Abstract
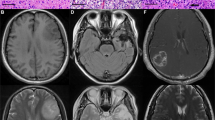
A new strategy for cancer gene therapy has been developed using a plant gene which encodes the enzyme, linamarase, that hydrolyzes the cyanogenic glucoside substrate, linamarin, into glucose, acetone and cyanide. Retroviral vectors that carry linamarase as a potential killer–suicide gene cause a marked sensitization to the innocuous substrate, linamarin, followed by cell death. We show that the system can eradicate very large intracerebral gliomas in vivo helped by a cyanide bystander effect. Animals showing a total regression of the tumor by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), do not show other appreciable toxic effects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortés, M., de Felipe, P., Martín, V. et al. Successful use of a plant gene in the treatment of cancer in vivo. Gene Ther 5, 1499–1507 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300751
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300751
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Short interfering RNAs as a tool for cancer gene therapy
Cancer Gene Therapy (2005)
-
Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir–induced cell death is enhanced by co-expression of caspase-3 in ovarian carcinoma cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2001)
-
Anti-tumoral action of cannabinoids: Involvement of sustained ceramide accumulation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation
Nature Medicine (2000)
-
Gene therapy for carcinoma of the breast: Genetic toxins
Breast Cancer Research (1999)