We have found that rat tissues5,6 and human5 and rabbit lungs7 contain a protein able to bind all-trans-retinol, the most potent vitamin A compound, with high affinity and specificity. In all species studied so far, this protein has the same apparent size (molecular weight 14,000, sedimenting in the 2S region on sucrose gradients) and seems to carry retinol as a non-covalently bound ligand in vivo6,7. It has a lower molecular weight and a different fluorescence excitation spectrum6 than that reported for the intensively studied retinol binding protein of serum8, demonstrating that we are dealing with a different protein. We have purified this cellular binding protein 1,000-fold from rat testes6 and 600-fold from rabbit lung7 and report here its specificity in binding various compounds exhibiting vitamin A activity in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore, T., in The vitamins, 1 (edit. by Sebrell, W. H., and Harris, R. S.), 245–266 (Academic, New York, 1972).
Wolbach, S. B., and Howe, P. R., J. exp. Med., 42, 753–777 (1925).
Thompson, J. N., Howell, J. McC., and Pitt, G. A., Proc. R. Soc., B 159, 510–535 (1964).
Raspe, G. (ed.), Schering workshop on steroid hormone receptors, Advances in biosciences, 7 (Pergamon–Vieweg, 1971).
Bashor, M. M., Toft, D. O., and Chytil, F., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 3483–3487 (1973).
Ong, D. E., and Chytil, F., J. biol. Chem. (in the press).
Ong, D. E., and Chytil, F., Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun., 59, 221–229 (1974).
Muto, Y., and Goodman, D. S., J. biol. Chem., 247, 2533–2541 (1972).
Ames, S. R., Swanson, W. J., and Harris, P. L., J. Am. chem. Soc., 77, 4134–4136 (1955).
Ames, S. R., Swanson, W. J., and Harris, P. L., J. Am. chem. Soc., 77, 4136–4138 (1955).
Shantz, E. M., and Brinkman, J. H., J. biol. Chem., 183, 467–471 (1950).
Van Dorp, D. A., and Arens, J. F., Nature, 158, 60 (1946).
Baxter, J. G., and Robeson, C. D., J. Am. chem. Soc., 64, 2407–2410 (1942).
Goodman, D. S., Smith, J. E., Hembry, R. M., and Dingle, J. T., J. Lipid Res., 15, 406–414 (1974).
Clamon, G. H., Sporn, M. B., Smith, J. M., and Saffiotti, U., Nature, 250, 64–66 (1974).
Glover, J., Goodwin, T. W., and Morton, R. A., Biochem. J., 43, 109–114 (1948).
Mahadevan, S., Seshadri Sastry, P., and Ganguly, J., Biochem. J., 88, 531–539 (1963).
Dowling, J. E., and Wald, G., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 46, 587–608 (1960).
Sani, B. P., and Hill, D. L., Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun., 61, 1276–1282 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ONG, D., CHYTIL, F. Specificity of cellular retinol-binding protein for compounds with vitamin A activity. Nature 255, 74–75 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255074a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255074a0
This article is cited by
-
Relationship between cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and histology of human lung tumors
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1984)
-
Structure-activity relationship of retinoids in fetal rat bone cultures
Calcified Tissue International (1981)
-
Localization of vitamin a by autofluorescence during induced metaplastic changes in cultures of skin
In Vitro (1979)
-
Retinoids, a new class of compounds with prophylactic and therapeutic activities in oncology and dermatology
Experientia (1978)
-
Mediation of retinoic acid-induced growth and anti-tumour activity
Nature (1976)