Abstract
Aim:
Auditory neuropathy (AN) is a hearing disorder characterized by abnormal auditory nerve function with preservation of normal cochlear hair cells. This study was designed to investigate whether treatment with molecular hydrogen (H2), which can remedy damage in various organs via reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis, is beneficial to ouabain-induced AN in gerbils.
Methods:
AN model was made by local application of ouabain (1 mmol/L, 20 mL) to the round window membrane in male Mongolian gerbils. H2 treatment was given twice by exposing the animals to H2 (1%, 2%, and 4%) for 60 min at 1 h and 6 h after ouabain application. Before and 7 d after ouabain application, the hearing status of the animals was evaluated using the auditory brainstem response (ABR) approach, the hear cell function was evaluated with distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAE). Seven days after ouabain application, the changes in the cochleae, especially the spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs), were morphologically studied. TUNEL staining and immunofluorescent staining for activated caspase-3 were used to assess the apoptosis of SGNs.
Results:
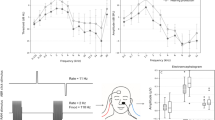
Treatment with H2 (2% and 4%) markedly attenuated the click and tone burst-evoked ABR threshold shift at 4, 8, and 16 kHz in ouabain-exposed animals. Neither local ouabain application, nor H2 treatment changed the amplitude of DPOAE at 4, 8, and 16 kHz. Morphological study showed that treatment with H2 (2%) significantly alleviated SGN damage and attenuated the loss of SGN density for each turn of cochlea in ouabain-exposed animals. Furthermore, ouabain caused significantly higher numbers of apoptotic SGNs in the cochlea, which was significantly attenuated by the H2 treatment. However, ouabain did not change the morphology of cochlear hair cells.
Conclusion:
The results demonstrate that H2 treatment is beneficial to ouabain-induced AN via reducing apoptosis. Thus, H2 might be a potential agent for treating hearing impairment in AN patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Rance G . Auditory neuropathy/dys-synchrony and its perceptual consequences. Trends Amplif 2005; 9: 1–43.
Starr A, Picton TW, Sininger Y, Hood LJ, Berlin CI . Auditory neuropathy. Brain 1996; 119: 741–53.
Vlastarakos PV, Nikolopoulos TP, Tavoulari E, Papacharalambous G, Korres S . Auditory neuropathy: endocochlear lesion or temporal processing impairment? Implications for diagnosis and management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2008; 72: 1135–50.
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 2007; 13: 688–94.
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu WW, Luo X, Qiang S, Zhang JH, et al. Hydrogen therapy reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Neurosci Lett 2008; 441: 167–72.
Cardinal JS, Zhan J, Wang Y, Sugimoto R, Tsung A, McCurry KR, et al. Oral hydrogen water prevents chronic allograft nephropathy in rats. Kidney Int 2010; 77: 101–9.
Dole M, Wilson FR, Fife WP . Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: a possible treatment for cancer. Science 1975; 190: 152–4.
Huang CS, Kawamura T, Toyoda Y, Nakao A . Recent advances in hydrogen research as a therapeutic medical gas. Free Radic Res 2010; 44: 971–82.
Huang Y, Xie K, Li J, Xu N, Gong G, Wang G, et al. Beneficial effects of hydrogen gas against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits. Brain Res 2011; 1378: 125–36.
Ji X, Liu W, Xie K, Qu Y, Chao X, Chen T, et al. Beneficial effects of hydrogen gas in a rat model of traumatic brain injury via reducing oxidative stress. Brain Res 2010; 1354: 196–205.
Kajiyama S, Hasegawa G, Asano M, Hosoda H, Fukui M, Nakamura N, et al. Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutr Res 2008; 28: 137–43.
Xie K, Yu Y, Pei Y, Hou L, Chen S, Xiong L, et al. Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine polymicrobial sepsis via reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1 release. Shock 2010; 34: 90–7.
Xie K, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Liu W, Pei Y, Xiong L, et al. Hydrogen gas improves survival rate and organ damage in zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. Shock 2010; 34: 495–501.
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu K, Liu W, Li R, Zhang JH, et al. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen saline in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Brain Res 2009; 1256: 129–37.
Kikkawa YS, Nakagawa T, Horie RT, Ito J . Hydrogen protects auditory hair cells from free radicals. Neuroreport 2009; 20: 689–94.
Lin Y, Kashio A, Sakamoto T, Suzukawa K, Kakigi A, Yamasoba T . Hydrogen in drinking water attenuates noise-induced hearing loss in guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 2011; 487: 12–6.
Schmiedt RA, Okamura HO, Lang H, Schulte BA . Ouabain application to the round window of the gerbil cochlea: a model of auditory neuropathy and apoptosis. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2002; 3: 223–33.
Lang H, Schulte BA, Schmiedt RA . Ouabain induces apoptotic cell death in type I spiral ganglion neurons, but not type II neurons. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2005; 6: 63–74.
Lang H, Schulte BA, Goddard JC, Hedrick M, Schulte JB, Wei L, et al. Transplantation of mouse embryonic stem cells into the cochlea of an auditory-neuropathy animal model: effects of timing after injury. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2008; 9: 225–40
Gorga MP, Johnson TA, Kaminski JR, Beauchaine KL, Garner CA, Neely ST . Using a combination of click- and tone burst-evoked auditory brain stem response measurements to estimate pure-tone thresholds. Ear Hear 2006; 27: 60–74.
Li J, Wang C, Zhang JH, Cai JM, Cao YP, Sun XJ . Hydrogen-rich saline improves memory function in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer's disease by reduction of oxidative stress. Brain Res 2010; 1328: 152–61.
Sun H, Chen L, Zhou W, Hu L, Li L, Tu Q, et al. The protective role of hydrogen-rich saline in experimental liver injury in mice. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 471–80.
Elmore S . Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 2007; 35: 495–516.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30930098 to Jian-hua QIU), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No 2011CB504505 to Jian-hua QIU) and the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30801287 to Juan QU; 81101409 to Ke-liang XIE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Gan, Yn., Xie, Kl. et al. Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates ouabain-induced auditory neuropathy in gerbils. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 445–451 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.190
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.190
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Taurine enhances mouse cochlear neural stem cell transplantation via the cochlear lateral wall for replacement of degenerated spiral ganglion neurons via sonic hedgehog signaling pathway
Cell and Tissue Research (2019)
-
Molecular hydrogen alleviates asphyxia-induced neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in newborn pigs
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)
-
The hydrogen molecule as antioxidant therapy: clinical application in hemodialysis and perspectives
Renal Replacement Therapy (2016)
-
Beneficial biological effects and the underlying mechanisms of molecular hydrogen - comprehensive review of 321 original articles -
Medical Gas Research (2015)