Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the epidemiological characteristics and related risk factors for primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) in Taiwan.
Methods
The case–control study was based on retrospective chart review of hospital patients treated for primary RRD from 1995 to 2001, inclusively. The preoperative fundus findings and refractive status were collected for each patient. Controls were selected from a nationwide survey of visual impairment in the adult population during the same period. Risk factors for RRD were analysed by logistic regression. A total of 1032 RRD cases and 3537 controls were enrolled for the study.
Results
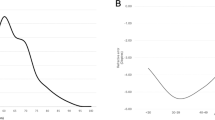
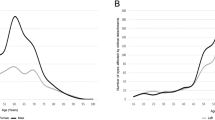
A pronounced bipeak pattern was evident in the age distribution for primary RRD in the third and sixth decades of life. Atrophic hole with lattice degeneration was preferential to younger (20–30 years) and highly myopic individuals (−7.4±5 D), whereas the flap tear tended to occur in middle-aged individuals (50–60 years) and those with moderate myopia (−4.1±5 D). The odds ratio for primary RRD with myopia, male gender, and older age (>40 years) were 1.33/D, 2.15, and 1.69, respectively.
Conclusions
Myopia is an important RRD risk factor for young Taiwanese. The increasing prevalence of myopia has predisposed the young population to RRD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Sasaki K, Ideta H, Yonemoto J, Tanaka S, Hirose A, Oka C . Epidemiologic characteristics of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Kumamoto, Japan. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1995; 233: 772–776.
Zou H, Zhang X, Xu X, Wang X, Liu K, Ho PC . Epidemiology survey of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Beixinjing District, Shanghai, China. Retina 2002; 22: 294–299.
Li X, Beijing Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Study Group. Incidence and epidemiological characteristics of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Beijing, China. Ophthalmology 2003; 110: 2413–2417.
Polkinghorne PJ, Craig JP . Northern New Zealand Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Study: epidemiology and risk factors. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004; 32: 159–163.
Ivanisevic M, Bojic L, Eterovic D . Epidemiological study of nontraumatic phakic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Ophthalmic Res 2000; 32: 237–239.
Wong TY, Tielsch JM, Schein OD . Racial difference in the incidence of retinal detachment in Singapore. Arch Ophthalmol 1999; 117: 379–383.
Rowe JA, Erie JC, Baratz KH, Hodge DO, Gray DT, Butterfield L et al. Retinal detachment in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976 through 1995. Ophthalmology 1999; 106: 154–159.
Laatikainen L, Tolppanen EM, Harju H . Epidemiology of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in a Finnish population. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenhagen) 1985; 63: 59–64.
Wilkes SR, Beard CM, Kurland LT, Robertson DM, O'Fallon WM . The incidence of retinal detachment in Rochester, Minnesota, 1970-1978. Am J Ophthalmol 1982; 94: 670–673.
Haimann MH, Burton TC, Brown CK . Epidemiology of retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol 1982; 100: 289–292.
Yorston DB, Wood ML, Gilbert C . Retinal detachment in East Africa. Ophthalmology 2002; 109: 2279–2283.
Rosman M, Wong TY, Ong SG, Ang CL . Retinal detachment in Chinese, Malay and Indian residents in Singapore: a comparative study on risk factors, clinical presentation and surgical outcomes. Int Ophthalmol 2001; 24: 101–106.
Algvere PV, Jahnberg P, Textorius O . The Swedish Retinal Detachment Register. I. A database for epidemiological and clinical studies. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1999; 237: 137–144.
Tornquist R, Stenkula S, Tornquist P . Retinal detachment. A study of a population-based patient material in Sweden 1971–1981. I. Epidemiology. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenhagen) 1987; 65: 213–222.
Tornquist R, Tornquist P, Stenkula S . Retinal detachment. A study of a population-based patient material in Sweden 1971–1981. II. Pre-operative findings. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenhagen) 1987; 65: 223–230.
The Eye Disease Case-Control Study Group. Risk factors for idiopathic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Am J Epidemiol 1993; 137: 749–757.
Austin KL, Palmer JR, Seddon JM, Glynn RJ, Rosenberg L, Gragoudas ES et al. Case-control study of idiopathic retinal detachment. Int J Epidemiol 1990; 19: 1045–1050.
Lin LL, Shih YF, Tsai CB, Chen CJ, Lee LA, Hung PT et al. Epidemiologic study of ocular refraction among schoolchildren in Taiwan in 1995. Optom Vis Sci 1999; 76: 275–281.
Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ, Lee LA, Hung PT . Epidemiologic study of the prevalence and severity of myopia among schoolchildren in Taiwan in 2000. J Formos Med Assoc 2001; 100: 684–691.
Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ . Prevalence of myopia in Taiwanese schoolchildren: 1983 to 2000. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2004; 33: 27–33.
Ogawa A, Tanaka M . The relationship between refractive errors and retinal detachment – analysis of 1,166 retinal detachment cases. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1988; 32: 310–315.
Sperduto RD, Seigel D, Roberts J, Rowland M . Prevalence of myopia in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol 1983; 101: 405–407.
Burton TC . The influence of refractive error and lattice degeneration on the incidence of retinal detachment. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1989; 87: 143–155.
Uemura A, Ohba N . Age of onset of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment analyzed by Weibull distribution function. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zassh 1996; 100: 624–627.
Lewis H . Peripheral retinal degenerations and the risk of retinal detachment. Am J Ophthalmol 2003; 136: 155–160.
Celorio JM, Pruett RC . Prevalence of lattice degeneration and its relation to axial length in severe myopia. Am J Ophthalmol 1991; 111: 20–23.
Tillery WV, Lucier AC . Round atrophic holes in lattice degeneration – an important cause of phakic retinal detachment. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol 1976; 81: 509–518.
Murakami-Nagasako F, Ohba N . Phakic retinal detachment associated with atrophic hole of lattice degeneration of the retina. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1983; 220: 175–178.
Sasaki K, Ideta H, Yonemoto J, Tanaka S, Hirose A, Oka C . Risk of retinal detachment in patients with lattice degeneration. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1998; 42: 308–313.
Margherio RR, Schepens CL . Macular breaks: diagnosis, etiology and observations. Am J Ophthalmol 1972; 74: 219–232.
Zhang C, Hu C . High incidence of retinal detachment secondary to macular hole in a Chinese population. Am J Ophthalmol 1982; 94: 817–819.
Ung T, Comer MB, Ang AJS, Sherad R, Lee C, Poulson AV et al. Clinical features and surgical management of retinal detachment secondary to round retinal holes. Eye 2005; 19: 665–669.
Mastropasqua L, Carpineto P, Ciancaglini M, Falconio G, Gallenga PE . Treatment of retinal tears and lattice degenerations in fellow eyes in high risk patients suffering retinal detachment: a prospective study. Br J Ophthalmol 1999; 83: 1046–1049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is supported by Grant DOH91-TD-1033 from the Health Promotion Bureau, Department of Health, Executive Yuen, Republic of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, SC., Yang, CH., Lee, CH. et al. Characteristics of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Taiwan. Eye 21, 1056–1061 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702397
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702397
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epidemiology of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in commercially insured myopes in the United States
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Anatomical and functional outcomes of retinal detachment associated with nontraumatic giant retinal tears compared to simple rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
International Journal of Retina and Vitreous (2022)
-
Managing paediatric giant retinal tears
Eye (2021)
-
Scleral buckling—a brief historical overview and current indications
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2020)