Abstract
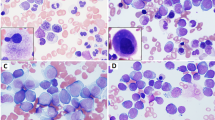
It is now well established that solid tumour growth depends on angiogenesis. However, less is known about the generation of new vessels in haematological malignancies and, in particular, in preleukaemic-myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). In this study, bone marrow microvessel density (MVD) was assessed by immunohistochemistry and compared in trephine biopsies from 14 controls, five infectious disease (ID), 82 MDS, 15 acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and 14 myeloproliferative disorder (MPD) patients. Statistical analysis (P < 0.001) demonstrated that MDS MVD was higher than in controls and ID (21 ± 9 vs 6 ± 2 and 10 ± 8 respectively) but lower than AML (30 ± 12) and MPD (40 ± 12). Among MDS-FAB subtypes, MVD was significantly higher in RAEB-t, CMML and fibrosis subsets compared to RA, RARS and RAEB subsets (P = 0.008). To further investigate angiogenesis machinery, the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was evaluated by means of immunohistochemistry in control, MDS, AML and MPD biopsies. Even though VEGF mRNA expression was reported in the past in AML cell cultures and cell lines, in our samples VEGF expression was found to be particularly strong in most of the megakaryocytes but significantly less prominent in other cell populations including blasts. Since our findings suggest a correlation between angiogenesis and progression to leukaemia, additional work is now warranted to determine what regulates the generation of new vessels in MDS and leukaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Banks, RE, Forbes, MA, Kinsey, SE, Stanley, A, Ingham, E, Walters, C & Selby, PJ (1998). Release of the angiogenic cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from platelets: significance for VEGF measurements and cancer biology. Br J Cancer 77: 956–964.
Bohem, T, Folkman, J, Browder, T & O'Reilly, MS (1997). Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390: 404–407.
Fernandez-Acenero, MJ, Gonzalez, JF, Galindo Gallego, M & Aragoncillo Ballestreros, P (1998). Vascular enumeration as a significant prognosticator for invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 16: 1684–1688.
Ferrara, N & Davis-Smyth, T (1997). The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocrine Rev 18: 4–25.
Fiedler, W, Graeven, U, Ergun, S, Verago, S, Kilic, N, Stockschlader, M & Hossfeld, DK (1997). Vascular endothelial growth factor, a possible paracrine factor in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 89: 1870–1875.
Folkman, J (1990). What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent?. J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4–6.
Folkman, J (1995). Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases. Nature Med 1: 27–31.
Foss, HD, Araujo, I, Demel, G, Klotzback, H, Hummel, M & Stein, H (1997). Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in lymphomas and Castleman's disease. J Pathol 183: 44–50.
Fukumura, D, Xavier, R, Sugiura, T, Chen, Y, Park, E, Lu, N, Selig, M, Nielsen, G, Taksir, T, Jain, RK & Seed, B (1998). Tumor induction of VEGF promoter activity in stromal cells. Cell 94: 715–725.
Gimbrone, MA, Leapman, SB, Cotran, RS & Folkman, J (1972). Tumor dormancy in vivo by prevention of neovascularization. J Exp Med 136: 261–276.
Graham, C, Rivers, J, Kerbel, R, Stankiewicz, K & White, W (1994). Extent of neovascularization as a prognostic indicator in thin (<0.76 mm) melanomas. Am J Pathol 145: 510–514.
Greenberg, P, Cox, C, LeBeau, MM, Fenaux, P, Morel, P, Sanz, G, Sanz, M, Vallespi, T, Hamblin, T, Oscier, D, Ohyashiki, K, Toyama, K, Aul, C, Mufti, G & Bennett, J (1997). International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 89: 2079–2088.
Harris, AL (1997). Antiangiogenesis for cancer therapy. Lancet 349: 13–15.
Lewis, CE, Leek, R, Harris, A & McGee, JO (1995). Cytokine regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leuk Biol 57: 747–751.
Linderholm, B, Tavelin, B, Grankvist, K & Henriksson, R (1998). Vascular endothelial growth factor is of high prognostic value in node-negative breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 16: 3121–3128.
Mohle, R, Green, D, Moore, MA, Nachman, RL & Rafii, S (1997). Constitutive production and thrombin-induced release of vascular endothelial growth factor by human megakaryocytes and platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 663–668.
Nguyen, M, Watanabe, H, Budson, AE, Richie, JP, Hayes, DF & Folkman, J (1994). Elevated levels of an angiogenic peptide, basic fibroblast growth factor, in the urine of patients with a wide spectrum of cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 86: 356–361.
Perez-Atayde, AR, Sallan, SE, Tedrow, U, Connors, S, Allred, E & Folkman, J (1997). Spectrum of tumor angiogenesis in the bone marrow of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Pathol 150: 815–821.
Salven, P, Teerenhovi, L & Joensuu, H (1997). A high pretreatment serum vascular endothelial growth factor concentration is associated with poor outcome in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood 90: 3167–3172.
Solanilla, A, Grosset, C, Lemercier, C, Dupouy, M, Mahon, FX, Schweitzer, K, Reiffers, J, Weksler, B & Ripoche, J (1998). Expression of Flt3-ligand by the endothelial cell. Regulation by IL-1α, glucocorticoids, IFN-α, MIP-1α and TGFβ. Key role in the proliferation of primitive hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 92: 580a (abstract)
Vacca, A, Ribatti, D, Roncali, L, Ranieri, G, Serio, G, Silvestris, F & Dammacco, F (1994). Bone marrow angiogenesis and progression in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 87: 503–508.
Weidner, N, Semple, JP, Welch, WR & Folkman, J (1991). Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis – correlation with invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324: 1–8.
Yamaguchi, H, Ishii, E, Saito, S, Tashiro, K, Fujita, I, Yoshiodomi, S, Ohtubo, M, Akazawa, K & Miyazaki, S (1996). Umbilical vein endothelial cells are an important source of c-kit and stem cell factor which regulate the proliferation of haemopoietic progenitor cells. Br J Haematol 94: 606–611.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Pruneri, G., Bertolini, F., Soligo, D. et al. Angiogenesis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Cancer 81, 1398–1401 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6693515
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6693515
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dysfunctional bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells are involved in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Role of the microenvironment in myeloid malignancies
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
Profile of fibrosis-related gene transcripts and megakaryocytic changes in the bone marrow of myelodysplastic syndromes with fibrosis
Annals of Hematology (2018)
-
Adult haematopoietic stem cell niches
Nature Reviews Immunology (2017)
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 facilitates the growth and chemo-resistance of leukemia cells in the bone marrow by modulating osteoblast functions
Scientific Reports (2016)