Abstract
Purpose To evaluate the additive ocular hypotensive effect of the combination of brimonidine and timolol on intraocular pressure (IOP) reduction in patients with glaucoma.
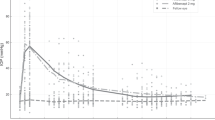
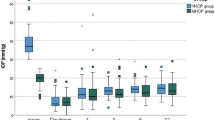
Methods This was a prospective, randomized, double-masked, crossover study in 20 patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) on therapy receiving timolol maleate 0.5% twice daily, with IOP greater than or equal to 22 mmHg in one eye. The treatment period was 3 weeks and during this period timolol + brimonidine or timolol + placebo were applied topically twice daily and IOP, blood pressure, heart rate and pupil size were measured.Results Combined therapy (timolol + brimonidine) had clinically significant IOP-lowering effect during the treatment period (P < 0.01). The mean diurnal IOP was significantly reduced by an average of 5.1–5.9 mmHg (21.2–24.5%) compared with baseline value. The timolol + placebo combination had no clinically significant IOP-lowering effect (P > 0.05). No clinically significant side effects were observed during the treatment of both groups.
Conclusions This study showed that the combination of topically applied brimonidine and timolol cause a marked and sustained IOP reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cambridge D . UK – 14,304, a potent and selective α-agonist for the characterization of α-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 1981; 72: 413–415
Toris CB, Gleason ML, Camras CB, Yablonski ME . Effects of brimonidine on aqueous humour dynamics in human eye. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113: 1154–1157
Derick RJ, Robin AL, Walters TR et al. Brimonidine tartrate: a one month dose response study. Ophthalmology 1997; 104: 131–136
David R, Walters TR, Sargent JB et al. The safety and efficacy of brimonidine tartrate 0.08%, 0.2%, 0.35% and 0.5% in normotensive subjects. Eur J Ophthalmol 1995; 5 (Suppl 2A): 156 (Abstract)
Serle JB the Brimonidine Study Group III. A comparison of the safety and efficacy of twice-daily brimonidine 0.2% versus betaxolol 0.25% in subjects with elevated intraocular pressure. Surv Ophthalmol 1996; 41 (Suppl): 39–47
Schuman JS, Horwitz B, Choplin NT, David R, Albracht D, Chen K . A 1-year study of brimonidine twice daly in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. A controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial. Chronic Brimonidine Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol 1997; 117: 417–419
Nordlund JR, Pasquale LR, Robin AL et al. The cardiovascular, pulmonary and ocular hypotensive effects of 0.2% brimonidine. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113: 77–83
Joel SS . Clinical experience with brimonidine 0.2% and timolol 0.5% in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Surv Ophthalmol 1996; 41 (Suppl 1): 27–37
Melamed S, David R . Ongoing clinical assessment of the safety and efficacy of brimonidine compared with timolol: year-three results. Brimonidine Study Group II. Clin Ther 2000; 22: 103–111
LeBlanc RP . Twelve-month results of an ongoing randomized trial comparing brimonidine tartrate 0.2% and timolol 0.5% given twice daily in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Brimonidine Study Group 2. Ophthalmology 1998; 105: 1960–1967
Yablonski ME, Zimmerman TJ, Waltman SR, Becker B . A fluorophotometric study of the effect of topical timolol on aqueous humour dynamics. Exp Eye Res 1978; 27: 1135–1142
Coakes RL, Brubaker RF . The mechanism of timolol in lowering intraocular pressure in the normal eye. Arch Opthalmol 1978; 96: 2045–2048
Centofanti M, Manni GL, Gregori D, Parisi V, Cocco F, Bucci MG . Brimonidine 0.2% behaviour on intraocular pressure in timolol-uncontrolled glaucomatous patients. Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl 1999; 77: 52
Yüksel N, Altintaş O, Karabaş L, Alp B, Çağlar Y . The short-term effect of adding brimonidine 0.2% to timolol treatment in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Ophthaomologica 1999; 213: 228–233
Stewart CW, Sharpe ED, Harbin TS, Pastor SA, Day DG, Holmes KT et al. Brimonidine 0.2% versus dorzolamide 2% each given three times daily to reduce intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol 2000; 129: 723–727
Stewart WC, Sharpe ED, Day DG, Kolker AE, Konstas AG, Lee WH et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of latanoprost 0.005% compared to brimonidine 0.2% or dorzolamide 2% when added to a topical beta-adrenergic blocker in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 2000; 16: 251–259
Simmons ST, Samuelson TW . Comparison of brimonidine with latanoprost in the adjunctive treatment of glaucoma. Clin Therapeut 2000; 22: 388–399
Hoskins HD Jr, Kass MA . Becker–Shaffer’s Diagnosis and Therapy of the Glaucoma, 6th edn CV Mosby: St Louis 1989 Chs 23, 26
Schuman JS . Effects of systemic beta-blocker therapy on the efficacy and safety of topical brimonidine and timolol. Brimonidine Study Groups 1 and 2. Ophthalmology 2000; 107: 1171–117
Acknowledgements
This study not supported by any sponsor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arici, M., Sayici, M., Toker, M. et al. A short term study of the additive effect of timolol and brimonidine on intraocular pressure. Eye 16, 39–43 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6700035
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6700035