Abstract
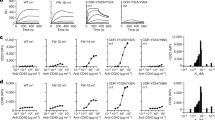
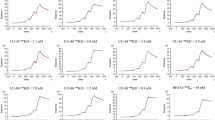
In various clinical studies, Hodgkin’s patients have been treated with anti-CD30 immunotherapeutic agents and have shown promising responses. One of the problems that appeared from these studies is the development of an immune response against the non-human therapeutics, which limits repeated administration and reduces efficacy. We have set out to make a recombinant, human anti-CD30 single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibody, which may serve as a targeting moiety with reduced immunogenicity and more rapid tumour penetration in similar clinical applications. Rather than selecting a naive phage antibody library on recombinant CD30 antigen, we used guided selection of a murine antibody in combination with panning on the CD30-positive cell line L540. The murine monoclonal antibody Ki-4 was chosen as starting antibody, because it inhibits the shedding of the extracellular part of the CD30 antigen. This makes the antibody better suited for CD30-targeting than most other anti-CD30 antibodies. We have previously isolated the murine Ki-4 scFv by selecting a mini-library of hybridoma-derived phage scFv-antibodies via panning on L540 cells. Here, we report that phage display technology was successfully used to obtain a human Ki-4 scFv version by guided selection. The murine variable heavy (VH) and light (VL) chain genes of the Ki-4 scFv were sequentially replaced by human V gene repertoires, while retaining only the major determinant for epitope-specificity: the heavy-chain complementarity determining region 3 (CDR3) of murine Ki-4. After two rounds of chain shuffling and selection by panning on L540 cells, a fully human anti-CD30 scFv was selected. It competes with the parental monoclonal antibody Ki-4 for binding to CD30, inhibits the shedding of the extracellular part of the CD30 receptor from L540 cells and is thus a promising candidate for the generation of anti-CD30 immunotherapeutics. © 2000 Cancer Research Campaign
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Barth S, Huhn M, Matthey B, Klimka A, Galinski EA and Engert A (2000) Compatible solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 1572–1579
Beiboer SH, Reurs A, Roovers RC, Arends JW, Whitelegg NR, Rees AR and Hoogenboom HR (2000) Guided selection of a pan carcinoma specific antibody reveals similar binding characteristics yet structural divergence between the original murine antibody and its human equivalent. J Mol Biol 296: 833–849
Bosslet K, Mennel HD, Rodden F, Bauer BL, Wagner F, Altmannsberger A, Sedlacek HH and Wiegandt H (1989) Monoclonal antibodies against epitopes on ganglioside GD2 and its lactones. Markers for gliomas and neuroblastomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother 29: 171–178
Brüggemann M and Neuberger MS (1996) Strategies for expressing human antibody repertoires in transgenic mice. Immunol Today 17: 391–397
Chothia C, Lesk AM, Tramontano A, Levitt M, Smith-Gill SJ, Air G, Sheriff S, Padlan EA, Davies D and Tulip WR (1989) Conformations of immunoglobulin hypervariable regions. Nature 342: 877–883
Chothia C, Lesk AM, Gherardi E, Tomlinson IM, Walter G, Marks JD, Llewelyn MB and Winter G (1992) Structural repertoire of the human VH segments. Mol Biol 227: 799–817
Diehl V, Kirchner HH, Schaadt M, Fonatsch C, Stein H, Gerdes J and Boie C (1981) Hodgkin’s disease: establishment and characterization of four in vitro cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 101: 111–124
Dower WJ, Miller JF and Ragsdale CW (1988) High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 6127–6145
Figini M, Marks JD, Winter G and Griffiths AD (1994) in vitro assembly of repertoires of antibody chains on the surface of phage by renaturation. J Mol Biol 239: 68–78
Figini M, Obici L, Mezzanzanica D, Griffiths A, Colnaghi MI, Winter G and Canevari S (1998) Panning phage antibody libraries on cells: isolation of human Fab fragments against ovarian carcinoma using guided selection. Cancer Res 58: 991–996
Gruss HJ and Dower SK (1995) The TNF ligand superfamily and its relevance for human diseases. Cytokines Mol Ther 1: 75–105
Hoogenboom HR (1997) Designing and optimizing library selection strategies for generating high-affinity antibodies. Trends Biotechnol 15: 62–70
Hoogenboom HR, de Bruine AP, Hufton SE, Hoet RM, Arends JW and Roovers RC (1998) Antibody phage display technology and its applications. Immunotechnology 4: 1–20
Hoogenboom HR, Lutgerink JT, Pelsers MM, Rousch MJ, Coote J, Van Neer N, DeBruine A, Van Nieuwenhoven FA, Glatz JF and Arends JW (2000) Selection-dominant and nonaccessible epitopes on cell-surface receptors revealed by cell-panning with a large phage antibody library. Eur J Biochem 260: 274–284
Horn-Lohrens O, Tiemann M, Lange H, Kobarg J, Hafner M, Hansen H, Sterry W, Parwaresch RM and Lemke H (1995) Shedding of the soluble form of CD30 from the Hodgkin-analogous cell line L540 is strongly inhibited by a new CD30-specific antibody (Ki-4). Int J Cancer 60: 539–544
Huston JS, McCartney J, Tai MS, Mottola-Hartshorn C, Jin D, Warren F, Keck P and Oppermann H (1993) Medical applications of single-chain antibodies. Int Rev Immunol 10: 195–217
Jespers LS, Roberts A, Mahler SM, Winter G and Hoogenboom HR (1994) Guiding the selection of human antibodies from phage display repertoires to a single epitope of an antigen. Bio/Technology 12: 899–903
Kabat EA and Wu TT (1991) Identical V region amino acid sequences and segments of sequences in antibodies of different specificities. Relative contributions of VH and VL genes, minigenes, and complementarity-determining regions to binding of antibody-combining sites. J Immunol 147: 1709–1719
Khazaeli MB, Conry RM and LoBuglio AF (1994) Human immune response to monoclonal antibodies. J Immunother 15: 42–52
Klimka A, Barth S, Matthey B, Roovers R, Lemke H, Hansen H, Arends JW, Diehl V, Hoogenboom HR and Engert A (2000) An anti-CD30 single-chain Fv selected by phage display and fused to Pseudomonas exotoxin A (Ki- (scFv)-ETA) is a potent immunotoxin against a Hodgkin-derived cell line. Br J Cancer 80: 1214–1222
Köhler G and Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256: 495–497
Marks JD, Hoogenboom HR, Bonnert TP, McCafferty J, Griffiths AD and Winter G (1991) By-passing immunization. Human antibodies from V-gene libraries displayed on phage. J Mol Biol 222: 581–597
McCafferty J, Fitzgerald KJ, Earnshaw J, Chiswell DJ, Link J, Smith R and Kenten J (1994) Selection and rapid purification of murine antibody fragments that bind a transition-state analog by phage display. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 47: 157–171
McCall AM, Amoroso AR, Sautes C, Marks JD and Weiner LM (1998) Characterization of anti-mouse Fc gamma RII single-chain Fv fragments derived from human phage display libraries. Immunotechnology 4: 71–87
Meredith RF, Khazaeli MB, Grizzle WE, Orr RA, Plott G, Urist MM, Liu T, Russell CD, Wheeler RH and Schlom J (1993) Direct localization comparison of murine and chimeric B72.3 antibodies in patients with colon cancer. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas 4: 190–197
Newton DL, Xue Y, Olson KA, Fett JW and Rybak SM (1996) Angiogenin single-chain immunofusions: influence of peptide linkers and spacers between fusion protein domains. Biochemistry 35: 545–553
Persic L, Horn IR, Rybak S, Cattaneo A, Hoogenboom HR and Bradbury A (2000) Single-chain variable fragments selected on the 57–76 p21Ras neutralising epitope from phage antibody libraries recognise the parental protein. FEBS Lett 443: 112–116
Sanger F, Nicklen S and Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Schnell R, Linnartz C, Katouzi AA, Schon G, Bohlen H, Horn-Lohrens O, Parwaresch RM, Lange H, Diehl V and Lemke H (1995) Development of new ricin A-chain immunotoxins with potent anti-tumor effects against human Hodgkin cells in vitro and disseminated Hodgkin tumors in SCID mice using high-affinity monoclonal antibodies directed against the CD30 antigen. Int J Cancer 63: 238–244
Schwab U, Stein H, Gerdes J, Lemke H, Kirchner H, Schaadt M and Diehl V (1982) Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg–Reed cells of Hodgkin’s disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature 299: 65–67
Schwarting R, Gerdes J, Durkop H, Falini B, Pileri S and Stein H (1989) BER-H2: a new anti-Ki-1 (CD30) monoclonal antibody directed at a formol-resistant epitope. Blood 74: 1678–1689
Shawler DL, Bartholomew RM, Smith LM and Dillman RO (1985) Human immune response to multiple injections of murine monoclonal IgG. J Immunol 135: 1530–1535
Smith TJ (1993) Purification of mouse antibodies and Fab fragments. Methods Cell Biol 37: 75–93
Tai MS, McCartney JE, Adams GP, Jin D, Hudziak RM, Oppermann H, Laminet AA, Bookman MA, Wolf EJ and Liu S (1995) Targeting c-erbB-2 expressing tumors using single-chain Fv monomers and dimers. Cancer Res 55 (23 Suppl): 5983s–5989s
Watzka H, Pfizenmaier K and Moosmayer D (1998) Guided selection of antibody fragments specific for human interferon gamma receptor 1 from a human VH- and VL-gene repertoire. Immunotechnology 3: 279–291
Winter G, Griffiths AD, Hawkins RE and Hoogenboom HR (1994) Making antibodies by phage display technology. Annu Rev Immunol 12: 433–455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Klimka, A., Matthey, B., Roovers, R. et al. Human anti-CD30 recombinant antibodies by guided phage antibody selection using cell panning. Br J Cancer 83, 252–260 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1226
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1226
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A single-chain antibody generation system yielding CAR-T cells with superior antitumor function
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Efficacy of an adapted granzyme B-based anti-CD30 cytolytic fusion protein against PI-9-positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells in a murine model
Blood Cancer Journal (2013)
-
An efficient strategy for cell-based antibody library selection using an integrated vector system
BMC Biotechnology (2012)