Abstract
Purpose
To compare best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and contrast sensitivity (CS) under different levels of illumination in patients who had monofocal and multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) and to establish the effect of different lighting conditions on vision in the two groups of patients.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 27 patients who underwent phacoemulsification for age-related cataract and IOL implantation of either monofocal (SI30NB; n=10, 37%) or multifocal (SA40N; n=17, 63%) IOLs. Binocular distance and near BCVA and CS were tested using logMAR and Pelli-Robson charts that were externally illuminated with 20, 200, 400, and 1600 lux, and were compared using repeated-measures analysis of variance. A questionnaire was administered to establish the lighting preference in the two groups and the effect of lighting conditions on their vision.
Results
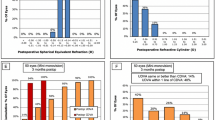
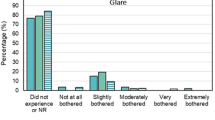
Binocular distance and near BCVA and CS significantly increased with increasing illumination from 20 to 200 lux in the monofocal (mean=0.04 vs −0.07; P=0.006; 0.37 vs 0.26, P=0.002 and 1.47 vs 1.60, P=0.01) as well as in the multifocal group (mean=0.03 vs −0.12, P<0.001; 0.38 vs 0.23, P<0.001 and 1.47 vs 1.61, P=0.002). No significant difference in BCVA or CS was found between the two groups at any of the four illumination levels. Both groups had similar lighting preference, but 43.8% of patients in the multifocal group experienced subjective worsening of their vision in bright outdoor lights.
Conclusions
Distance and near BCVA and CS improve with increasing illumination in patients with monofocal and multifocal IOLs, but remain comparable in the two groups under common levels of indoor illumination. Patients with multifocal IOLs may experience worsening of their vision in bright outdoor lights.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Vaquero-Ruano M, Encinas JL, Millan I, Hijos M, Cajigal C . AMO array multifocal versus monofocal intraocular lenses: long-term follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: 118–123.
Brydon KW, Tokarewicz AC, Nichols BD . AMO array multifocal lens versus monofocal correction in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 2000; 26: 96–100.
Javitt J, Brauweiler HP, Jacobi KW, Klemen U, Kohnen S, Quentin CD et al. Cataract extraction with multifocal intraocular lens implantation: clinical, functional, and quality-of-life outcomes. Multicenter clinical trial in Germany and Austria. J Cataract Refract Surg 2000; 26: 1356–1366.
Steinert RF . Visual outcomes with multifocal intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2000; 11: 12–21.
Leyland MD, Langan L, Goolfee F, Lee N, Bloom PA . Prospective randomised double-masked trial of bilateral multifocal, bifocal or monofocal intraocular lenses. Eye 2002; 16: 481–490.
Steinert RF, Aker BL, Trentacost DJ, Smith PJ, Tarantino N . A prospective comparative study of the AMO ARRAY zonal-progressive multifocal silicone intraocular lens and a monofocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology 1999; 106: 1243–1255.
Schmitz S, Dick HB, Krummenauer F, Schwenn O, Krist R . Contrast sensitivity and glare disability by halogen light after monofocal and multifocal lens implantation. Br J Ophthalmol 2000; 84: 1109–1112.
Williamson W, Poirier L, Coulon P, Verin P . Compared optical performances of multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses (contrast sensitivity and dynamic visual acuity). Br J Ophthalmol 1994; 78: 249–251.
Haring G, Dick HB, Krummenauer F, Weissmantel U, Kroncke W . Subjective photic phenomena with refractive multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses, results of a multicenter questionnaire. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001; 27: 245–249.
Hecht S . Relation between visual acuity and illumination. J Gen Physiol 1928; 255–281.
Williams B . Footcandles and lux for architechtural lighting (An introduction to illuminance). I.E.S. Recommendations 1999. www.mts.net/~william5/library/illum.htm.
Lythgoe RJ . The Measurement of Visual Acuity. Medical Research Council. Special Report Series. London: H.M.Stationary, 1932.
Sheedy JE, Bailey IL, Raasch TW . Visual acuity and chart luminance. Am J Optom Physiol Opt 1984; 61: 595–600.
Arens B, Freudenthaler N, Quentin CD . Binocular function after bilateral implantation of monofocal and refractive multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg 1999; 25: 399–404.
Montes-Mico R, Alio JL . Distance and near contrast sensitivity function after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003; 29: 703–711.
Leyland M, Zinicola E . Multifocal versus monofocal intraocular lenses in cataract surgery: a systematic review. Ophthalmology 2003; 110: 1789–1798.
Dick HB, Krummenauer F, Schwenn O, Krist R, Pfeiffer N . Objective and subjective evaluation of photic phenomena after monofocal and multifocal intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology 1999; 106: 1878–1886.
Acknowledgements
We thank Miss Michelle Bradley at the Department of Public Health and Primary Care, University of Cambridge for the statistical consultation and advice and Miss Kay Bernacki at Essex County Hospital, Colchester, for her help with the patient recruitment and the study administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Meeting presentation: Part of the data was presented as a poster at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) annual meeting, Fort Lauderdale, 2003 and at Oxford Annual Congress, Oxford, UK, 2003
Proprietary interests: None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgohary, M., Beckingsale, A. Effect of illumination on visual function after monofocal and multifocal intraocular lens implantation. Eye 20, 144–149 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6701820
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6701820