Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the routes of elimination and excretion for triptolide recovered in rats.
Methods:
After a single oral administration of [3H]triptolide (0.8 mg/kg, 100 μCi/kg) in Sprague Dawley rats, urine and fecal samples were collected for 168 h. To study biliary excretion, bile samples were collected for 24 h through bile duct cannulation. Radioactivity was measured using a liquid scintillation analyzer, and excretion pathway analysis was performed using an HPLC/on-line radioactivity detector.
Results:
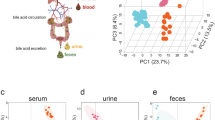
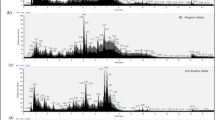
The total radioactivity recovered from the urine and feces of rats without bile duct ligation ranged from 86.6%–89.1%. Most of the radioactivity (68.6%–72.0%) was recovered in the feces within 72 h after oral administration, while the radioactivity recovered in the urine and bile was 17.1%–18.0% and 39.0%–39.4%, respectively. The HPLC/on-line radiochromatographic analysis revealed that most of the drug-related radioactivity was in the form of metabolites. In addition, significant gender differences in the quantity of these metabolites were found: monohydroxytriptolide sulfates were the major metabolites detected in the urine, feces, and bile of female rats, while only traces of these metabolites were found in male rats.
Conclusion:
Radiolabeled triptolide is mainly secreted in bile and eliminated in feces. The absorbed radioactivity is primarily eliminated in the form of metabolites, and significant gender differences are observed in the quantity of recovered metabolites, which are likely caused by the gender-specific expression of sulfotransferases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Pan XD, Chen XC . Advances in the study of immunopharmacological effects and mechanisms of extracts of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in neuroimmunologic disorders. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2008; 43: 1179–85.
Tao X, Lipsky PE . The Chinese anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive herbal remedy Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2000; 26: 29–50.
Chen BJ . Triptolide, a novel immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory agent purified from a Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Leuk Lymphoma 2001; 42: 253–65.
Zhang G, Liu Y, Guo H, Sun Z, Zhou YH . Triptolide promotes generation of FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 125: 41–6.
Wang Y, Mei Y, Feng D, Xu L . Triptolide modulates T-cell inflammatory responses and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res 2008; 86: 2441–9.
Wang Y, Jia L, Wu CY . Triptolide inhibits the differentiation of Th17 cells and suppresses collagen-induced arthritis. Scand J Immunol 2008; 68: 383–90.
Gong Y, Xue B, Jiao J, Jing L, Wang X . Triptolide inhibits COX-2 expression and PGE2 release by suppressing the activity of NF-kappaB and JNK in LPS-treated microglia. J Neurochem 2008; 107: 779–88.
Manzo SG, Zhou ZL, Wang YQ, Marinello J, He JX, Li YC, et al. Natural product triptolide mediates cancer cell death by triggering CDK7-dependent degradation of RNA polymerase II. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 5363–73.
Mei Z, Li X, Wu Q, Hu S, Yang X . The research on the anti-inflammatory activity and hepatotoxicity of triptolide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle. Pharmacol Res 2005; 51: 345–51.
Ni B, Jiang Z, Huang X, Xu F, Zhang R, Zhang Z, et al. Male reproductive toxicity and toxicokinetics of triptolide in rats. Arzneimittelforschung 2008; 58: 673–80.
Shao F, Wang G, Xie H, Zhu X, Sun J, A J . Pharmacokinetic study of triptolide, a constituent of immunosuppressive Chinese herb medicine, in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 2007; 30: 702–7.
Marathe PH, Shyu WC, Humphreys WG . The use of radiolabeled compounds for ADME studies in discovery and exploratory development. Curr Pharm Des 2004; 10: 2991–3008.
Liu J, Li L, Zhou X, Chen X, Huang H, Zhao S, et al. Metabolite profiling and identification of triptolide in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2013; 939: 51–8.
Zhou R, Zhang F, He PL, Zhou WL, Wu QL, Xu JY, et al. (5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8), a novel triptolide analog mediates immunosuppressive effects in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol 2005; 5: 1895–903.
Liu L, Jiang ZZ, Liu J, Huang X, Wang T, Zhang Y, et al. Sex differences in subacute toxicity and hepatic microsomal metabolism of triptolide in rats. Toxicology 2010; 271: 57–63.
Zhong WZ, Zhan J, Kang P, Yamazaki S . Gender specific drug metabolism of PF-02341066 in rats — role of sulfoconjugation. Curr Drug Metab 2010; 11: 296–306.
Meerman JH, Nijland C, Mulder GJ . Sex differences in sulfation and glucuronidation of phenol, 4-nitrophenol and N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene in the rat in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 1987; 36: 2605–8.
Singer SS, Giera D, Johnson J, Sylvester S . Enzymatic sulfation of steroids: I. The enzymatic basis for the sex difference in cortisol sulfation by rat liver preparations. Endocrinology 1976; 98: 963–74.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30901831 and 81373479).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhou, X., Chen, Xy. et al. Excretion of [3H]triptolide and its metabolites in rats after oral administration. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35, 549–554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2013.192
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2013.192
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CYP3A4 inducer and inhibitor strongly affect the pharmacokinetics of triptolide and its derivative in rats
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)
-
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein Gene Expression and Function Enhances Triptolide-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice
Scientific Reports (2015)