Abstract
Aim:
The aim of the present study was to investigate the electrophysiological effect of ibuprofen on the cardiac action potentials (AP) and electrocardiograms (ECG), and to identify its arrhythmiogenic mechanism.
Methods:
The intracellular microelectrode recording technique was employed to record the fast- and slow-response AP in guinea pig papillary muscles. The cardiac responses of ibuprofen were monitored by ECG, both in in vivo and in vitro studies.
Results:
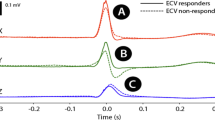
The ECG recording revealed that ibuprofen could induce arrhythmias, both in vitro and in vivo. Fatal ventricular fibrillations are readily produced in in vitro experiments by ibuprofen. Our results show that ibuprofen could dose dependently shorten the duration of AP and the effective refractory period (ERP), and it could also decrease the maximum depolarization velocity of phase 0 (Vmax) in both the fast- and slow-response AP. The duration of the QRS complex wave (QRS duration) in ECG was prolonged. Although the heart rate was depressed by ibuprofen, the corrected QT interval duration (QTc) decreased.
Conclusion:
Ibuprofen could inhibit cardiac Na+ and Ca2+ channels as it slows Vmax in both fast- and slow-response AP. Furthermore, ibuprofen shortens the ERP and decreases the excitation propagation within the heart, which might provide a substrate for an arrhythmiogenic re-entry circuit. Taken together, we conclude that ibuprofen, when used improperly, may impose a potential hazard in inducing cardiac arrhythmias in patients with existing heart diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Pratt CM, Hertz RP, Ellis BE, Crowell SP, Louv W, Moyé L . Risk of developing life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia associated with tefenadine in comparison with over-the-counter antihistamines, ibuprofen and clemastine. Am J Cardiol 1994; 15: 346–52.
Wu ZG, Zhou XL, Shu CM . Arrhythmia induced by the use of ibuprofen. Chin Foreign Med J 2005; 3: 88–9.
Shi YL, Wang YZ, Zhao XL . One case of atrial fibrillation induced by ibuprofen. J Med Theor Prac 2004; 17: 447.
Huerta C, Varas-Lorenzo C, Castellsague J, Garcia Rodriguez LA . Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of first hospital admission for heart failure in the general population. Heart 2006; 92: 1610–5.
Hudson M, Richard H, Pilote L . Differences in outcomes of patients with congestive heart failure prescribed celecoxib, rofecoxib, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: population based study. Br Med J 2005; 300: 1370–3.
Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, Bolognese JA, Oxenius B, Horgan K, et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemop prevention trial. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1092–102.
Yang ZF, Shi GZ, Li CZ, Wang HW, Liu K, Liu YM . Electrophysiologic effects of nicorandil on the guinea pig long QT1 syndrome model. J Cardiovasc Electr 2004; 15: 815–20.
Lu HL, Li CZ, Liu YM, Weng EQ, Liu B . The effects of Guanxinling on coronary blood flow-contraction force of cardiac muscle and electrical activity of the heart. Chin Heart J 2004; 16: 323–6.
Buchanan FG, Holla V, Katkuri S, Matta P, Dubois RN . Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 and the epidermal growth factor receptor for prevention and treatment of intestinal cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 9380–8.
Martinez-Gonzalez J, Badimon L . Mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular effects of Cox-inhibition: benefits and risks. Curr Pharm Res 2007; 13: 2215–27.
Graham DJ, Campen D, Hui R, Spence M, Cheetham C, Levy G, et al. Risk of acute myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death in patients treated with cyclo-oxygenase 2 selective and non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: nested case-control study. Lancet 2005; 365: 475–81.
Mukherjee D, Nissen SE, Topol EJ . Risk of cardiovascular events associated with selective COX-2 inhibitors. JAMA 2001; 286: 954–9.
Leroy S, Mosca A, Landre-Peigne C, Cosson MA, Pons G . Ibuprofen in childhood: evidence-based review of efficacy and safety. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2007; 3: 51–8.
Huang WF, Hsiao FY, Wen YW, Tsai YW . Cardiovascular events associated with the use of four nonselective NSAIDs (etodolac, nabumetone, ibuprofen, or naproxen) versus a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor (celecoxib): a population-based analysis in Taiwanese adults. Clin Ther 2006; 28: 1827–36.
Johnsen SP, Larsson H, Tarone RE, McLaughlin JK, Norgard B, Friis S, et al. Risk of hospitalization for myocardial infarction among users of rofecoxib, celecoxib, and other NSAIDs: a population-based case-control study. Arch Intern Med 2005; 165: 978–84.
Liu XK, Tosaki A, Engleman RM, Das DK . Salicylate reduces ventricular dysfunction and arrhythmias during reperfusion in isolated rat hearts. J Cardiovasc Pharm 1992; 19: 209–15.
Liu XK, Tosaki, A, Engleman RM, Das DK . Reduction of postischaemic ventricular dysfunction and arrhythmias by trapping hydroxyl radicals with salicylic acid. Int J Tissue React 1993; 15: 25–30.
Cheruku KK, Ghani A, Ahmad F, Pappas P, Silverman PR, Zelinger A, et al. Efficacy of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for prevention of atrial fibrillation following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Prev Cardiol 2004; 7: 13–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Science Foundation of Shanghai Education Committee (No 05BZ12) and the Science Foundation of Shanghai Jiaotong University Medical School (No 2005JY01).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Zf., Wang, Hw., Zheng, Yq. et al. Possible arrhythmiogenic mechanism produced by ibuprofen. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29, 421–429 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00754.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00754.x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ibuprofen Exerts Antiepileptic and Neuroprotective Effects in the Rat Model of Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Epilepsy via the COX-2/NLRP3/IL-18 Pathway
Neurochemical Research (2020)
-
Electrophysiological mechanisms of sophocarpine as a potential antiarrhythmic agent
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)
-
Palpitations following regular ibuprofen dosing in a 13-year-old girl: a case report
Journal of Medical Case Reports (2010)