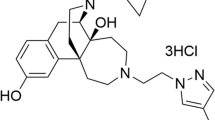
Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the effects of ATPM-ET [(−)-3-N-Ethylaminothiazolo [5,4-b]-N-cyclopropylmethylmorphinan hydrochloride] on physical dependence and behavioral sensitization to morphine in mice.
Methods:
The pharmacological profile of ATPM-ET was characterized using competitive binding and GTPγS binding assays. We then examined the antinociceptive effects of ATPM-ET in the hot plate test. Morphine dependence assay and behavioral sensitization assay were used to determine the effect of ATPM-ET on physical dependence and behavior sensitization to morphine in mice.
Results:
The binding assay indicated that ATPM-ET ATPM-ET exhibited a high affinity to both κ- and μ-opioid receptors with Ki values of 0.15 nmol/L and 4.7 nmol/L, respectively, indicating it was a full κ-opioid receptor agonist and a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist. In the hot plate test, ATPM-ET produced a dose-dependent antinociceptive effect, with an ED50 value of 2.68 (2.34–3.07) mg/kg. Administration of ATPM-ET (1 and 2 mg/kg, sc) prior to naloxone (3.0 mg/kg, sc) injection significantly inhibited withdrawal jumping of mice. In addition, ATPM-ET (1 and 2 mg/kg, sc) also showed a trend toward decreasing morphine withdrawal-induced weight loss. ATPM-ET (1.5 and 3 mg/kg, sc) 15 min before the morphine challenge significantly inhibited the morphine-induced behavior sensitization (P<0.05).
Conclusion:
ATPM-ET may have potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of drug abuse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Wells JL, Bartlett JL, Ananthan S, Bilsky EJ . In vivo pharmacological characterization of SoRI 9409, a nonpeptidic opioid mu-agonist/delta-antagonist that produces limited antinociceptive tolerance and attenuates morphine physical dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 297: 597–605.
Sepulveda J, Ortega A, Zapata G, Contreras E . Acamprosate decreases the induction of tolerance and physical dependence in morphine-treated mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2002; 445: 87–91.
Fattore L, Spano MS, Deiana S, Melis V, Cossu G, Fadda P, et al. An endocannabinoid mechanism in relapse to drug seeking: a review of animal studies and clinical perspectives. Brain Res Rev 2007; 53: 1–16.
Lyvers M . Drug addiction as a physical disease: the role of physical dependence and other chronic drug-induced neurophysiological changes in compulsive drug self-administration. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 1998; 6: 107–25.
Bell K, Salmon A . Pain, physical dependence and pseudoaddiction: redefining addiction for 'nice' people? Int J Drug Policy 2009; 20: 170–8.
Suzuki T, Shiozaki Y, Masukawa Y, Misawa M, Nagase H . The role of mu- and kappa-opioid receptors in cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Jpn J Pharmacol 1992; 58: 435–42.
Crawford CA, McDougall SA, Bolanos CA, Hall S, Berger SP . The effects of the kappa agonist U-50,488 on cocaine-induced conditioned and unconditioned behaviors and Fos immunoreactivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995; 120: 392–9.
Shippenberg TS, LeFevour A, Heidbreder C . Kappa-opioid receptor agonists prevent sensitization to the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996; 276: 545–54.
Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM, Raucci J, Archer S . Kappa opioid inhibition of morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res 1995; 681: 147–52.
Negus SS, Mello NK, Portoghese PS, Lin CE . Effects of kappa opioids on cocaine self-administration by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 282: 44–55.
Mello NK, Negus SS . Effects of kappa opioid agonists on cocaine- and food-maintained responding by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998; 286: 812–24.
Schenk S, Partridge B, Shippenberg TS . U69593, a kappa-opioid agonist, decreases cocaine self-administration and decreases cocaine-produced drug-seeking. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999; 144: 339–46.
Schenk S, Partridge B, Shippenberg TS . Reinstatement of extinguished drug-taking behavior in rats: effect of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, U69593. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000; 151: 85–90.
Mello NK, Negus SS . Interactions between kappa opioid agonists and cocaine. Preclinical studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000; 909: 104–32.
Bowen CA, Negus SS, Zong R, Neumeyer JL, Bidlack JM, Mello NK . Effects of mixed-action kappa/mu opioids on cocaine self-administration and cocaine discrimination by rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003; 28: 1125–39.
Neumeyer JL, Gu XH, van Vliet LA, DeNunzio NJ, Rusovici DE, Cohen DJ, et al. Mixed kappa agonists and mu agonists/antagonists as potential pharmacotherapeutics for cocaine abuse: synthesis and opioid receptor binding affinity of N-substituted derivatives of morphinan. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2001; 11: 2735–40.
Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM . Development of novel medications for drug addiction. The legacy of an African shrub. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000; 909: 88–103.
Wang YJ, Tao YM, Li FY, Wang YH, Xu XJ, Chen J, et al. Pharmacological characterization of ATPM [(−)-3-aminothiazolo[5,4-b]-N-cyclopropylmethylmorphinan hydrochloride], a novel mixed kappa-agonist and mu-agonist/-antagonist that attenuates morphine antinociceptive tolerance and heroin self-administration behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2009; 329: 306–13.
Tao YM, Li QL, Zhang CF, Xu XJ, Chen J, Ju YW, et al. LPK-26, a novel kappa-opioid receptor agonist with potent antinociceptive effects and low dependence potential. Eur J Pharmacol 2008; 584: 306–11.
Li JX, Zhang Q, Liang JH . Valproate prevents the induction, but not the expression of morphine sensitization in mice. Behav Brain Res 2004; 152: 251–7.
Tsuji M, Takeda H, Matsumiya T, Nagase H, Yamazaki M, Narita M, et al. A novel kappa-opioid receptor agonist, TRK-820, blocks the development of physical dependence on morphine in mice. Life Sci 2000; 66: PL353–8.
Puig-Ramos A, Santiago GS, Segarra AC . U-69593, a kappa opioid receptor agonist, decreases cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in female rats. Behav Neurosci 2008; 122: 151–60.
Collins SL, D'Addario C, Izenwasser S . Effects of kappa-opioid receptor agonists on long-term cocaine use and dopamine neurotransmission. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 426: 25–34.
Li JX, Zhao WL, Liang JH . Effects of carbamazepine on morphine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice. Brain Res 2004; 1019: 77–83.
Zhang A, Xiong W, Hilbert JE, DeVita EK, Bidlack JM, Neumeyer JL . 2-Aminothiazole-derived opioids. Bioisosteric replacement of phenols. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 1886–8.
Neumeyer JL, Zhang A, Xiong W, Gu XH, Hilbert JE, Knapp BI, et al. Design and synthesis of novel dimeric morphinan ligands for kappa and micro opioid receptors. J Med Chem 2003; 46: 5162–70.
Stevenson GW, Wentland MP, Bidlack JM, Mello NK, Negus SS . Effects of the mixed-action kappa/mu opioid agonist 8-carboxamidocyclazocine on cocaine- and food-maintained responding in rhesus monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 506: 133–41.
Neumeyer JL, Mello NK, Negus SS, Bidlack JM . Kappa opioid agonists as targets for pharmacotherapies in cocaine abuse. Pharm Acta Helv 2000; 74: 337–44.
Mello NK, Mendelson JH, Sholar MB, Jaszyna-Gasior M, Goletiani N, Siegel AJ . Effects of the mixed mu/kappa opioid nalbuphine on cocaine-induced changes in subjective and cardiovascular responses in men. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 618–32.
Robinson TE, Berridge KC . The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1993; 18: 247–91.
Hao Y, Yang JY, Wu CF, Wu MF . Pseudoginsenoside-F11 decreases morphine-induced behavioral sensitization and extracellular glutamate levels in the medial prefrontal cortex in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2007; 86: 660–6.
Kotlinska J, Bochenski M . Comparison of the effects of mGluR1 and mGluR5 antagonists on the expression of behavioral sensitization to the locomotor effect of morphine and the morphine withdrawal jumping in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2007; 558: 113–8.
Zarrindast MR, Heidari-Darvishani A, Rezayof A, Fathi-Azarbaijani F, Jafari-Sabet M, Hajizadeh-Moghaddam A . Morphine-induced sensitization in mice: changes in locomotor activity by prior scheduled exposure to GABAA receptor agents. Behav Pharmacol 2007; 18: 303–10.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2009CB522000, 2009ZX09301-001), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30873050) and a fund granted by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-YW-R-253).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Jf., Wang, Yh., Li, Fy. et al. Effects of ATPM-ET, a novel κ agonist with partial μ activity, on physical dependence and behavior sensitization in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 1547–1552 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.164
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of ATPM-ET, a novel κ agonist and μ partial agonist, in mice
Psychopharmacology (2016)
-
Novel κ-opioid receptor agonist MB-1C-OH produces potent analgesia with less depression and sedation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2015)