Abstract
Design
A split-mouth randomised controlled trial (RCT) was conducted.
Intervention
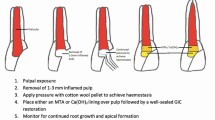
Standard noncarious pulp exposures were treated with either enamel matrix derivative (EMD) or calcium hydroxide and restored with a preformed metal crown (PMC). Patients were followed up at 1, 6 and 12 months.
Outcome measure
The appearance of any of the following was considered to signify treatment failure: internal dentin resorption, spontaneous pain, gingival abscess (sinus tract), external root resorption, or pathologic mobility.
Results
In total, 90 direct pulp capping (DPC) treatments were performed (45 in the experimental group and 45 in the control group) and followed for 12 months. There were 88 successful treatments at the end of this period, with only two failures (one in each study group)
Conclusions
Both capping materials showed a similar effectiveness in this pulp procedure with a postoperative observation time of 12 months. On the basis of this study, we recommend the use of DCP treatment on primary molars as a standard technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Rodd HD, Waterhouse PJ, Fuks AB, Fayle SA, Moffat MA . British Society of Paediatric Dentistry. Pulp therapy for primary molars. Int J Paediatric Dentistry 2006; 16 (suppl. 1): S15–S23.
Ni Chaollai A, Monteiro J, Duggal MS . The teaching of management of the pulp in primary molars in Europe: a preliminary investigation in Ireland and the UK. Eur Archive Paediatr Dent 2009; 10: 98–103.
Holan G, Fuks A B, Ketlz N . Success rate of formocresol pulpotomy in primary molars restored with stainless steel crown vs amalga. Pediatr Dent 2002; 24: 212–216.
Farooq NS, Coll JA, Kuwabara A, Shelton P . Success rates of formocresol pulpotomy and indirect pulp therapy in the treatment of deep dentinal caries in primary teeth. Pediatr Dent 2000; 22: 278–286.
Sonmez D, Duruturk L . Success rate of calcium hydroxide pulpotomy in primary molars restored with amalgam and stainless steel crowns. Br Dent J 2009; 208: 408–409.
Marchi JJ, de Araujo FB, Fröner AM, Straffon LH, Nör JE . Indirect pulp capping in the primary dentition: a 4 year follow-up study. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2006; 31: 68–71.
Magnusson BO, Sundell SO . Stepwise excavation of deep carious lesions in primary molars. J Int Assoc Dent Children 1977; 8: 36–40.
Ribeiro CCC, Baratieri LN, Perdigão J, Baratieri NMM, Ritter AV. A clinical, radiographic, and scanning electron microscopic evaluation of adhesive restorations on carious dentin in primary teeth. Quintessence Int 1999; 30: 591–599.
Innes NP, Evans DJ, Stirrups DR . The Hall Technique: a randomized controlled clinical trial of a novel method of managing carious primary molars in general dental practice: acceptability of the technique and outcomes at 23 months. BMC Oral Health 2007 Dec 20; 7: 18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address for correspondence: Dr Amaury de Jesús Pozos Guillén, Facultad de Estomatología, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, Av. Dr. Manuel Nava #2, Zona Universitaria, C.P. 78290, San Luis Potosí, México. E-mail: apozos@uaslp.mx
Garrocho-Rangel A, Flores H, Silva-Herzog D, Hernandez-Sierra F, Mandeville P, Pozos-Guillen AJ. Efficacy of EMD versus calcium hydroxide in direct pulp capping of primary molars: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009; 107: 733–738
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Innes, N. Enamel matrix derivative for direct pulp capping. Evid Based Dent 11, 45–46 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ebd.6400719
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ebd.6400719