Abstract
Aim:
To develop a population pharmacokinetics model of oxcarbazepine in Chinese pediatric patients with epilepsy, and to study the interactions between oxcarbazepine and other antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
Methods:
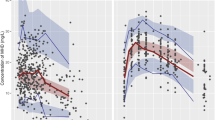
A total of 688 patients with epilepsy aged 2 months to 18 years were divided into model (n=573) and valid (n=115) groups. Serum concentrations of the main active metabolite of oxcarbazepine, 10-hydroxycarbazepine (MHD), were determined 0.5–48 h after the last dosage. A population pharmacokinetics (PPK) model was constructed using NLME software. This model was internally evaluated using Bootstrapping and goodness-of-fit plots inspection. The data of the valid group were used to calculate the mean prediction error (MPE), mean absolute prediction error (MAE), mean squared prediction error (MSE) and the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) to externally evaluate the model.
Results:
The population values of pharmacokinetic parameters estimated in the final model were as follows: Ka=0.83 h-1, Vd=0.67 L/kg, and CL=0.035 L·kg−1·h−1. The enzyme-inducing AEDs (carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital) and newer generation AEDs (levetiracetam, lamotrigine, topiramate) increased the weight-normalized CL value of MHD by 17.4% and 10.5%, respectively, whereas the enzyme-inhibiting AED valproic acid decreased it by 3%. No significant association was found between the CL value of MHD and the other covariates. For the final model, the evaluation results (95% CI) were MPE=0.01 (−0.07–0.10) mg/L, MAE=0.46 (0.40–0.51) mg/L, MSE=0.39 (0.27–0.51) (mg/L)2.
Conclusion:
A PPK model of OXC in Chinese pediatric patients with epilepsy is established. The enzyme-inducing AEDs and some newer generation AEDs (lamotrigine, topiramate) could slightly increase the metabolism of MHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Northam RS, Hernandez AW, Litzinger MJ, Minecan DN, Glauser TA, Mangat S, et al. Oxcarbazepine in infants and young children with partial seizures. Pediatr Neurol 2005; 33: 337–44.
Sallas WM, Milosavljev S, D'Souza J, Hossain M . Pharmacokinetic drug interactions in children taking oxcarbazepine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2003; 74: 138–49.
Park KJ, Kim JR, Joo EY, Seo DW, Hong SB, Ko JW, et al. Drug interaction and pharmacokinetic modeling of oxcarbazepine in korean patients with epilepsy. Clin Neuropharmacol 2012; 35: 40–4.
May DTW, Korn-Merker E, Rambeck B . Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine. Clin Pharmacokinet 2003; 42: 1023–42.
Flesch G . Overview of the clinical pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine. Clin Drug Investig 2004; 24: 185–203.
Patsalos PN, Berry DJ, Bourgeois BF, Cloyd JC, Glauser TA, Johannessen SI, et al. Antiepileptic drugs-best practice guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring: a position paper by the subcommission on therapeutic drug monitoring, ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 1239–76.
Volosov A, Xiaodong S, Perucca E, Yagen B, Sintov A, Bialer M . Enantioselective pharmacokinetics of 10-hydroxycarbazepine after oral administration of oxcarbazepine to healthy Chinese subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1999; 66: 547–53.
Flesch G, Czendlik C, Renard D, Lloyd P . Pharmacokinetics of the monohydroxy derivative of oxcarbazepine and its enantiomers after a single intravenous dose given as racemate compared with a single oral dose of oxcarbazepine. Drug Metab Dispos 2011; 39: 1103–10.
Schmutz M, Brugger F, Gentsch C, McLean MJ, Olpe HR . Oxcarbazepine: preclinical anticonvulsant profile and putative mechanisms of action. Epilepsia 1994; 35 Suppl 5: S47–50.
Viola MS, Bercellini MA, Saidón P, Rubio MC . Pharmacokinetic variability of oxcarbazepine in epileptic patients. Medicina 2000; 60: 914–8.
Armijo JA, Vega-Gil N, Shushtarian M, Adin J, Herranz JL . 10-Hydroxycarbazepine serum concentration-to-oxcarbazepine dose ratio: influence of age and concomitant antiepileptic drugs. Ther Drug Monit 2005; 27: 199–204.
Hossain M, Sallas W, Gasparini M, D Souza J . Drug-drug interaction profile of oxcarbazepine in children and adults. Neurology 1999; 52: 525.
May TW, Rambeck B, Jurgens U . Influence of oxcarbazepine and methsuximide on lamotrigine concentrations in epileptic patients with and without valproic acid comedication: results of a retrospective study. Ther Drug Monit 1999; 21: 175–81.
Johannessen SI, Landmark CJ . Antiepileptic drug interactions - principles and clinical implications. Curr Neuropharmacol 2010; 8: 254–67.
Lloyd P, Flesch G, Dieterle W . Clinical pharmacology and pharmcokinetics of oxcarbazepine. Epilepsia 1994; 35: 10–3.
Schutz H, Feldmann KF, Faigle JW, Kriemler HP, Winkler T . The metabolism of 14C-oxcarbazepine in man. Xenobiotica 1986; 16: 769–78.
Kim DW, Gu N, Jang IJ, Chu K, Yu KS, Cho JY, et al. Efficacy, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine oral loading in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2012; 53: e9–12.
Flesch G, Tudor D, Souppart C, D'Souza J, Hossain M . Oxcarbazepine final market image tablet formulation bioequivalence study after single administration and at steady state in healthy subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 40: 524–32.
Wegner I, Wilhelm AJ, Sander JW, Lindhout D . The impact of age on lamotrigine and oxcarbazepine kinetics: a historical cohort study. Epilepsy Behav 2013; 29: 217–21.
Tartara A, Galimberti CA, Manni R, Morini R, Limido G, Gatti G, et al. The pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine and its active metabolite 10-hydroxy-carbazepine in healthy subjects and in epileptic patients treated with phenobarbitone or valproic acid. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1993; 36: 366–8.
Bring P, Ensom MH . Does oxcarbazepine warrant therapeutic drug monitoring? A critical review. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47: 767–78.
McKee PJ, Blacklaw J, Forrest G, Gillham RA, Walker SM, Connelly D, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled interaction study between oxcarbazepine and carbamazepine, sodium valproate and phenytoin in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1994; 37: 27–32.
Johannessen LC, Baftiu A, Tysse I, Valso B, Larsson PG, Rytter E, et al. Pharmacokinetic variability of four newer antiepileptic drugs, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, and topiramate: a comparison of the impact of age and comedication. Ther Drug Monit 2012; 34: 440–5.
Wegner I, Edelbroek P, de Haan GJ, Lindhout D, Sander JW . Drug monitoring of lamotrigine and oxcarbazepine combination during pregnancy. Epilepsia 2010; 51: 2500–2.
Nallani SC, Glauser TA, Hariparsad N, Setchell K, Buckley DJ, Buckley AR, et al. Dose-dependent induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and activation of pregnane X receptor by topiramate. Epilepsia 2003; 44: 1521–28.
Perucca E . Pharmacokinetic variability of new antiepileptic drugs at different ages. Ther Drug Monit 2005; 27: 714–7.
Rouan MC, Lecaillon JB, Godbillon J, Menard F, Darragon T, Meyer P, et al. The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine and its metabolites. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1994; 47: 161–7.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Clinical Medicine of Wuhan City (No WX14C47).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, Hn., Niu, Ch. et al. Population pharmacokinetics modeling of oxcarbazepine to characterize drug interactions in Chinese children with epilepsy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35, 1342–1350 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.76
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.76
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Population pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine active metabolite in Chinese children with epilepsy
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
Synthesis of rod-like CeO2 nanoparticles and their application to catalyze the luminal–O2 chemiluminescence reaction used in the determination of oxcarbazepine and ascorbic acid
Analytical Sciences (2022)
-
Population pharmacokinetic model development and its relationship with adverse events of oxcarbazepine in adult patients with epilepsy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Population pharmacokinetics of oxcarbazepine active metabolite in Chinese paediatric epilepsy patients and its application in individualised dosage regimens
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2019)
-
Population pharmacokinetic models of lamotrigine in different age groups of Chinese children with epilepsy
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2017)