Abstract
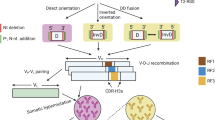
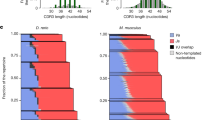
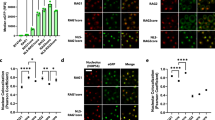
AMONG site-directed DNA recombination systems, V(D)J recombination is noteworthy in that identical reactants yield different recombination products at the junction of joined segments. This variation is the basis for diversity at the base of antigen receptor binding pockets and corresponds to V-(D)-J DNA junctions. An abundance of certain junctions has been noted1–5. It has been proposed that these junctions are favoured because they occur where short regions of homology in participating coding ends might align preferentially1. Here we use a system that is entirely free from cellular selection to show that the diversity of coding joints can be severely restricted when the coding ends participating in the reaction have short regions of homology. This constraint on diversity is diminished but not eliminated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, a mechanistic feature that has implications for the establishment of the immune repertoire.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu, H., Forster, I. & Rajewsky, K. EMBO J. 9, 2133–2140 (1990).
Gu, H., Kitamura, D. & Rajewsky, K. Cell 65, 47–54 (1991).
Feeney, A. J. J. Immun. 147, 4343–4350 (1991).
Feeney, A. J. J. Immun. 149, 222–229 (1992).
Chang, Y., Paige, C. J. & Wu, G. E. EMBO J. 11, 1891–1899 (1992).
Lieber, M. R., Hesse, J. E., Mizuuchi, K. & Gellert, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 8588–8592 (1988).
Kallenbach, S., Doyen, N., D'Andon, M. F. & Rougeon, F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2799–2803 (1992).
Lafaille, J. J., DeCloux, A., Bonneville, M., Takegaki, Y. & Tonegawa, S. Cell 59, 859–870 (1989).
Schatz, D. G., Oettinger, M. A. & Baltimore, D. Cell 59, 1035–1048 (1989).
Oettinger, M. A., Schatz, D. G., Gorka, C. & Baltimore, D. Science 248, 1517–1523 (1990).
Pergola, F., Zdzienicka, M. Z. & Lieber, M. R. Molec. cell. Biol. (in the press).
Hesse, J. E., Lieber, M. R., Mizuuchi, K. & Gellert, M. Genes Dev. 3, 1053–1061 (1989).
Hesse, J. E., Lieber, M. R., Gellert, M. & Mizuuchi, K. Cell 49, 775–783 (1987).
Meek, K. Science 250, 820–823 (1990).
Feeney, A. J. J. exp. Med. 172, 1377–1390 (1990).
Lieber, M. R. FASEB J. 5, 2934–2944 (1991).
Roth, D. B., Menetski, J. P., Nakajima, P. B., Bosma, M. J. & Gellert, M. Cell 70, 983–991 (1992).
Gearhart, P. J., Johnson, N. D., Douglas, R. & Hood, L. Nature 291, 29–34 (1981).
Claflin, J. L. & Berry, J. J. Immun. 141, 4012–4019 (1988).
Feeney, A. J., Clarke, S. H. & Mosier, D. E. J. Immun. 141, 1267–1272 (1988).
Pollok, B. A., Kearney, J. F., Vakil, M. & Perry, R. P. Nature 311, 376–379 (1984).
Briles, D. E., Forman, C., Hudak, S. & Claflin, J. L. J. exp. Med. 156, 1177–1185 (1982).
Potter, M. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 190, 306–321 (1971).
Claflin, J. L., Berry, J., Flaherty, D. & Dunnick, W. J. Immun. 138, 3060–3068 (1987).
Lal, R. B., Paranjape, R. S., Briles, D. E., Nutman, T. B. & Ottesen, E. A. J. Immun. 138, 3454–3460 (1987).
Herzenberg, L. A. & Herzenberg, L. A. Cell 59, 953–954 (1989).
Gauss, G. H. & Lieber, M. R. Genes Dev. 6, 1553–1561 (1992).
Alt, F. et al. EMBO J. 3, 1209–1219 (1984).
Kao, F.-T., Chasin, L. & Puck, T. T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 64, 1284–1291 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerstein, R., Lieber, M. Extent to which homology can constrain coding exon junctional diversity in V(D)J recombination. Nature 363, 625–627 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363625a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/363625a0
This article is cited by
-
Origin and evolutionary malleability of T cell receptor α diversity
Nature (2023)
-
Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2003)
-
Activity of DNA ligase IV stimulated by complex formation with XRCC4 protein in mammalian cells
Nature (1997)
-
Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system
Nature (1996)