Abstract
Aim:
To study the influence of β-receptor activation on sodium channel current and the physiological significance of increased sodium current with regard to the increased cardiac output caused by sympathetic excitation.
Methods:
Multiple experimental approaches, including ECG, action potential recording with conventional microelectrodes, whole-cell current measurements, single-channel recordings, and pumping-force measurements, were applied to guinea pig hearts and isolated ventricular myocytes.
Results:
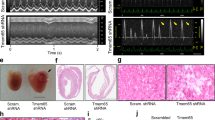
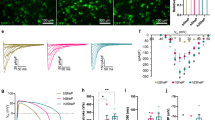
Isoprenaline was found to dose-dependently shorten QRS waves, increase the amplitude and the Vmax of action potentials, augment the fast sodium current, and increase the occurrence frequencies and open time constants of the long-open and burst modes of the sodium channel. Increased levels of membrane-permeable cAMP have similar effects. In the presence of a calcium channel blocker, TTX reversed the increased pumping force produced by isoprenaline.
Conclusion:
Beta-adrenergic modulation increases the inward sodium current and accelerates the conduction velocity within the ventricles by changing the sodium channel modes, which might both be conducive to the synchronous contraction of the heart and enhance its pumping function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Matsuda JJ, Lee H, Shibata EF . Enhancement of rabbit cardiac sodium channels by β-adrenergic stimulation. Circ Res 1992; 70: 199–207.
Ono K, Fozzard HA, Hanck DA . Mechanism of cAMP-dependent modulation of cardiac sodium channel current kinetics. Circ Res 1993; 72: 807–15.
Schreibmayer W, Frohnwieser B, Dascal N, Platzer D, Spreitzer B, Zechner R, et al. β-Adrenergic modulation of currents produced by rat cardiac Na+ channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Receptors Channels 1994; 2: 339–50.
Kirstein M, Eickhorn R, Kochsiek K, Langenfeld H . Dose-dependent alteration of rat cardiac sodium current by isoproterenol: results from direct measurements on multicellular preparations. Pflügers Arch 1996; 431: 395–401.
Murphy BJ, Rogers J, Perdichizzi AP, Colvin AA, Catterall WA . cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of two sites in the subunit of the cardiac sodium channel. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 28837–43.
Lu T, Lee HC, Kabat JA, Shibata EF . Modulation of rat cardiac sodium channel by the stimulatory G protein subunit. J Physiol 1999; 518: 371–84.
Frohnweiser B, Chen LQ, Schreibmayer W, Kallen RG . Modulation of the human cardiac sodium channelα-subunit by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the responsible sequence domain. J Physiol (Lond) 1997; 498: 309–18.
Sunami A, Fan Z, Nakamura F, Naka M, Tanaka T, Sawanobori T, et al. The catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase directly inhibits sodium channel activities in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pflügers Arch 1991; 419: 415–7.
Fozzard HA, Hanck DA . Structure and function of voltage-dependent sodium channels: comparison of brain II and cardiac isoforms. Physiol Rev 1996; 76: 887–900,
Schubert B, VanDongen AMJ, Kirsch GE, Brown AM . Inhibition of cardiac Na+ currents by isoproterenol. Science 1989; 245: 516–9.
Gintant GA, Liu DW . β-Adrenergic modulation of fast inward sodium current in canine myocardium: syncytial preparations versus isolated myocytes. Circ Res 1992; 42: 844–50.
Zhou J, Yi J, Hu N, George AL, Murray KT . Activation of protein kinase A modulates trafficking of the human cardiac sodium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Circ Res 2000; 87: 33–8.
Li CZ, Huang HW, Liu YM . Four types of late Na channel current in isolated ventricular myocytes and their contribution to the lastingness of action potential plateau. Acta Physiol Sin 1997; 49: 241–8.
Liu YM, DeFelice LJ, Mazzanti M . Na channels that remain open throughout the cardiac action potential plateau. Biophys J 1992; 83: 654–62.
Zilberter YuI, Starmer CF, Starobin J, Grant AO . Late Na channels in cardiac cells: the physiological role of background Na channels. Biophys J 1994; 67: 153–60.
Liu YM, DeFelice LJ . Na channels that remain open throughout the cardiac action potential plateau. Biophys J 1992; 63: 654–62.
Li CZ, Wang HW, Liu JL, Liu K, Yang ZF, Liu YM . Effect of ATX II on opening modes of myocyte sodium channel, action potential and QT intervals of ECG. Acta Physiol Sin 2001; 53: 111–6.
De Boer TP, van Rijen HV, Van der Heyden MA, Kok B, Opthof T, Vos MA, et al. Beta-, not alpha-adrenergic stimulation enhances conduction velocity in cultures of neonatal cardiomyocytes. Circ J 2007; 71: 973–81.
Lowenstein WR . Regulation of cell-to-cell communication by phosphorylation. Biochem Soc Symp 1985; 50: 43–58
Arnar DO, Van Why KJ, Gleed K, Foreman B, Hopson JR, Lee HC, et al. Effect of beta-adrenergic stimulation on the QRS duration of the signal-averaged electrocardiogram. Am Heart J 1997; 134: 395–8.
Palygin OA, Pettus JM, Shibata EF . Regulation of caveolar cardiac sodium current by a single Gsalpha histidine residue. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2008; 294: H1693–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science Foundation of the Shanghai Education Committee, No 05BZ12 and 2005JY01 and the Shanghai Science Committee Foundation No 06JC14045.
We would like to express our thanks to Professor Louise J DeFELICE (Dept of Pharmacology, Vanderbilt University, USA) for consultation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hw., Yang, Zf., Zhang, Y. et al. Beta-receptor activation increases sodium current in guinea pig heart. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 1115–1122 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.96
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.96
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bacterial toxins and heart function: heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin B promotes changes in cardiac function with possible relevance for sudden cardiac death
Biophysical Reviews (2023)
-
β1-Adrenergic blocker bisoprolol reverses down-regulated ion channels in sinoatrial node of heart failure rats
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2016)
-
Epinephrine reversed high-concentration bupivacaine- induced inhibition of calcium channels and transient outward potassium current channels, but not on sodium channel in ventricular myocytes of rats
BMC Anesthesiology (2015)
-
Electrophysiological mechanisms of sophocarpine as a potential antiarrhythmic agent
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)