Abstract
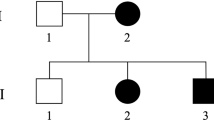
Mutations in spastin cause the most common form of pure autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraparesis (SPG4). Here, we report two Italian families affected with SPG4-linked HSP harboring two novel spastin mutations. SSCP/sequencing analysis of the spastin gene showed a single base pair deletion causing a frame-shift in one family (1442delT) and a missense mutation (1726T>C) resulting in a leucine to proline amino-acid change (L534P) in the other family. Total RNA from the mutant and the wild-type spastin allele in muscle biopsies from patients from the two affected families was quantitated. RNA expression was almost absent from the spastin allele harboring the single base pair deletion, while it was nearly normal for the spastin allele harboring the missense mutation. These data suggest that varying spastin RNA levels are found in out-of-frame and missense spastin mutations and imply different mechanisms involved in the molecular pathology of SPG4 linked HSP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hazan J, Fonknechten N, Mavel D et al: Spastin, a new AAA protein, is altered in the most frequent form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 296–303.
Fonknechten N, Mavel D, Byrne P et al: Spectrum of SPG4 mutations in autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia. Hum Mol Genet 2000; 9: 637–644.
Charvin D, Cifuentes-Diaz C, Fonknechten N et al: Mutations of SPG4 are responsible for a loss of function of spastin, an abundant neuronal protein localized in the nucleus. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 71–78.
Errico A, Ballabio A, Rugarli EI: Spastin, the protein mutated in autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia, is involved in microtubule dynamics. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 153–156.
Morrone A, Pegoraro E, Angelini C, Zammarchi C, Marconi G, Hoffman EP: RNA metabolism in myotonic dystrophy. Patient muscle shows decreased insulin receptor RNA and protein consistent with abnormal insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 1691–1698.
Acknowledgements
We thank the family members for their cooperation in this study. This work was Supported by a University of Padova grant (‘Fondi Destro’), a University of Padova grant for Young Investigators (AM), a Thelethon grant (TF0003Y01) and MURST 2001068328001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molon, A., Montagna, P., Angelini, C. et al. Novel spastin mutations and their expression analysis in two Italian families. Eur J Hum Genet 11, 710–713 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201027
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201027