Abstract
Aim:
To study the molecular mechanisms underlying α-tocopheryl succinate (α-TOS)-induced apoptosis in erbB2-positive breast cancer cells and to determine whether α-TOS and the human recombinant TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (hrTRAIL) act synergically to induce cell death of erbB2-expressing breast cancer cells.
Methods:
The annexin V binding method was used to measure apoptosis induced by α-TOS and/or hrTRAIL. RT-PCR and Western blotting were performed to detect gene and protein expression. A colorimetric assay was performed to detect caspase activity. The TransAMTM NF-κB p65 kit was used to assess NF-κB activation.
Results:
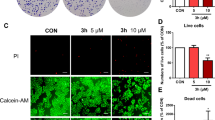
α-TOS (100 μmol/L) significantly inhibited NF-κB nuclear translocation in erbB2-expressing breast cancer cells; this inhibition is expected to result in the inactivation of NF-κB. α-TOS (50 and 100 μmol/L) inhibited the expression of Flice-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (c-IAP1) in erbB2-positive cells. α-TOS (100 μmol/L) inhibited Akt activation and augmented the activity of caspase 3 and caspase 8 in breast cancer cells expressing erbB2. α-TOS (50 μmol/L) and hrTRAIL (30 mg/mL) acted synergically to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. α-TOS also decreased the hrTRAIL-induced transient activation of NF-κB .
Conclusion:
Our results suggest that α-TOS mediates the apoptosis of erbB2-positive breast cancer cells and acts synergically with hrTRAIL via the NF-κB pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Roskoski R . The ErbB/HER receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 319: 1–11.
Jarvinen TA, Liu ET . Simultaneous amplification of Her (ErbB2) and topoisomerase IIα (TOP2A) genes in combination therapy in cancer. Curr cancer drug targets 2006; 6: 579–602.
Ward SG, Finan P . Isoform-specific phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2003; 3: 426–34.
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, et al. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 2003; 17: 590–603.
Kane LP, Shapiro VS, Stokoe D, Weiss A . Induction of NF--κB by the Akt/PDK kinase. Curr Biol 1999; 9: 601–4.
Shukla S, Maclennan GT, Marengo SR, Resnick MI, Gupta S . Constitutive activation of PI3K-Akt and NF-kappaB during prostate cancer progression in autochthonous transgenic mouse model. Prostate 2005; 64: 224–39.
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, MacKenzie AE . The inhibitors of apoptosis protein (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 1998; 17: 3247–59.
Kim KM, Lee YJ . Amiloride augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death by inhibiting phosphorylation of kinases and phosphatases associated with the P13KAkt pathway. Oncogene 2005; 24: 355–66.
Neuzil J, Tomasetti M, Mellick AS, Alleva R, Salvatore BA, Birringer M, et al. Vitamin E analogues: A new class of inducers of apoptosis with selective anti-cancer effect. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2004; 4: 267–84.
Wang XF, Witting PK, Salvatore BA, Neuzil J . Vitamin E analogs trigger apoptosis in HER2/erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by signaling via the mitochondrial pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 326: 282–9.
Gliniak B, Le T . Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand's anti-tumor activity in vivo is enhanced by the chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 6153–8.
Matsuzaki H, Schmied BM, Ulrich A, Standop J, Scheider MB, Batra SK, et al. Combination of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and actinomycin D induces apoptosis even in TRAIL-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 407–14.
Bernard D, Quatannens B, Vandenbunder B, Abbadie C . Rel/NF--κB transcription factors protect against tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by up-regulating the TRAIL decoy receptor DcR1. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 27322–8.
Tomasetti M, Rippo MR, Alleva R, Moretti S, Andera L, Neuzil J, et al. α-Tocopheryl succinate and TRAIL selectively synergise in induction of apoptosis in human alignant mesothelioma cells. Br J Cancer 2004; 90: 1644–53.
Wang XF, Birringer M, Dong LF, Veprek P, Low P, Swettenham E, et al. A peptide conjugate of vitamin E succinate targets breast cancer cells with high erbB2 expression. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 3337–44.
Dalen H, Neuzil J . α-Tocopheryl succinate sensitises T lymphoma cells to TRAIL killing by suppressing NF--κB activation. Br J Cancer 2003; 88: 153–8.
Weber T, Dalen H, Andera L, Nègre-Salvayre A, Augé N, Sticha M, et al. Mitochondria play a central role in apoptosis induced by α-tocopheryl succinate, an agent with anticancer activity: comparison with receptor-mediated pro-apoptotic signaling. Biochemistry 2003; 42: 4277–91.
Holcik M . The IAP proteins. Trends Genet 2002; 18: 537–8.
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M, et al. The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF kappaB and Erk signaling pathway. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 640–8.
Mathiasen IS, Lademann U, Jäättelä M . Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4848–56.
Liu N, Zhang J, Zhang J, Liu S, Liu Y, Zheng D . Erbin-regulated sensitivity of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to TRAIL via ErbB2/AKT/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biochem 2008; 143: 793–801.
Akazawa A, Nishikawa K, Suzuki K, Asano R, Kumadaki I, Satoh H, et al. Induction of apoptosis in a human breast cancer cell overexpressing ErbB-2 receptor by α-tocopheryloxybutyric acid. Jpn J Pharmacol 2002; 89: 417–21.
Erl W, Weber C, Wardemann C, Weber PC . α-Tocopheryl succinate inhibits monocytic cell adhesion to endothelial cells by suppressing NF-κB mobilization. Am J Physiol 1997; 273: H634–40.
Bonavida B, Ng CP, Jazirehi A, Schiller G, Mizutani Y . Selectivity of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells and synergy with drugs: the trail to nontoxic cancer therapeutics. Int J Oncol 1999; 15: 793–802.
French LE, Tschopp J . The TRAIL to selective tumor death. Nat Med 1999; 5: 146–7.
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X . An APAF-1·cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 11549–56.
Trauzold A, Schniewind B, Egberts J . TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7434–9.
Weber T, Lu M, Andera L, Lahm H, Gellert N, Fariss MW, et al. Vitamin E succinate is a potent novel antineoplastic agent with high tumor selectivity and cooperativity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL, Apo2L) in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 863–9.
Wang XF, Dong LF, Zhao Y, Tomasetti M, Wu K, Neuzil J . Vitamin E analogues as anti-cancer agents: lessons from studies with α-tocopheryl succinate. Mol Nutr Food Res 2006; 50: 675–85.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No 30873001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Xf., Xie, Y., Wang, Hg. et al. α-Tocopheryl succinate induces apoptosis in erbB2-expressing breast cancer cell via NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 1604–1610 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.171
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.171
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The interrelationship between HER2 and CASP3/8 with apoptosis in different cancer cell lines
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
TRAIL and vitamins: opting for keys to castle of cancer proteome instead of open sesame
Cancer Cell International (2012)
-
(+)α-Tocopheryl succinate inhibits the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I and is as effective as arsenic trioxide or ATRA against acute promyelocytic leukemia in vivo
Leukemia (2012)