Abstract
Aim:
Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase (GP) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) play an important role in the control of blood glucose homeostasis and are proposed to be potential targets for anti-diabetic drugs. Geniposide is an iridoid glucoside extracted from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis fruits and has been reported to have a hypoglycemic effect. However, little is known about the biochemical mechanisms by which geniposide regulates hepatic glucose-metabolizing enzymes. The present study investigates whether the hypoglycemic effect of geniposide is mediated by GP or G6Pase.
Methods:
Type 2 diabetic mice, induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin injection, were treated with or without geniposide for 2 weeks. Blood glucose levels were monitored by a glucometer. Insulin concentrations were analyzed by the ELISA method. Total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels were measured using Labassay™ kits. Activities of hepatic GP and G6Pase were measured by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-coupled reaction. Real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting were used to determine the mRNA and protein levels of both enzymes.
Results:
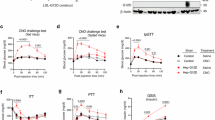
Geniposide (200 and 400 mg/kg) significantly decreased the blood glucose, insulin and TG levels in diabetic mice in a dose-dependent manner. This compound also decreased the expression of GP and G6Pase at mRNA and immunoreactive protein levels, as well as enzyme activity.
Conclusion:
Geniposide is an effective hypoglycemic agent in diabetic mice. The hypoglycemic effect of this compound may be mediated, at least in part, by inhibiting the GP and G6Pase activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barf T . Intervention of hepatic glucose production. Small molecule regulators of potential targets for type 2 diabetes therapy. Mini Rev Med Chem 2004; 4: 897–908.
Taguchi T, Yamashita E, Mizutani T, Nakajima H, Yabuuchi M, Asano N, et al. Hepatic glycogen breakdown is implicated in the maintenance of plasma mannose concentration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 288: E534–40.
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Park YB, Kang MA, Choi MS . Effect of citrus flavonoids on lipid metabolism and glucose-regulating enzyme mRNA levels in type-2 diabetic mice. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2006; 38: 1134–45.
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Jeong KS, Choi MS . The hypoglycemic effects of hesperidin and naringin are partly mediated by hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in c57bl/ksj-db/db mice. J Nutr 2004; 134: 2499–503.
Agius L . New hepatic targets for glycaemic control in diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 21: 587–605.
Onda K, Suzuki T, Shiraki R, Yonetoku Y, Negoro K, Momose K, et al. Synthesis of 5-chloro-n-aryl-1h-indole-2-carboxamide derivatives as inhibitors of human liver glycogen phosphorylase a. Bioorg Med Chem 2008; 16: 5452–64.
Kurukulasuriya R, Link JT, Madar DJ, Pei Z, Richards SJ, Rohde JJ, et al. Potential drug targets and progress towards pharmacologic inhibition of hepatic glucose production. Curr Med Chem 2003; 10: 123–53.
McCormack JG, Westergaard N, Kristiansen M, Brand CL, Lau J . Pharmacological approaches to inhibit endogenous glucose production as a means of anti-diabetic therapy. Curr Pharm Des 2001; 7: 1451–74.
Miyasita S . A historical study of Chinese drugs for the treatment of jaundice. Am J Chin Med (Gard City NY) 1976; 4: 239–43.
Kimura Y, Okuda H, Arichi S . Effects of geniposide isolated from gardenia jasminoides on metabolic alterations in high sugar diet-fed rats. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982; 30: 4444–7.
Koo HJ, Song YS, Kim HJ, Lee YH, Hong SM, Kim SJ, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of genipin, an active principle of gardenia. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 495: 201–8.
Kuo WH, Wang CJ, Young SC, Sun YC, Chen YJ, Chou FP . Differential induction of the expression of gst subunits by geniposide in rat hepatocytes. Pharmacology 2004; 70: 15–22.
Pham TQ, Cormier F, Farnworth E, Tong VH, Van Calsteren MR . Antioxidant properties of crocin from gardenia jasminoides ellis and study of the reactions of crocin with linoleic acid and crocin with oxygen. J Agric Food Chem 2000; 48: 1455–61.
Park EH, Joo MH, Kim SH, Lim CJ . Antiangiogenic activity of gardenia jasminoides. Fruit Phytother Res 2003; 17: 961–2.
Yan JE, Li WC, Bian GX, Wen LQ, Ren JP . Effect of geniposide on blood sugar reduction and its activation to PPARγ receptor. J Sichuan Agric Univ 2007; 25: 415–8.
Zhang CY, Parton LE, Ye CP, Krauss S, Shen R, Lin CT, et al. Genipin inhibits ucp2-mediated proton leak and acutely reverses obesity- and high glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction in isolated pancreatic islets. Cell Metab 2006; 3: 417–27.
Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Committee on Standards for Nutritional Studies. J Nutr 1977; 107: 1340–8.
Luo J, Quan J, Tsai J, Hobensack CK, Sullivan C, Hector R, et al. Nongenetic mouse models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1998; 47: 663–8.
Wallis MG, Appleby GJ, Youd JM, Clark MG, Penschow JD . Reduced glycogen phosphorylase activity in denervated hindlimb muscles of rat is related to muscle atrophy and fibre type. Life Sci 1999; 64: 221–8.
Nordlie RC, Arion WJ . Liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase, inorganic pyrophosphatase, and pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase. 3. Associated nucleoside triphosphate- and nucleoside diphosphate-glucose phosphotransferase activities. J Biol Chem 1965; 240: 2155–64.
Nordlie RC, Arion WJ . Glucose-6-Phosphatase. Methods Enzymol 1966; 9: 619–25.
Nordlie RC, Arion WJ, Glende EA Jr . Liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase, inorganic pyrophosphatase, and pyrophosphate-glucose phosphotransferase. iv. effects of adrenalectomy and cortisone administration on activities assayed in the absence and presence of deoxycholate. J Biol Chem 1965; 240: 3479–84.
Yu K, Schomisch SJ, Chandramouli V, Lee Z . Hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase activity in woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2006; 143: 225–31.
Alegre M, Ciudad CJ, Fillat C, Guinovart JJ . Determination of glucose-6-phosphatase activity using the glucose dehydrogenase-coupled reaction. Anal Biochem 1988; 173: 185–9.
Lowry OH, Schulz DW, Passonneau JV . The kinetics of glycogen phosphorylases from brain and muscle. J Biol Chem 1967; 242: 271–80.
Freeman S, Bartlett JB, Convey G, Hardern I, Teague JL, Loxham SJ, et al. Sensitivity of glycogen phosphorylase isoforms to indole site inhibitors is markedly dependent on the activation state of the enzyme. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 149: 775–85.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–8.
Reed MJ, Scribner KA . In-vivo and in-vitro models of type 2 diabetes in pharmaceutical drug discovery. Diabetes Obes Metab 1999; 1: 75–86.
Chen D, Wang MW . Development and application of rodent models for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2005; 7: 307–17.
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC . Mechanistic insights into diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 2007; 14: 1729–38.
Nordlie RC, Foster JD, Lange AJ . Regulation of glucose production by the liver. Annu Rev Nutr 1999; 19: 379–406.
Bollen M, Keppens S, Stalmans W . Specific features of glycogen metabolism in the liver. Biochem J 1998; 336 (Pt 1): 19–31.
Nemeti B, Gregus Z . Glutathione-dependent reduction of arsenate by glycogen phosphorylase a reaction coupled to glycogenolysis. Toxicol Sci 2007; 100: 36–43.
Roden M, Perseghin G, Petersen KF, Hwang JH, Cline GW, Gerow K, et al. The roles of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of hepatic glycogen synthesis and turnover in humans. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 642–8.
Petersen KF, Laurent D, Rothman DL, Cline GW, Shulman GI . Mechanism by which glucose and insulin inhibit net hepatic glycogenolysis in humans. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1203–9.
Takeuchi S, Goto T, Mikami K, Miura K, Ohshima S, Yoneyama K, et al. Mechanistic insights into diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress. Hepatol Res 2005; 33: 298–305.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Guangzhou (2006Z1-E6021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Sy., Wang, Gf., Liu, Zq. et al. Effect of geniposide, a hypoglycemic glucoside, on hepatic regulating enzymes in diabetic mice induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 202–208 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.17
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.17
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multi-omics analysis reveals the molecular basis of flavonoid accumulation in fructus of Gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis)
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
A robust and miniaturized screening platform to study natural products affecting metabolism and survival in Caenorhabditis elegans
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Focusing on the Pharmacological Effects of Iridoids and Crocetin and Its Ester Derivatives of Gardenia jasminoides
Current Pharmacology Reports (2019)
-
Geniposide Attenuates LPS-Induced Injury via Up-Regulation of miR-145 in H9c2 Cells
Inflammation (2018)
-
5′-AMP-activated protein kinase plays an essential role in geniposide-regulated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in rat pancreatic INS-1 β cells
Journal of Natural Medicines (2017)