Abstract
Study design:
Descriptive study.
Objective:
To examine the individual heart rate–oxygen uptake (HR–VO2) relationship during exercise in persons with tetraplegia (TP).
Setting:
Rehabilitation Centre Heliomare, Wijk aan Zee, The Netherlands.
Methods:
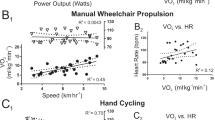
The HR–VO2 relationship was determined in untrained subjects with motor complete TP (C5 or C6, n=10 and C7 or C8, n=10) during a discontinuous graded exercise hand cycle test. The mean HR and VO2 of the final 60 s of 2-min exercise blocks were used for calculation of the individual correlation coefficient and the standard error of the estimate (SEE).
Results:
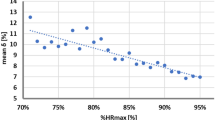
Two subjects of the C5–C6 group were not able to complete the test. Individual Pearson's correlation coefficients (r) ranged from 0.68 to 0.97 and SEE from 2.6 to 22.4% VO2-Reserve (VO2R). The mean Pearson's r and SEE were 0.81±0.12 and 10.6±5.6% VO2R in the C5–C6 group and 0.91±0.07 and 7.0±3.2% VO2R in the C7–C8 group, respectively. Two subjects of the C5–C6 group and six subjects of the C7–C8 group attained a linear HR–VO2 relationship with an acceptable SEE (⩽6.0%) and r (>0.90).
Conclusions:
The HR–VO2 relationship appeared linear in only eight out of 18 subjects. An individual analysis of the HR–VO2 relationship is necessary to determine whether HR can be used to quantify exercise intensity. The use of HR to prescribe training intensity should be reconsidered in persons with TP.
Sponsorship:
This study is supported from a grant by ZON-MW.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Figoni SF . Exercise management for persons with chronic diseases and disabilities. In: Durstine JL, Moore GE (eds). Spinal Cord Disabilities: Paraplegia and Tetraplegia. 2nd edn. Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2003, pp 247–253.
Dallmeijer AJ, van der Woude LH, Hollander AP, van As HH . Physical performance during rehabilitation in persons with spinal cord injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999; 31: 1330–1335.
Janssen TW, van Oers CA, Veeger HE, Hollander AP . Relationship between physical strain during standardised ADL tasks and physical capacity in men with spinal cord injuries. Paraplegia 1994; 32: 844–859.
Kilkens OJ, Post MW, van der Woude LH, Dallmeijer AJ, van den Heuvel WJ . The wheelchair circuit: reliability of a test to assess mobility in persons with spinal cord injuries. Arch Phys Med Rehab 2002; 83: 1783–1788.
Pollock ML et al. The recommended quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness in healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 975–991.
Hooker SP, Wells CL . Effects of low- and moderate-intensity training in spinal cord-injured persons. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1989; 21: 18–22.
DiCarlo SE . Effect on arm ergometry training on wheelchair propulsion endurance of individuals with quadriplegia. Phys Ther 1983; 63: 1104–1107.
Hopman TE, Dallmeijer AJ, Snoek G, van der Woude LHV . The effect of training on cardiovascular responses to arm exercise in individuals with tetraplegia. Eur J Appl Physiol 1996; 74: 172–179.
Bar-on ZH, Nene AV . Relationship between heart rate and oxygen uptake in thoracic level paraplegics. Paraplegia 1990; 28: 87–95.
Goosey-Tolfrey VL, Tolfrey K . The oxygen uptake–heart rate relationship in trained female wheelchair athletes. J Rehab Res Dev 2004; 41: 415–420.
Hjeltnes N . Oxygen uptake and cardiac output in graded arm exercise in paraplegics with low level spinal lesions. Scand J Rehab Med 1977; 9: 107–113.
Hooker SP, Greenwood JD, Hatae DT, Husson JS, Matthiesen TL, Waters AR . Oxygen uptake and heart rate relationship in persons with spinal cord injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1993; 25: 1115–1119.
Schmid A et al. Catecholamines, heart rate, and oxygen uptake during exercise in persons with spinal cord injury. J Appl Physiol 1998; 85: 635–641.
Tolfrey K, Goosey-Tolfrey VL, Campbell IG . Oxygen uptake–heart rate relationship in elite wheelchair racers. Eur J Appl Physiol 2001; 86: 174–178.
Glaser RM . Arm exercise training for wheelchair users. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1989; 21: S149–S157.
Freyschuss U, Knutsson E . Cardiovascular control in man with transverse cervical cord lesions. Life Sci 1969; 8: 421–424.
Hjeltnes N, Christensen CC, Rostrup M, Walberg-Hendriksson H . Altered Blood Pressure Response to Graded Exercise in Tetraplegic Subjects With Low Levels of Catecholamines. In: Hjeltnes N (ed). Thesis: Physical exercise and electrical stimulation in the management of metabolic, cardiovascular and skeletal-muscle alterations in people with tetraplegia (paper III), 1998.
Eltorai I, Kim R, Vulpe M, Kasravi H, Ho W . Fatal cerebral haemorrhage due to autonomic dysreflexia in a tetraplegic patient: case report and review. Paraplegia 1992; 30: 355–360.
Schmid A et al. Catecholamines response of high performance wheelchair athletes at rest and during exercise with autonomic dysreflexia. Int J Sports Med 2001; 22: 2–7.
McLean KP, Jones PP, Skinner JS . Exercise prescription fot sitting and supine exercise in subjects with quadriplegia. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1995; 27: 15–21.
Coutts KD, Rhodes EC, McKenzie DC . Submaximal exercise responses of tetraplegics and paraplegics. J Appl Physiol 1985; 59: 237–241.
Dallmeijer AJ, Zentgraaff ID, Zijp NI, van der Woude LHV . Submaximal physical strain and peak performance in handcycling versus handrim wheelchair propulsion. Spinal Cord 2004; 42: 91–98.
van der Woude LHV et al. Alternative modes of manual wheelchair ambulation: An overview. Am J Phys Med Rehab 2001; 80: 765–777.
Maynard Jr FM et al. International standards for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. American Spinal Injury Association. Spinal Cord 1997; 35: 266–274.
Mathias CJ, Frankel HL . Autonomic failure; a textbook of clinical disorders of the autonomic nervous system. In: Bannister R, Mathias CJ (eds). Autonomic Disturbances in Spinal Cord Lesions. 3rd edn. Oxford University Press: Oxford 1992, pp 839–881.
Borg GAV . Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1982; 4: 377–381.
van der Woude LHV et al. Wheelchair ergonomics and physiology testing of prototypes. Ergonomics 1986; 29: 1561–1573.
Swain DP, Leutholtz BC . Heart rate is equivalent to %VO2Reserve, not to%VO2max. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1997; 29: 410–414.
Furlan JC, Fehlings MG, Shannon P, Norenberg MD, Krassioukov AV . Descending vasomotor pathways in humans: correlation between axonal preservation and cardiovascular dysfunction after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2003; 20: 1351–1362.
Grimm DR, De Meersman RE, Almenoff PL, Spungen AM, Bauman WA . Sympathovagal balance of the heart in subjects with spinal cord injury. Am J Physiol 1997; 272: 835–842.
Wecht JM, de Meersman RE, Weir JP, Bauman WA, Grimm DR . Effects of autonomic disruption and inactivity on venous vascular function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2000; 278: 515–520.
Mc Crory MA, Mole PA, Nommsen-Rivers LA, Dewey KG . Between-day and within-day variability in the relation between heart rate and oxygen consumption: effect on the estimation of energy expenditure by heart-rate monitoring. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 66: 18–25.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by ZON-MW (Grant number: 014-32-012), The Netherlands Organisation for Health, Research and Development, The Hague.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valent, L., Dallmeijer, A., Houdijk, H. et al. The individual relationship between heart rate and oxygen uptake in people with a tetraplegia during exercise. Spinal Cord 45, 104–111 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101946
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101946
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The ability of heart rate or perceived exertion to predict oxygen uptake varies across exercise modes in persons with tetraplegia
Spinal Cord (2021)
-
Interrater and intrarater reliability of ventilatory thresholds determined in individuals with spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2019)
-
The influence of protocol design on the identification of ventilatory thresholds and the attainment of peak physiological responses during synchronous arm crank ergometry in able-bodied participants
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2019)
-
The intensity and match load comparison between high spinal cord injury and non-spinal cord injury wheelchair basketball players: a case report
Spinal Cord Series and Cases (2016)
-
Validity of heart rate indexes to assess wheeling efficiency in patients with spinal cord injuries
Spinal Cord (2014)