Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the anti-arthritis and immunomodulatory activities of ginsenoside compound K (C-K) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
Methods:
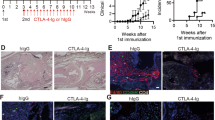
DBA/1 mice with CIA were treated with C-K (28, 56 or 112 mg·kg−1 ·d−1, ig) or the positive control methotrexate (2 mg/kg, ig, every 3 d) for 34 d. Splenic T and B lymphocytes were positively isolated using anti-CD3-coated magnetic beads or a pan B cell isolation kit. T lymphocyte subsets, and CD28, T cell receptor (TCR), cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed death-1 (PD-1) expression in purified splenic T lymphocytes were analyzed using flow cytometry, Western blotting and laser confocal microscopy.
Results:
C-K treatment significantly ameliorated the pathologic manifestations of CIA mice, remarkably inhibited T lymphocyte proliferation, and marginally inhibited the proliferation of B lymphocytes. C-K treatment significantly suppressed TNF-α and anti-CII antibody levels, and increased IFN-γ level in the joints of CIA mice, but did not alter IL-4 production. Treatment of CIA mice with C-K significantly decreased the percentages of activated T cells, co-stimulatory molecule-expressing T cells and effector memory T cells, and increased the frequencies of naive T cells and regulatory T cells. Furthermore, C-K treatment significantly decreased the expression of CD28 and TCR, whereas it increased the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T lymphocytes of CIA mice. Methotrexate treatment exerted comparable effects in all these experiments.
Conclusion:
C-K suppresses the progression of CIA through regulating TCR, CD28, CTLA-4 and PD-1 expression, thus inhibiting the abnormal activation and differentiation of T lymphocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Smolen JS, Aletaha D . Developments in the clinical understanding of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2009; 11: 204.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P . New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007; 370: 1861–74.
McInnes IB, Schett G . Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 429–42.
Schulze-Koops H, Kalden JR . The balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2001; 15: 677–91.
Leah E . Rheumatoid arthritis: Metabolic reprogramming of T cells in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2013; 9: 635.
Boissier MC, Semerano L, Challal S, Saidenberg-Kermanac'h N, Falgarone G . Rheumatoid arthritis: from autoimmunity to synovitis and joint destruction. J Autoimmun 2012; 39: 222–8.
Kaufmann DE, Walker BD . PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitory cosignaling pathways in HIV infection and the potential for therapeutic intervention. J Immunol 2009; 182: 5891–7.
Chen L, Flies DB . Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 227–42.
Chen L . Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 4: 336–47.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH . The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 515–48.
Brownlie RJ, Zamoyska R . T cell receptor signalling networks: branched, diversified and bounded. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 257–69.
Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J . A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 65–97.
Snauwaert S, Verstichel G, Bonte S, Goetgeluk G, Vanhee S, Van Caeneghem Y, et al. In vitro generation of mature, naive antigen-specific CD8+ T cells with single T cell receptor by agonist selection. Leukemia 2013 Oct 4. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.285.
Lan KH, Liu YC, Shih YS, Tsaid CL, Yen SH, Lan KL . A DNA vaccine against cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) prevents tumor growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 440: 222–8.
Im DS, Nah SY . Yin and Yang of ginseng pharmacology: ginsenosides vs gintonin. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 136773.
Bae J, Koo J, Kim S, Park TY, Kim MY . Ginsenoside Rp1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects via activation of dendritic cells and regulatory T cells. J Ginseng Res 2012; 36: 375–82.
Shi J, Xue W, Zhao WJ, Li KX . Pharmacokinetics and dopamine/acetylcholine releasing effects of ginsenoside Re in hippocampus and mPFC of freely moving rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 214–20.
Mochizuki M, Yoo YC, Matsuzawa K, Sato K, Saiki I, Tono-oka S, Samukawa K, et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3 of red ginseng. Biol Pharm Bull 1995; 18: 1197–202.
Sun J, Song X, Hu S . Ginsenoside Rg1 and aluminum hydroxide synergistically promote immune responses to ovalbumin in BALB/c mice. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2008; 15: 303–7.
Kim JS, Kim Y, Han SH, Jeon JY, Hwang M, Im YJ, et al. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for determination of compound K in human plasma and clinical application. J Ginseng Res 2013; 37: 135–41.
Quan LH, Piao JY, Min JW, Yang DU, Lee HN, Yang DC . Bioconversion of ginsenoside Rb1 into compound K by Leuconostoccitreum LH1 isolated from kimchi. Braz J Microbiol 2011; 42: 1227–37.
Cho SH, Chung KS, Choi JH, Kim DH, Lee KT . Compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, induces apoptosis via caspase-8-dependent pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2009; 9: 449.
Choi KT . Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 1109–18.
Choo MK, Sakurai H, Kim DH, Saiki I . A ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α-promoted metastasis by suppressing nuclear factor-κ B signaling in murine colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep 2008; 19: 595–600.
Kim DY, Yuan HD, Chung IK, Chung SH . Compound K, intestinal metabolite of ginsenoside, attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMPK activation in human hepatoma cells. J Agric Food Chem 2009; 57: 1532–7.
Trentham DE, Townes AS, Kang AH . Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med 1977; 146: 857–68.
Brand DD, Kang AH, Rosloniec EF . Immunopathogenesis of collagen arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2003; 25: 3–18.
Huang B, Wang QT, Song SS, Wu YJ, Ma YK, Zhang LL, et al. Combined use of etanercept and MTX restores CD4+/CD8+ ratio and Tregs in spleen and thymus in collagen-induced arthritis. Inflamm Res 2012; 61: 1229–39.
Tong T, Zhao W, Wu YQ, Chang Y, Wang QT, Zhang LL, et al. Chicken type II collagen induced immune balance of main subtype of helper T cells in mesenteric lymph node lymphocytes in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Inflamm Res 2010; 59: 369–77.
Wang QT, Wu YJ, Huang B, Ma YK, Song SS, Zhang LL, et al. Etanercept attenuates collagen-induced arthritis by modulating the association between BAFFR expression and the production of splenic memory B cells. Pharmacol Res 2013; 68: 38–45.
Dibra D, Cutrera JJ, Li S . Coordination between TLR9 signaling in macrophages and CD3 signaling in T cells induces robust expression of IL30. J Immunol 2012; 188: 3709–15.
Wu HX, Chen JY, Wang QT, Sun WY, Liu LH, Zhang LL, et al. Expression and function of β-arrestin 2 stimulated by IL-1β in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and the effect of paeoniflorin. Int Immunopharmacol 2012; 12: 701–6.
Wang QT, Ma YK, Huang B, Liu DD, Wei W . Effect of rhTACI-Ig fusion protein on antigen-specific T cell responses from keyhole limpet haemocyanin challenged mice. Mol Immunol 2011; 49: 380–6.
Sakaguchi S, Benham H, Cope AP, Thomas R . T-cell receptor signaling and the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis: insights from mouse and man. Immunol Cell Biol 2012; 90: 277–87.
Wang QT, Zhang LL, Wu HX, Wei W . The expression change of β-arrestins in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rats with collagen-induced arthritis and the effect of total glucosides of paeony. J Ethnopharmacol 2011; 133: 511–6.
Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M . The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2007; 25: S4–11.
Skapenko A, Leipe J, Lipsky PE, Schulze-Koops H . The role of the T cell in autoimmune inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 2005; 2: S4–14.
McInnes IB, Schett G . Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 429–42.
Ehrenstein MR, Evans JG, Singh A, Moore S, Warnes G, Isenberg DA, et al. Compromised function of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by anti-TNFα therapy. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 277–85.
Lee EJ, Ko E, Lee J, Pho S, Ko S, Shin MK, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 enhances CD4+ T-cell activities and modulates Th1/Th2 differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol 2004; 4: 235–44.
Shin YW, Bae EA, Kim SS, Lee YC, Kim DH . Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K in chronic oxazolone-induced mouse dermatitis. Int Immunopharmacol 2005; 5: 1183–91.
Wu H, Wei W, Song L, Zhang L, Chen Y, Hu X . Paeoniflorin induced immune tolerance of mesenteric lymph node lymphocytes via enhancing beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 2007; 7: 662–73.
Li Q, Shen HH . Neonatal bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccination inhibits de novo allergic inflammatory response in mice via alteration of CD4+CD25+ T-regulatory cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2009; 30: 125–33.
Bacchetta R, Gambineri E, Roncarolo MG . Role of regulatory T cells and FOXP3 in human diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 227–35.
Klimiuk PA, Yang H, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM . Production of cytokines and metalloproteinases in rheumatoid synovitis is T cell dependent. Clin Immunol 1999; 90: 65–78.
Brownlie RJ, Zamoyska R . T cell receptor signalling networks: branched, diversified and bounded. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 257–69.
Jerome KR . Viral modulation of T-cell receptor signaling. J Virol 2008; 82: 4194–204.
Riley JL, June CH . The CD28 family: a T-cell rheostat for therapeutic control of T-cell activation. Blood 2005; 105: 13–21.
Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J . A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 65–97.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973543, 81173075, 81202541, and 81330081), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1208085QH146), the Grants for Scientific Research of BSKY (XJ201213), the Foundation for Young Academic Backbone of Anhui Medical University, and the Grants for Young Talents of Anhui Medical University (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Kk., Wang, Qt., Yang, Sm. et al. Ginsenoside compound K suppresses the abnormal activation of T lymphocytes in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35, 599–612 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic effect of various ginsenosides on rheumatoid arthritis
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2021)
-
Deficiency of β-arrestin2 exacerbates inflammatory arthritis by facilitating plasma cell formation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2021)
-
Ginsenoside compound-K inhibits the activity of B cells through inducing IgD-B cell receptor endocytosis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis
Inflammopharmacology (2019)
-
Ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects via downregulating COX2
Inflammopharmacology (2019)
-
Ginsenoside G-Rh2 synergizes with SMI-4a in anti-melanoma activity through autophagic cell death
Chinese Medicine (2018)