Abstract
Aim:
To evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) and primary tolerability of an anti-CD11a monoclonal antibody (CMAB001) in Chinese healthy volunteers and psoriatic patients.
Methods:
Two open-label studies were conducted. One was a parallel-group, single-center, dose-escalation test, including 24 healthy adult volunteers from 18 to 45 years in age. All subjects randomly received a single subcutaneous injection dose of 0.5, 1.0 or 2.0 mg/kg. The other was a multiple-dose study: 10 adult psoriatic patients were administered weekly subcutaneous injections of 1.0 mg/kg for 7 weeks.
Results:
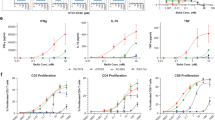
CMAB001 was well tolerated in the single- and multiple-dose studies. Slow absorption was observed in both studies. In the single-dose study, the concentration of CMAB001 reached its highest level 2 d later after the injection, and the Cmax increased in an approximate dose-proportionate manner, while the area under curve (AUC) showed much greater than dose-proportionate increase. In the multiple-dose study, the steady-state serum concentration level was attained following the 4th injection.
Conclusion:
CMAB001 exhibited a nonlinear pharmacokinetic profile over the dose range from 0.5 to 2.0 mg/kg, and was well tolerated in healthy volunteers and psoriatic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Li S, Wang H, Peng B, Zhang M, Zhang D, Hou S, et al. Efalizumab binding to the LFA-1 αL I domain blocks ICAM-1 binding via steric hindrance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 4349–54.
Mehlis SL, Gordon KB . The immunology of psoriasis and biologic immunotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 49: S44–50.
Jullien D, Prinz JC, Langley RG, Caro I, Dummer W, Joshi A, et al. T-cell modulation for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis with efalizumab (Raptiva): mechanisms of action. Dermatology 2004; 208: 297–306.
Lee KH, Dinner AR, Tu C, Campi G, Raychaudhuri S, Varma R, et al. The immunological synapse balances T cell receptor signaling and degradation. Science 2003; 302: 1218–22.
Gottlieb A, Krueger JG, Bright R, Ling M, Lebwohl M, Kang S, et al. Effects of administration of a single dose of a humanized monoclonal antibody to CD11a on the immunobiology and clinical activity of psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2000; 42: 428–35.
Papp K, Bissonnette R, Krueger JG, Carey W, Gratton D, Gulliver WP, et al. The treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis with a new anti-CD11a monoclonal antibody. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001; 45: 665–74.
Dedrick RL, Bodary S, Garovoy MR . Adhesion molecules as therapeutic targets to autoimmune diseases and transplant refection. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2003; 3: 85–95.
Mortensen DL, Walicke PA, Wang X, Kwon P, Kuebler P, Gottlieb AB, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of multiple weekly subcutaneous efalizumab doses in patients with plaque psoriasis. J Clin Pharmacol 2005; 45: 286–98.
Gottlieb AB, Krueger JG, Wittkowski K, Dedrick R, Walicke PA, Garovoy M . Psoriasis as a model for T cell-mediated disease: immunobiologic and clinical effects with multiple doses of efalizumab, an anti-CD11a antibody. Arch Dermatol 2002; 138: 591–600.
Dedrick RL, Walicke P, Garovoy M . Anti-adhesion antibodies efalizumab, a humanized anti-CD11a monoclonal antibody. Transpl Immunol 2002; 9: 181–6.
Singri P, West DP, Gordon KB . Biologic therapy for psoriasis: the new therapeutic frontier. Arch Dermatol 2002; 138: 657–63.
Gottlieb AB, Miller B, Lowe N, Shapiro W, Hudson C, Bright R, et al. Subcutaneously administered efalizumab (anti-CD11a) improves signs and symptoms of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. J Cutan Med Surg 2003; 7: 198–207.
Springer TA . Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 1990; 346: 425–34.
Kuypers TW, Roos D . Leukocyte membrane adhesion proteins LFA-1, CR3 and p150, 95: a review of functional and regulatory aspects. Res Immunol 1989; 140: 461–86.
Gordon EJ, Myers KJ, Dougherty JP, Rosen H, Ron Y . Both efalizumab (LFA-1) and anti-CD11b (MAC-1) therapy delay the onset and diminish the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 1995; 62: 153–60.
Coffey GP, Stefanich E, Palmieri S, Eckert R, Padilla-Eagar J, Fielder PJ, et al. In vitro internalization, intercellular transport, and clearance of an anti-CD11a antibody (Raptiva) by human T-cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004; 310: 896–904.
Berger JR, Houff SA, Major EO . Monoclonal antibodies and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. MAbs 2009; 1: 583–9.
James DG, Seo DH, Chen J, Vemulapalli C, Stone CD . Efalizumab, a human monoclonal anti-CD11a antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe Crohn's disease: An open-label pilot study. Dig Dis Sci 2011; 56: 1806–10.
Homepage of the Food and Drug Administration. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/ac/03/briefing/3983B1_01_Genentech-Raptiva.pdf.
Coffey GP, Fox JA, Pippig S, Palmieri S, Reitz B, Gonzales M, et al. Tissue distribution and receptor-mediated clearance of anti-CD11a antibody in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 2005; 33: 623–9.
Langewouters AM, van Erp PE, de Jong EM, van de Kerkhof PC . Lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood of patients with moderate-to-severe versus mild plaque psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 2008; 300: 107–13.
Joshi A, Bauer R, Kuebler P, White M, Leddy C, Comptom P, et al. An overview of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of efalizumab: a monoclonal antibody appoved for use in psoriasis. J Clin Pharmacol 2006; 46: 10–20.
Vugmeyster Y, Kikuchi T, Lowes MA, Chamian F, Kagen M, Gilleaudeau P, et al. Efalizumab (anti-CD11a)-induced increase in peripheral blood leukocytes in psoriasis patients is preferentially mediated by altered trafficking of memory CD8+ T cells into lesional skin. Clin Immunol 2004; 113: 38–46.
Shear NH, Langley RG, Ho V . Efalizumab, a reversible T-cell modulator for psoriasis. J Cutan Med Surg 2006; 9: 4–9.
Harper EG, Simpson EL, Takiquchi RH, Boyd MD, Kurtz SE, Bakke AC, et al. Efalizumab therapy for Atopic Dermatitis causes marked increases in circulating effector memory CD4+ T cells that express cutaneous lymphocyte antigen. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 1173–81.
Krueger JG . The immunologic basis for the treatment of psoriasis with new biologic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 46: 1–23.
Bonnekoh B, Malykh Y, Bockelmann R, Bartsch S, Pommer AJ, Gollnick H . Profiling lymphocyte subpopulations in peripheral blood under efalizumab treatment of psoriasis by multi epitope ligand cartography (MELC) robot microscopy. Eur J Dermatol 2006; 16: 623–35.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai Commission of Science & Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology of China (973 & 863 Program Projects), National Key projects for New Drug Development and Manufacture, Shanghai Pudong Commission of Science & Technology and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (B905). Special thanks to the study subjects and referring physicians for their participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xp., Li, J., Yan, H. et al. Tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of CMAB001, an anti-CD11a antibody, in Chinese healthy volunteers and psoriatic patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 1085–1094 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.65
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.65