Abstract
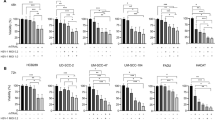
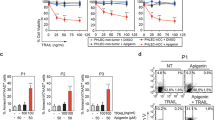
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) will cause greater than 12 000 deaths in the United States this year. The lack of effective therapy for disseminated RCC has stimulated the search for novel treatments including immunotherapeutic strategies, but poor therapeutic responses and marked toxicity have limited their use. The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family member TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/Apo-2L induces apoptosis in various tumor cell types, while having little cytotoxicity against normal cells. In this study, we investigated the tumoricidal potential of a recombinant adenovirus encoding human TNFSF10 (Ad5-TRAIL), alone and in combination with a panel of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), against the TRAIL/Apo-2L-resistant RCC line 786-O and normal human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTEC). Ad5-TRAIL was unable to induce apoptosis in either 786-O or RPTEC alone; however, tumor cell apoptosis occurred when Ad5-TRAIL was combined with HDAC inhibition. Except when combined with trichostatin A, RPTEC were not sensitized to Ad5-TRAIL by HDACi. In 786-O, HDAC inhibition induced CAR expression, permitting increased adenoviral infection and transgene expression. It also induced TRAIL-R2 expression, accelerated the death-inducing signaling complex formation and enhanced caspase-8 activation. Our results demonstrate the utility of combining Ad5-TRAIL with HDACi against RCC, and mechanistically define how this combination modulates RCC sensitivity to TRAIL/Apo-2L and adenoviral infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995; 3: 673–682.
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A . Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 12687–12690.
Griffith TS, Chin WA, Jackson GC, Lynch DH, Kubin MZ . Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J Immunol 1998; 161: 2833–2840.
Griffith TS, Anderson RD, Davidson BL, Williams RD, Ratliff TL . Adenoviral-mediated transfer of the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2 ligand gene induces tumor cell apoptosis. J Immunol 2000; 165: 2886–2894.
Griffith TS, Broghammer EL . Suppression of tumor growth following intralesional therapy with TRAIL recombinant adenovirus. Mol Ther 2001; 4: 257–266.
Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA, Xiong M et al. Long-term tumor-free survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2002; 21: 8020–8028.
Seol JY, Park KH, Hwang CI, Park WY, Yoo CG, Kim YW et al. Adenovirus-TRAIL can overcome TRAIL resistance and induce a bystander effect. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10: 540–548.
Johnstone RW . Histone-deacetylase inhibitors: novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 287–299.
Anderson RD, Haskell RE, Xia H, Roessler BJ, Davidson BL . A simple method for the rapid generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1034–1038.
Fischle W, Kiermer V, Dequiedt F, Verdin E . The emerging role of class II histone deacetylases. Biochem Cell Biol 2001; 79: 337–348.
Yamano T, Ura K, Morishita R, Nakajima H, Monden M, Kaneda Y . Amplification of transgene expression in vitro and in vivo using a novel inhibitor of histone deacetylase. Mol Ther 2000; 1: 574–580.
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi T, Wakada M, Sakai T . Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6261–6271.
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM . Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 1998; 281: 1305–1308.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A . Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 2000; 12: 611–620.
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N et al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 1997; 16: 5386–5397.
Davie JR, Spencer VA . Signal transduction pathways and the modification of chromatin structure. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 2001; 65: 299–340.
Imhof A, Yang XJ, Ogryzko VV, Nakatani Y, Wolffe AP, Ge H . Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 689–692.
Kitazono M, Goldsmith ME, Aikou T, Bates S, Fojo T . Enhanced adenovirus transgene expression in malignant cells treated with the histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 6328–6330.
Okegawa T, Li Y, Pong RC, Bergelson JM, Zhou J, Hsieh JT . The dual impact of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor expression on human prostate cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5031–5036.
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by Pilot & Feasibility Grant administered by the O'Brien Kidney Disease Center Program Project (2 P50 DK052617-06A1) and the National Cancer Institute (CA109446).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VanOosten, R., Earel, J. & Griffith, T. Enhancement of Ad5-TRAIL cytotoxicity against renal cell carcinoma with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Gene Ther 13, 628–632 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700939
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700939
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mechanism and therapeutic prospect of resveratrol combined with TRAIL in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2020)
-
Enhancement of adenovirus infection and adenoviral vector-mediated gene delivery by bromodomain inhibitor JQ1
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Expression of the coxsackie adenovirus receptor in neuroendocrine lung cancers and its implications for oncolytic adenoviral infection
Cancer Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Enhanced delivery of mda-7/IL-24 using a serotype chimeric adenovirus (Ad.5/3) improves therapeutic efficacy in low CAR prostate cancer cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2010)
-
Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in renal cell cancer
BMC Cancer (2008)