Abstract
Aim:
To quantitatively assess the effect of lowering external Ca2+ ([Ca2+]o) on both endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxations in rabbit aorta.
Methods:
Isometric contractions and relaxations of isolated aortae were recorded. When assessing the effect of reduced [Ca2+]o on relaxations, the normal [Ca2+]o solution was substituted with one of the reduced [Ca2+]o solutions for one aorta, while a paired aorta was replenished with normal [Ca2+]o solution.
Results:
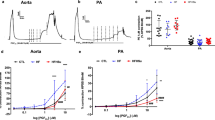
The extent of acetylcholine (ACh)-induced relaxation, which is dependent on an intact endothelium, is time-dependent, and inversely related to [Ca2+]o in a range of 0.02–2 mmol/L. ACh-induced relaxations were not significantly altered by the magnitude of the precontraction induced by PGF2α. Nitroprusside-induced relaxations, which are independent of the endothelium, are also attenuated by reduced [Ca2+]o. Relaxant responses to ACh were significantly more susceptible to reduced [Ca2+]o than nitroprusside-induced relaxations. A maximally effective relaxing concentration of D600, an L-type Ca channel blocker methoxyverapamil, (10−5 mol/L) attenuated ACh-induced relaxations, whereas nitroprusside-induced relaxations were unaffected by D600.
Conclusion:
Thus, endothelium-dependent relaxation is more dependent on [Ca2+]o than endothelium-independent relaxation, and it seems likely that [Ca2+]o plays an important role not only in contractile processes, but also in relaxant processes as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bohr DF . Vascular smooth muscle updated. Circ Res 1973; 32: 665–72.
Johansson B, Somlyo AP . Electrophysiology and Excitation-contraction coupling. In: Bohr DF, Somlyo AP, and Sparks HV Jr, editors. Handbook of physiology, Sect 2, Vol II, Vascular Smooth Muscle, Bethesda, Maryland, USA: Am Physiol Soc; 1980. p 301–323.
Hayashi S, Toda N . Inhibition by Cd2+, verapamil and papaverine of Ca2+-induced contraction in isolated cerebral and peripheral arteries of the dog. Br J Pharmacol 1977; 60: 35–43.
Hester RK, Weiss GB, Fry WJ . Effects of norepinephrine, dopamine and potassium on tension and 45Ca fluxes in canine and rabbit renal arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1978; 207: 364–71.
Hester RK, Weiss GB . Comparison of the degree of dependence of canine renal arteries and veins on high and low affinity calcium for responses to norepinephrine and potassium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1981; 216: 239–46.
Ratz PH, Flaim SF . Species and blood vessel specificity in the use of calcium for contraction. In: Flaim SF and Zelis R, editors. Calcium Blockers. Baltimore, USA: Urban and Schwarzenberg; 1982. p 77–98.
Furchgott RF . Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res 1983; 53: 557–73.
Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE, Chaudhuri G . Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 9265–9.
Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S . Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 1987; 327: 524–6.
Rapoport RM, Schwartz K, Murad F . Effect of sodium-potassium pump inhibitors and membrane-depolarizing agents on sodium nitroprusside-induced relaxation and cyclic guanosine monophosphate accumulation in rat aorta. Circ Res 1985; 57: 164–70.
Winquist RJ, Bunting PB, Schofield TL . Blockade of endothelium-dependent relaxation by the amiloride analog dichlorobenzamil: Possible role of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in the release of endothelium-derived relaxant factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1985; 235: 644–50.
Miller RC, Schoeffter P, Stoclet JC . Insensitivity of calcium-dependent endothelial stimulation in rat isolated aorta to the calcium entry blocker, flunarizine. Br J Pharmacol 1985; 85: 481–7.
Long CJ, Stone TW . The release of endothelium-derived relaxant factor is calcium dependent. Blood Vessels 1985; 22: 205–8.
Singer HA, Peach MJ . Calcium- and endothelial-mediated vascular smooth muscle relaxation in rabbit aorta. Hypertension 1982; 4: 19–25.
Carrier O Jr, Wedell EK, Barron KW . Specific α-adrenergic receptor desensitization in vascular smooth muscle. Blood Vessels 1978; 15: 247–58.
Hayashi S, Park MK, Kuehl TJ . Relaxant and contractile responses to prostaglandins in premature, newborn and adult baboon cerebral arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1985; 233: 628–35.
Hester RK . The effect of 2-nicotinamidoethyl nitrate on agonist-sensitive Ca2+ release and Ca2+ entry in rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1985; 233; 100–11.
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV . Vascular smooth muscle. I. Normal structure, pathology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Pharmacol Rev 1968; 20: 197–272.
Shanes AM . Electrochemical aspects of physiological and pharmacological action in excitable cells. I. The resting cell and its alteration by extrinsic factors. Pharmacol Rev 1958; 10: 59–164.
Casteels R, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H, Suzuki H . The membrane properties of the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol 1977; 271: 41–61.
Webb RC, Bohr DF . Mechanism of membrane stabilization by calcium in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 1978; 235: C227–32.
Belardinelli L, Harder D, Sperelakis N, Rubio RM . Berne RM . Cardiac glycoside stimulation of inward Ca2+ current in vascular smooth muscle of canine coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1979; 209: 62–6.
Haddy FJ . Potassium effects on contraction in arterial smooth muscle mediated by Na+, K+-ATPase. Fed Proc 1983; 42: 239–45.
Hayashi S, Park MK . Neurogenic and myogenic contractile responses of dog mesenteric arteries to reduced K+ concentration and their interaction with ouabain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1984; 230: 527–33.
De Mey JG, Vanhoutte PM . Interaction between Na+, K+ exchanges and the direct inhibitory effect of acetylcholine on canine femoral arteries. Circ Res 1980; 46: 826–36.
Schultz KD, Schultz K, Schultz G . Sodium nitroprusside and other smooth muscle relaxants increase cyclic GMP levels in rat ductus deferens. Nature 1977; 265: 750–1.
Andersson R, Lundholm L, Mohme-Lundholm E, Nilsson K . Role of cyclic AMP and Ca2+ in metabolic and mechanical events in smooth muscle. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 1972; 1: 213–29.
Popescu LM, Panoiu C, Hinescu M, Nutu O . The mechanism of cGMP-induced relaxation in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 1985; 107: 393–4.
Bulbring E, den Hertog A . The action of isoprenaline on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol 1980; 304: 277–96.
Turlapaty, PDMV, Altura BM . Magnesium deficiency produces spasms of coronary arteries: Relationship to etiology of sudden death ischemic heart disease. Science 1980; 208: 198–200.
Kauser K, Rubanyi GM . Gender difference in endothelial dysfunction in the aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1995; 25 (4 Pt 1): 517–23.
Luksha L, Poston L, Gustafsson JA, Hultenby K, Kublickiene K . The oestrogen receptor beta contributes to sex related differences in endothelial function of murine small arteries via EDHF. J Physiol 2006; 577(Pt-3): 945–5.
Hayashi S, Park MK and Kuehl TJ . Higher sensitivity of cerebral arteries isolated from premature and newborn baboons to adrenergic and cholinergic stimulation. Life Sci 1984; 35: 253–60.
Rinner I, Doods HN, van Charldorp KJ, Davidesko D, van Zwieten PA . Binding of muscarine receptor antagonists to pig coronary smooth muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 1988; 337: 146–50.
Gluais P, Lonchampt M, Morrow JD, Vanhoutte PM, Feletou M . Acetylcholine-induced endothelium-dependent contractions in the SHR aorta: the Janus face of prostacyclin. Br J Pharmacol 2005; 146: 834–45.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NHLBI grant NHL 26L2I. Methoxyverapamil (D600) was generously supplied by Knoll AG, Ludwigshafen, West Germany. The authors would like to thank Mrs Beth BECKER for her technical assistance and Mrs Patty SAMPSON for her kind assistance in preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, S., Hester, R. Reduction in extracellular Ca2+ attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation more than nitroprusside-induced relaxation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 19–26 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.164
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.164