Abstract
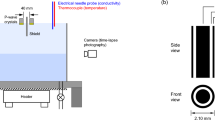
Sediment depth distributions and fluxes of dissolved chemical substances have been interpreted as being a result of reaction, diffusion, bioturbation and irrigation1,2. However, several studies suggest that density-driven convection3 can alter the depth distribution and increase the fluxes of dissolved substances when density decreases below the sediment surface4–7. We present here temperature–time series measurements for a freshwater lake undergoing autumn cooling. These are the first in situ observations of heat transport due to motion of interstitial waters over periods of less than 1 hour. Density, calculated from temperature, decreases with depth at the time and place that this motion occurs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner, R. A. Principles of Chemical Sedimentology (Princeton University Press, 1971).
Berner, R. S. Early Diagenesis. A Theoretical Approach (Princeton University Press, 1980).
Combarnous, M. A. & Bories, S. A. Adv. Hydrosci. 10, 232–309 (1974).
Hesslein, R. H. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37, 545–551 (1980).
Thorstensen, D. C. & Mackenzie, F. T. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 28, 1–19 (1974).
Harrison, W. D. & Osterkamp, T. E. J. geophys. Res. 83, 4707–4712 (1978).
Smetacek, V. F., von Bedungen, F., von Brockel, K. & Zeitzschel, B. Mar. Biol. 34, 373–378 (1976).
Brunskill, G. J., Povoledo, D., Graham, B. W. & Stainton, M. P. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 28, 277–294 (1971).
Kell, G. S. J. Chem. Engng Data 12, 66–69 (1967).
Quay, P. D. thesis, Columbia Univ. (1977).
Ray-shing Wu, Cheng, K. C. & Craggs, A. Numerical Heat Transfer 2, 303–318 (1979).
Chhuon, B. & Caltigorone, J. P. J. Heat Transfer 101, 244–248 (1979).
Green, T. & Freehill, R. L. J. appl. Phys. 40, 1759–1762 (1969).
Wooding, R. A. Proc. 2nd Workshop Geotherm Reservoir Engng, 339–345 (Stanford University Press, 1976).
Nield, D. A. Wat. Resour. Res. 4, 553–560 (1968).
Elder, J. W. J. Fluid Mech. 32, 69–96 (1968).
Carslaw, H. S. & Jaeger, J. C. Conduction of Heat in Solids 2nd edn (Oxford University Press, 1959).
Horne, R. N. & O'Sullivan, M. J. J. Fluid Mech. 66, 339–352 (1974).
Townsend, A. A. Q. Jl R. met. Soc. 90, 248–259 (1964).
Townsend, A. A., J. Fluid Mech. 24, 307–319 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musgrave, D., Reeburgh, W. Density-driven interstitial water motion in sediments. Nature 299, 331–334 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299331a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299331a0