Abstract
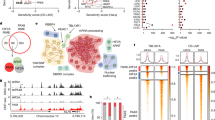
Conventional renal cell carcinoma (CRCC) may appear in families with germline translocations involving chromosome 3, although a recurrent responsible gene has not been found. We recently described a family with CRCC and a constitutional t(3;8)(p14.1;q24.23), and we demonstrated that no genes were disrupted by the translocation breakpoints. In order to investigate the genetic origin and features of the CRCC tumors that occurred in this family, we have extended the pedigree up to four generations, and analyzed peripheral blood samples from 36 members, CRCC tumors, normal renal tissues, and a gastric tumor. (1) By means of comparative genomic hybridization (CGH), we have detected loss of the derivative chromosome carrying 3p in all CRCC but not in the corresponding normal renal tissue. In addition, by means of the fluorescence in situ hybridization technique, we have observed that not all tumoral cells lose the der(3p), which suggests that, previous to this loss, another hit should occur to initiate the transformation of normal into tumoral cells. (2) All known mechanisms of inactivation of the candidate von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene have been studied in the tumors, detecting alterations in 65% of them. This confirms that inactivation of the VHL gene is not always required to develop CRCC, and that (an)other suppressor gene(s) on 3p could be involved. (3) We discard FHIT as an alternative pathway to VHL. We have not found new candidate regions along 3p by using a 1-Mb resolution array-based CGH. (4) The tumorigenesis mechanism of a second gastric tumor developed in the probandus is different from that of CRCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Maher ER, Bentley E, Yates JR et al: Mapping of the von Hippel-Lindau disease locus to a small region of chromosome 3p by genetic linkage analysis. Genomics 1991; 10: 957–960.
Maher ER, Bentley E, Yates JR et al: Mapping of von Hippel-Lindau disease to chromosome 3p confirmed by genetic linkage analysis. J Neurol Sci 1990; 100: 27–30.
Maher ER : The gene for von Hippel-Lindau disease. BMJ 1993; 307: 279–280.
Bodmer D, van den Hurk W, van Groningen JJ et al: Understanding familial and non-familial renal cell cancer. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 2489–2498.
Cohen AJ, Li FP, Berg S et al: Hereditary renal-cell carcinoma associated with a chromosomal translocation. N Engl J Med 1979; 301: 592–595.
Kovacs G, Brusa P, De Riese W : Tissue-specific expression of a constitutional 3;6 translocation: development of multiple bilateral renal-cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 1989; 43: 422–427.
Koolen MI, van der Meyden AP, Bodmer D et al: A familial case of renal cell carcinoma and a t(2;3) chromosome translocation. Kidney Int 1998; 53: 273–275.
Eleveld MJ, Bodmer D, Merkx G et al: Molecular analysis of a familial case of renal cell cancer and a t(3;6)(q12;q15). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2001; 31: 23–32.
Druck T, Podolski J, Byrski T et al: The DIRC1 gene at chromosome 2q33 spans a familial RCC-associated t(2;3)(q33;q21) chromosome translocation. J Hum Genet 2001; 46: 583–589.
Kanayama H, Lui WO, Takahashi M et al: Association of a novel constitutional translocation t(1q;3q) with familial renal cell carcinoma. J Med Genet 2001; 38: 165–170.
Kovacs G, Hoene E : Loss of der(3) in renal carcinoma cells of a patient with constitutional t(3;12). Hum Genet 1988; 78: 148–150.
Kajaczek S, Gronwald J, Kata G, Borowka A, Lubinski J : Familial clear renal cell cancer (CRCC) associated with constitutional reciprocal translocation t(2;3)(q33;q21). Cytogenet Cell Genet 1999; 85: 172.
Geurts van Kessel AWH, Bodmer D, Eleveld M et al: Renal cell cancer: chromosome 3 translocations as risk factors. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999; 91: 1159–1160.
Melendez B, Rodriguez-Perales S, Martinez-Delgado B et al: Molecular study of a new family with hereditary renal cell carcinoma and a translocation t(3;8)(p13;q24.1). Hum Genet 2003; 112: 178–185.
Glover TW, Coyle-Morris JF, Li FP et al: Translocation t(3;8)(p14.2;q24.1) in renal cell carcinoma affects expression of the common fragile site at 3p14(FRA3B) in lymphocytes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1988; 31: 69–73.
Gemmill RM, West JD, Boldog F et al: The hereditary renal cell carcinoma 3;8 translocation fuses FHIT to a patched-related gene, TRC8. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 9572–9577.
Bodmer D, Schepens M, Eleveld MJ, Schoenmakers EF, Geurts van Kessel A : Disruption of a novel gene, DIRC3, and expression of DIRC3-HSPBAP1 fusion transcripts in a case of familial renal cell cancer and t(2;3)(q35;q21). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003; 38: 107–116.
Bodmer D, Eleveld M, Kater-Baats E et al: Disruption of a novel MFS transporter gene, DIRC2, by a familial renal cell carcinoma-associated t(2;3)(q35;q21). Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 641–649.
Chen J, Lui WO, Vos MD et al: The t(1;3) breakpoint-spanning genes LSAMP and NORE1 are involved in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Cell 2003; 4: 405–413.
Rodriguez-Perales S, Melendez B, Gribble SM et al: Cloning of a new familial t(3;8) translocation associated with conventional renal cell carcinoma reveals a 5 kb microdeletion and no gene involved in the rearrangement. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 983–990.
Bodmer D, Eleveld M, Ligtenberg M et al: Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of early stage renal cell carcinomas in a family with a translocation (2;3)(q35;q21). Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2002; 134: 6–12.
Bodmer D, Eleveld MJ, Ligtenberg MJ et al: An alternative route for multistep tumorigenesis in a novel case of hereditary renal cell cancer and a t(2;3)(q35;q21) chromosome translocation. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 1475–1483.
Woodward ER, Clifford SC, Astuti D, Affara NA, Maher ER : Familial clear cell renal cell carcinoma (FCRC): clinical features and mutation analysis of the VHL, MET, and CUL2 candidate genes. J Med Genet 2000; 37: 348–353.
Knudson Jr AG : Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1971; 68: 820–823.
Kovacs G : Molecular cytogenetics of renal cell tumors. Adv Cancer Res 1993; 62: 89–124.
Kovacs G, Kung HF : Nonhomologous chromatid exchange in hereditary and sporadic renal cell carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 194–198.
Mitelman F : ISCN. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. Basel: S Karger, 1995.
Kallioniemi OP, Kallioniemi A, Piper J et al: Optimizing comparative genomic hybridization for analysis of DNA sequence copy number changes in solid tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1994; 10: 231–243.
Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J et al: Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene. Science 1993; 260: 1317–1320.
Chen F, Kishida T, Yao M et al: Germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene: correlations with phenotype. Hum Mutat 1995; 5: 66–75.
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB : Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 9821–9826.
Cascon A, Ruiz-Llorente S, Fraga M et al: Genetic and epigenetic profile of sporadic pheochromocytomas. J Med Genet 2004; 41: e30.
Ruiz-Llorente S, Bravo J, Cebrian A et al: Genetic characterization and structural analysis of VHL Spanish families to define genotype–phenotype correlations. Hum Mutat 2004; 23: 160–169.
Schouten JPMCJ, Waaijer R, Zwijnenburg D, Diepvens F, Pals G : Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acid Res 2002; 30.
Greshock J, Naylor TL, Margolin A et al: 1-Mb resolution array-based comparative genomic hybridization using a BAC clone set optimized for cancer gene analysis. Genome Res 2004; 14: 179–187.
Dagan E, Gershoni-Baruch R : Anticipation in hereditary breast cancer. Clin Genet 2002; 62: 147–150.
King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB : Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 2003; 302: 643–646.
Li FP, Decker HJ, Zbar B et al: Clinical and genetic studies of renal cell carcinomas in a family with a constitutional chromosome 3;8 translocation. Genetics of familial renal carcinoma. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: 106–111.
Boldog FL, Gemmill RM, Wilke CM et al: Positional cloning of the hereditary renal carcinoma 3;8 chromosome translocation breakpoint. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 8509–8513.
Ohta M, Inoue H, Cotticelli MG et al: The FHIT gene, spanning the chromosome 3p14.2 fragile site and renal carcinoma-associated t(3;8) breakpoint, is abnormal in digestive tract cancers. Cell 1996; 84: 587–597.
Croce CM, Sozzi G, Huebner K : Role of FHIT in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1618–1624.
Druck T, Berk L, Huebner K : FHITness and cancer. Oncol Res 1998; 10: 341–345.
Mao L : Tumor suppressor genes: does FHIT fit? J Natl Cancer Inst 1998; 90: 412–414.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Consejería de Sanidad of the Autonomous Community of Madrid (CAM). Laura Valle holds a Fellowship from the CAM. We thank Ma Carmen Carralero, Ma Carmen Martín, and Rocío Letón for technical assistance, Marta Cuadros for her help in the LOH study, and Ellen Alacid for linguistic corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valle, L., Cascón, A., Melchor, L. et al. About the origin and development of hereditary conventional renal cell carcinoma in a four-generation t(3;8)(p14.1;q24.23) family. Eur J Hum Genet 13, 570–578 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201371
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201371