Abstract
Aim:
Myostatin gene is a member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) family that negatively regulates skeletal muscle growth. Genetic polymorphisms in Myostatin were found to be associated with the peak bone mineral density (BMD) in Chinese women. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether Myostatin played a role in the normal variation in peak BMD, lean mass (LM), and fat mass (FM) of Chinese men.
Methods:
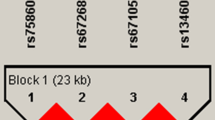
Four hundred male-offspring nuclear families of Chinese Han ethnic group were recruited. Anthropometric measurements, including the peak BMD, body LM and FM were measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) studied were tag-SNPs selected by sequencing. Both rs2293284 and +2278GA were genotyped using TaqMan assay, and rs3791783 was genotyped with PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis. The associations of the SNPs with anthropometric variations were analyzed using the quantitative transmission disequilibrium test (QTDT).
Results:
Using QTDT to detect within-family associations, neither single SNP nor haplotype was found to be associated with peak BMD at any bone site. However, rs3791783 was found to be significantly associated with fat mass of the trunk (P<0.001). Moreover, for within-family associations, haplotypes AGG, AAA, and TGG were found to be significantly associated with the trunk fat mass (all P<0.001).
Conclusion:
Our results suggest that genetic variation within Myostatin may play a role in regulating the variation in fat mass in Chinese males. Additionally, the Myostatin gene may be a candidate that determines body fat mass in Chinese men.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zhang ZL, He JW, Qin YJ, Hu YQ, Li M, Zhang H, et al. Association between Myostatin gene polymorphisms and peak BMD variation in Chinese nuclear families. Osteoporos Int 2008; 19: 39–47.
Zhao LJ, Jiang H, Papasian CJ, Maulik D, Drees B, Hamilton J, et al. Correlation of obesity and osteoporosis: effect of fat mass on the determination of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23: 17–29.
Zhou S, Eid K, Glowacki J . Cooperation between TGF-beta and Wnt pathways during chondrocyte and adipocyte differentiation of human marrow stromall cells. J Bone Miner Res 2004; 19: 463–70.
Zhou S, Lechpammer S, Greenberger JS, Glowacki J . Hypoxia inhibition of adipocytogenesis in human bone marrow stromall cells requires transforming growth factor-beta/Smad3 signaling. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 22688–96.
Wrighton KH, Lin X, Yu PB, Feng XH . TGFbeta can stimulate Smad1 phosphorylation idependently of BMP receptors. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 9755–63.
McPherron AC, Lawler AM, Lee SJ . Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta superfamily member. Nature 1997; 387: 83–90.
McPherron AC, Lee SJ . Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997; 94: 12457–61.
Schuelke M, Wagner KR, Stolz LE, Hübner C, Riebel T, Kömen W, et al. Myostatin mutation associated with gross muscle hypertrophy in a child. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2682–8.
Hamrick MW . Increased bone mineral density in the femoral of GDF8 gene knockout mice. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2003; 272: 388–91.
Hamrick MW, McPherron AC, Lovejoy CO, Hudson J . Femoral morphology and cross-sectional geometry of adult myostatin-deficient mice. Bone 2000; 27: 343–9.
Hamrick MW, McPherron AC, Lovejoy CO . Bone mineral concent and density in the humerous of adult myostatin-deficient mice. Calcif Tissue Int 2005; 71: 63–8.
Hamrick MW, Samaddar T, Pennington C, McCormick J . Increased muscle mass with myostatin deficiency improves gains in bone strength with exrcise. J Bone Miner Res 2006; 21: 477–83.
Zhang ZL, He JW, Qin YJ, Hu YQ, Li M, Liu YJ, et al. Association between the SNPs and haplotypes in the PPARGC1 and adiponectin genes and bone mineral density in Chinese women and men. Acta Pharmocal Sin 2007; 28: 287–95.
Gao G, Zhang ZL, Zhang H, Hu WW, Huang QR, Lu JH, et al. Hip axis length changes in 10,554 males and females and the association with femoral neck fracture. J Clin Densitom 2008; 11: 360–6.
Gu JM, Xiao WJ, He JW, Zhang H, Hu WW, Hu YQ, et al. Association between VDR and ESR1 gene polymorphisms with bone and obesity phenotypes in Chinese male nuclear families. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2009; 30: 1634–42.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P . A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–89.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–5.
Qin YJ, Shen H, Huang QR, Zhao LJ, Zhou Q, Li MX, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms and peak bone density in Chinese nuclear families. J Bone Miner Res 2003; 18: 1028–35.
Liu XH, Liu YJ, Jiang DK, Li YM, Li MX, Qin YJ, et al. No evidence for linkage and/or association of human Alpha2-HS glycoprotein gene with bone mineral density variation in Chinese nuclear families. Calcif Tissue Int 2003; 73: 244–50.
Deng FY, Liu MY, Li MX, Lei SF, Qin YJ, Zhou Q, et al. Tests of linkage and association of the COL1A2 gene with bone phenotypes variation in Chinese nuclear families. Bone 2003; 33: 614–9.
Taaffe DR, Lang TF, Fuerst T, Cauley JA, Nevitt MC, Harris TB . Sex- and race-related differences in cross-sectional geometry and bone density of the femoral mid-shaft in older adults. Ann Hum Biol 2003; 30: 329–46.
Beamer WG, Shultz KL, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Horton LG, Delahunty KM, Coombs HF 3rd, et al. Genetic dissection of mouse distal chromosome 1 reveals three linked BMD QTLs with sex-dependent regulation of bone phenotypes. J Bone Miner Res 2007; 22: 1187–96.
Edderkaoui B, Baylink DJ, Beamer WG, Shultz KL, Wergedal JE, Mohan S . Genetic regulation of femoral bone mineral density: complexity of sex effect in chromosome 1 revealed by congenic sublines of mice. Bone 2007; 41: 340–5.
Peacock M, Koller DL, Fishburn T, Krishnan S, Lai D, Hui S, et al. Sex-specific and non-sex-specific quantitative trait loci contribute to normal variation in bone mineral density in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 3060–6.
Long JR, Liu PY, Liu YJ, Lu Y, Shen H, Zhao LJ, et al. APOE haplotypes influence bone mineral density in Caucasian males but not females. Calcif Tissue Int 2004; 75: 299–304.
Duncan EL, Cardon LR, Sinsheimer JS, Wass JA, Brown MA . Site and gender specificity of inheritance of bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 2003; 18: 1531–8.
Ralston SH, Galwey N, MacKay I, Albagha OM, Cardon L, Comnston JE, et al. Loci for regulation of bone mineral density in men and women identified by genome wide linkage scan: The FAMOS study. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 943–51.
Kim WK, Choi HR, Park SG, Ko Y, Bae KH, Lee SC . Myostatin inhibits brown adipocyte differentiation via regulation of Smad3-mediated β-catenin stabilization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2012; 44: 327–34.
Deng B, Wen J, Ding Y, Peng J, Jiang S . Different regulation role of myostatin in differentiating pig ADSCs and MSCs into adipocytes. Cell Biochem Funct 2012; 30: 145–50.
Lebrasseur NK . Building muscle, browning fat and preventing obesity by inhibiting myostatin. Diabetologia 2012; 55: 13–7.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by grants from the project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170803, 81070692, 81000360, and 30800387), Shanghai Rising-star Program (11QA1404900), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (11ZR1427300), STCSM10DZ1950100, and Academic Leaders in Health Sciences in Shanghai (XBR2011014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, H., He, Jw., Zhang, H. et al. Contribution of Myostatin gene polymorphisms to normal variation in lean mass, fat mass and peak BMD in Chinese male offspring. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 660–667 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.12
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between LGR4 polymorphisms and peak bone mineral density and body composition
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2020)
-
Association between SNPs and haplotypes in the METTL21C gene and peak bone mineral density and body composition in Chinese male nuclear families
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2017)
-
BMP7 gene polymorphisms are not associated with bone mineral density or osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal Chinese women
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
-
Polymorphisms in Wnt signaling pathway genes are associated with peak bone mineral density, lean mass, and fat mass in Chinese male nuclear families
Osteoporosis International (2016)
-
The efficacy and safety of weekly 35-mg risedronate dosing regimen for Chinese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or osteopenia: 1-year data
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2015)