Summary
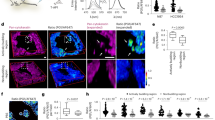
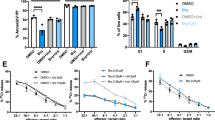
Induction of haem oxygenase-1 (HO-1) as well as nitric oxide (NO) biosynthesis during tumour growth was investigated in an experimental solid tumour model (AH136B hepatoma) in rats. An immunohistochemical study showed that the inducible isoform of NO synthase (iNOS) was localized in monocyte-derived macrophages, which infiltrated interstitial spaces of solid tumour, but not in the tumour cells. Excessive production of NO in the tumour tissue was unequivocally verified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Tumour growth was moderately suppressed by treatment with either Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) or S-methylisothiourea sulphate (SMT). In contrast, HO-1 was found only in tumour cells, not in macrophages, by in situ hybridization for HO-1 mRNA. HO-1 expression in AH136B cells in culture was strongly enhanced by an NO (NO+) donor S-nitroso-N-acetyl penicillamine. HO-1 mRNA expression in the solid tumour in vivo decreased significantly after treatment with low doses of NOS inhibitors such as L-NAME and SMT (6–20 mg kg–1). However, the level of HO-1 mRNA in the solid tumour treated with higher doses of NOS inhibitor was similar to that of the solid tumour without NOS inhibitor treatment. Strong induction of HO-1 was also observed in solid tumours after occlusion or embolization of the tumour-feeding artery, indicating that ischaemic stress which may involve oxidative stress triggers HO-1 induction in the solid tumour. Lastly, it is of great importance that an HO inhibitor, zinc protoporphyrin IX injected intra-arterially to the solid tumour suppressed the tumour growth to a great extent. In conclusion, HO-1 expression in the solid tumour may confer resistance of tumour cells to hypoxic stress as well as to NO-mediated cytotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Akaike, T., Inoue, K., Okamoto, T., Nishino, H., Otagiri, M., Fujii, S. & Maeda, H. (1997). Nanomolar quantification and identification of various nitrosothiols by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with flow reactors of metals and Griess reagent. J Biochem 122: 459–466.
Andrade, S. P., Hart, I. R. & Piper, P. J. (1992). Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase selectively reduce flow in tumor-associated neovasculature. Br J Pharmacol 107: 1092–1095.
Bastian, N. R., Yim, C. Y., Hibbs, Jr J. B. & Samlowski, W. E. (1994). Induction of iron-derived EPR signals in murine cancers by nitric oxide. Evidence for multiple intracellular targets. J Biol Chem 269: 5127–5131.
Buttery, L. D. K., Springall, D. R., Andrade, S. P., Riveros-Moreno, V., Hart, I., Piper, P. J. & Polak, J. M. (1993). Induction of nitric oxide synthase in the neo-vasculature of experimental tumors in mice. J Pathol 171: 311–319.
Cobbs, C. S., Brenman, J. E., Aldape, K. D., Bredt, D. S. & Israel, M. A. (1995). Expression of nitric oxide synthase in human central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res 55: 727–730.
Doi, K., Akaike, T., Horie, H., Noguchi, Y., Fujii, S., Beppu, T., Ogawa, M. & Maeda, H. (1996). Excessive production of nitric oxide in rat solid tumor and its implication in rapid tumor growth. Cancer 77: 1598–1604.
Goldman, A. I., Choudhury, M., da Silva, J. L. & Jiang, S. (1996). Quantitative measurement of haem oxygenase-1 in the human renal adenocarcinoma. J Cell Biochem 63: 342–348.
Hara, E., Takahashi, K., Tominaga, T., Kumabe, T., Kayama, T., Suzuki, H., Fujita, H., Yoshimoto, T., Shirato, K. & Shibahara, S. (1996). Expression of haem oxygenase and inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in human brain tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 224: 153–158.
Hibbs, J. B., Taintor, R. R., Varin, Z. & Rachlin, E. M. (1988). Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 157: 87–94.
Jenkins, D. C., Charles, I. G., Thomsen, L. L., Moss, D. W., Holmes, L. S., Baylis, S. A., Rhodes, P., Westmore, K., Emson, P. C. & Moncada, S. (1995). Role of nitric oxide in tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 4392–4396.
Kim, Y-M, Bergonia, H. & Lancaster, Jr J. R. (1995a). Nitrogen oxide-induced autoprotection in isolated rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 374: 228–232.
Kim, Y-M, Bergonia, H. A., Müller, C., Pitt, B. R., Watkins, W. D. & Lancaster, Jr J. R. (1995b). Loss and degradation of enzyme-bound haem induced by cellular nitric oxide synthesis. J Biol Chem 270: 5710–5713.
Lala, P. K. & Orucevic, A. (1998). Role of nitric oxide in tumor progression: lessons from experimental tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev 17: 91–106.
Lee, T. C. & Ho, I. C. (1994). Expression of haem oxygenase in arsenic-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 54: 1660–1664.
Leibovich, S. J., Polverini, P. J., Fong, T. W., Harlow, L. A. & Koch, A. E. (1994). Production of angiogenic activity by human monocytes requires an L-arginine/nitric oxide-synthase-dependent effector mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 4190–4194.
Lepoivre, M., Flamn, J. M., Bobe, P., Lemaire, G. & Henry, Y. (1994). Quenching of the tyrosyl free radical of ribonucleotide reductase by nitric oxide. Relationship to cytostasis induced in tumor cells by cytotoxic macrophage. J Biol Chem 269: 21891–21897.
Maeda, H., Noguchi, Y., Sato, K. & Akaike, T. (1994). Enhanced vascular permeability in solid tumor is mediated by nitric oxide and inhibited by both new nitric oxide scavenger and nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. Jpn J Cancer Res 85: 331–334.
Maines, M. D. (1981). Zinc-protoporphyrin is a selective inhibitor of haem oxygenase activity in the neonatal rat. Biochim Biophys Acta 673: 339–350.
Maines, M. D. (1997). The haem oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37: 517–554.
Maines, M. D. & Kappas, A. (1974). Cobalt induction of hepatic haem oxygenase: with evidence that cytochrome P-450 is not essential for this enzyme activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71: 4293–4297.
Maines, M. D., Kappas (1978). Prematurely evoked synthesis and induction of δ-aminolevulinate synthetase in neonatal liver. J Biol Chem 253: 2321–2326.
Matsumura, Y., Kimura, M., Yamamoto, T. & Maeda, H. (1988). Involvement of the kinin-generating cascade in enhanced vascular permeability in tumor tissue. Jpn J Cancer Res 79: 1327–1334.
Moncada, S. & Higgs, A. (1993). The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med 329: 2002–2012.
Nakano, S., Matsukado, K. & Black, K. L. (1996). Increased brain tumor microvessel permeability after intracarotid bradykinin infusion is mediated by nitric oxide. Cancer Res 56: 4072–4031.
Okamoto, T., Akaike, T., Nagano, T., Miyajima, S., Suga, M., Ando, M., Ichimori, K. & Maeda, H. (1997). Activation of human neutrophil procollagenase by nitrogen dioxide and peroxynitrite: a novel mechanism for procollagenase activation involving nitric oxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 342: 261–274.
Prabhakar, N. R., Dinerman, J. L., Agani, F. H. & Snyder, S. H. (1997). Carbon monoxide: a role in carotid body chemoreception. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1994–1997.
Setoguchi, K., Takeya, M., Akaike, T., Suga, M., Hattori, R., Maeda, H., Ando, M. & Takahashi, K. (1996). Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and its involvement in pulmonary granulomatous inflammation in rats. Am J Pathol 149: 2005–2022.
Shibahara, S., Müller, R., Taguchi, H. & Yoshida, T. (1985). Cloning and expression of cDNA for rat haem oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 7865–7869.
Stocker, R., Yamamoto, Y., McDonagh, A. F., Glazer, A. N. & Ames, B. N. (1987). Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science (Wash. DC) 235: 1043–1046.
Stuehr, D. J. & Griffith, O. W. (1992). Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 65: 287–346.
Suematsu, M., Goda, N., Sano, T., Kashiwagi, S., Egawa, T., Shinoda, Y. & Ishimura, Y. (1995). Carbon monoxide: an endogenous modulator of sinusoidal tone in the perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest 96: 2431–2437.
Suzuki, K., Hayashi, N., Miyamoto, M., Yamamoto, M., Ohkawa, K., Ito, Y., Sasaki, Y., Yamaguchi, Y., Nakase, H., Noda, K., Enomoto, N., Arai, K., Yamada, Y., Yoshihara, H., Tsujimura, T., Kawano, K., Yoshikawa, K. & Kamada, T. (1996). Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 56: 3004–3009.
Takahashi, K., Hara, E., Suzuki, H., Sasano, H. & Shibahara, S. (1996). Expression of haem oxygenase isozyme mRNAs in the human brain and induction of haem oxygenase-1 by nitric oxide donors. J Neurochem 67: 482–489.
Takeda, A., Onodera, H., Sugimoto, A., Itoyama, Y., Kogure, K. & Shibahara, S. (1994). Increased expression of haem oxygenase mRNA in rat brain following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 666: 120–124.
Takeya, M., Hsiao, L. & Takahashi, K. (1987). A new monoclonal antibody, TRPM-3, binds specifically to certain rat macrophage populations. Immunohistochemical and immunoelectron microscopic analysis. J Leukoc Biol 41: 187–195.
Tenhunen, R., Marver, H. S. & Schmid, R. (1968). The enzymatic conversion of haem to bilirubin by microsomal haem oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61: 748–755.
Thomsen, L. L., Lawton, F. G., Knowles, R. G., Beesley, J. E., Riveros-Moreno, V. & Moncada, S. (1994). Nitric oxide synthase activity in human gynecological cancer. Cancer Res 54: 1352–1354.
Thomsen, L. L., Scott, J. M. J., Topley, P., Knowles, R. G., Keerie, A-J & Frend, A. J. (1997). Selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibits tumor growth in vivo: studies with 1400W, a novel inhibitor. Cancer Res 57: 3300–3304.
Tozer, G. M., Prise, V. E. & Bell, K. M. (1995). The influence of nitric oxide on tumor vascular tone. Acta Oncol 34: 373–377.
Tozer, G. M., Prise, V. E. & Chaplin, D. J. (1997). Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase induces a selective reduction in tumor blood flow that is reversible with L-arginine. Cancer Res 57: 948–955.
Vaupel, P., Kallinowski, F. & Okunieff, P. (1989). Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res 49: 6449–6465.
Wood, P. J., Sansom, J. M., Butler, S. A., Stratford, I. J., Cole, S. M., Szabó, C., Thiemermann, C. & Adams, G. E. (1994). Induction of hypoxia in experimental murine tumors by the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine. Cancer Res 54: 6458–6463.
Wu, J., Akaike, T. & Maeda, H. (1998). Modulation of enhanced vascular permeability in tumor by a bradykinin antagonist, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, and an NO scavenger. Cancer Res 58: 159–165.
Yamasaki, K., Konno, T., Miyauchi, Y. & Maeda, H. (1987). Reduction of hepatic metastasis in rabbits by administration of an oily anticancer agent into the portal vein. Cancer Res 47: 852–855.
Yet, S-F, Pellacani, A., Patterson, C., Tan, L., Folta, S. C., Foster, L., Lee, W-S, Hsieh, C-M & Perella, M. A. (1997). Induction of haem oxygenase-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. A link to endotoxic shock. J Biol Chem 272: 4295–4301.
Yoshimura, T., Yokoyama, H., Fuji, S., Takayama, F., Oikawa, K. & Kamada, H. (1996). In vivo ESR detection and imaging of endogenous nitric oxide in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Nature Biotechnol 14: 992–994.
Ziche, M., Morbidelli, L., Choudhuri, R., Zhang, H-T, Donnini, S., Granger, H. J. & Bicknell, R. (1997). Nitric oxide synthase lies downstream from vascular endothelial growth factor-induced but not basic fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 99: 2625–2634.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Doi, K., Akaike, T., Fujii, S. et al. Induction of haem oxygenase-1 by nitric oxide and ischaemia in experimental solid tumours and implications for tumour growth. Br J Cancer 80, 1945–1954 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690624
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690624
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
HMOX1 is partly responsible for phenotypic and functional abnormalities in mesenchymal stem cells/stromal cells from placenta of preeclampsia (PE) patients
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Zinc-substituted hemoglobin with specific drug binding sites and fatty acid resistance ability for enhanced photodynamic therapy
Nano Research (2019)
-
Reactive oxygen species in haematopoiesis: leukaemic cells take a walk on the wild side
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
Overexpression of Nrf2 attenuates Carmustine-induced cytotoxicity in U87MG human glioma cells
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 in colorectal cancer patients with increased circulation carbon monoxide levels, potentially affects chemotherapeutic sensitivity
BMC Cancer (2014)