Abstract
Aim:
Aconiti Lateralis Radix Preparata is a traditional Chinese medicine used to treat chronic arthritis and is highly effective against rheumatoid arthritis. However, the effects of aconine, a derivative of aconitum alkaloids, on osteoclasts, which can absorb bone, remain unknown. Here, we investigated the effects of aconine on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro.
Methods:
The viability of mouse leukemic monocyte/macrophage cell line RAW264.7 was measured using CCK-8 assays. Osteoclast differentiation was induced by incubation of RAW264.7 cells in the presence of RANKL, and assessed with TRAP staining assay. Bone resorption was examined with bone resorption pits assay. The expression of relevant genes and proteins was analyzed using RT-PCR and Western blots. The activation of NF-κB and nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) was examined using stable NF-κB and NFATc1 luciferase reporter gene systems, RT-PCR and Western blot analysis.
Results:
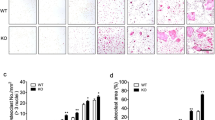
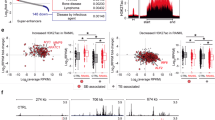
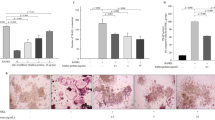
Aconine (0.125, 0.25 μmol/L) did not affect the viability of RAW264.7 cells, but dose-dependently inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorptive activity. Furthermore, aconine dose-dependently inhibited the RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and NFATc1 in RAW264.7 cells, and subsequently reduced the expression of osteoclast-specific genes (c-Src, β3-Integrin, cathepsin K and MMP-9) and the expression of dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP), which played an important role in cell-cell fusion.
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and NFATc1 and the expression of the cell-cell fusion molecule DC-STAMP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL . Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003; 423: 337–42.
Kukita T, Wada N, Kukita A, Kakimoto T, Sandra F, Toh K, et al. RANKL-induced DC-STAMP is essential for osteoclastogenesis. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 941–6.
Walsh MC, Kim N, Kadono Y, Rho J, Lee SY, Lorenzo J, et al. Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 33–63.
Takayanagi H . Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 292–304.
Negishi-Koga T, Takayanagi H . Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast differentiation. Immunol Rev 2009; 231: 241–56.
Zeng Z, Zhang C, Chen J . Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference of DC-STAMP expression inhibits the fusion and resorptive activity of human osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Metab 2013; 31: 409–16.
Islam R, Bae HS, Yoon WJ, Woo KM, Baek JH, Kim HH, et al. Pin1 regulates osteoclast fusion through suppression of the master regulator of cell fusion DC-STAMP. J Cell Physiol 2014; 229: 2166–74.
Zhang C, Dou CE, Xu J, Dong S . DC-STAMP, the key fusion-mediating molecule in osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Physiol 2014; 229: 1330–5.
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Sawatani Y, Iwamoto K, Hosogane N, Fujita N, et al. DC-STAMP is essential for cell-cell fusion in osteoclasts and foreign body giant cells. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 345–51.
Tong P, Wu C, Wang X, Hu H, Jin H, Li C, et al. Development and assessment of a complete-detoxication strategy for Fuzi (lateral root of Aconitum carmichaeli) and its application in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J Ethnopharmacol 2013; 146: 562–71.
Zhang HG, Sun Y, Duan MY, Chen YJ, Zhong DF, Zhang HQ . Separation and identification of Aconitum alkaloids and their metabolites in human urine. Toxicon 2005; 46: 500–6.
Chan TY . Aconite poisoning. Clin Toxicol 2009; 47: 279–85.
Kim MH, Shim KS, Kim SH . Inhibitory effect of cantharidin on osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Arch Pharm Res 2010; 33: 457–62.
Li X, He L, Hu Y, Duan H, Li X, Tan S, et al. Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast formation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by modulating RANKL signaling pathways. PLoS One 2013; 8: e 74274.
Xiao W, Beibei F, Guangsi S, Yu J, Wen Z, Xi H, et al. Iron overload increases osteoclastogenesis and aggravates the effects of ovariectomy on bone mass. J Endocrinol 2015. doi:10.1530/joe-14-0657.
Singh PP, van der Kraan AG, Xu J, Gillespie MT, Quinn JM . Membrane-bound receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand (RANKL) activity displayed by osteoblasts is differentially regulated by osteolytic factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 422: 48–53.
Kim MH, Ryu SY, Choi JS, Min YK, Kim SH . Saurolactam inhibits osteoclast differentiation and stimulates apoptosis of mature osteoclasts. J Cell Physiol 2009; 221: 618–28.
Park KH, Park B, Yoon DS, Kwon SH, Shin DM, Lee JW, et al. Zinc inhibits osteoclast differentiation by suppression of Ca2+-Calcineurin-NFATc1 signaling pathway. Cell Commun Signal 2013; 11: 74.
He LG, Li XL, Zeng XZ, Duan H, Wang S, Lei LS, et al. Sinomenine induces apoptosis in RAW264.7 cell-derived osteoclasts in vitro via caspase-3 activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2014; 35: 203–10.
Asagiri M, Takayanagi H . The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 2007; 40: 251–64.
Boyce BF, Xing L, Franzoso G, Siebenlist U . Required and nonessential functions of nuclear factor-kappa B in bone cells. Bone 1999; 25: 137–9.
Takayanagi H . The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007; 1116: 227–37.
Song I, Kim JH, Kim K, Jin HM, Youn BU, Kim N . Regulatory mechanism of NFATc1 in RANKL-induced osteoclast activation. FEBS Lett 2009; 583: 2435–40.
Wei ZF, Tong B, Xia YF, Lu Q, Chou GX, Wang ZT, et al. Norisoboldine suppresses osteoclast differentiation through preventing the accumulation of TRAF6-TAK1 complexes and activation of MAPKs/NF-kB/c-Fos/NFATc1 pathways. PLoS One 2013; 8: e 59171.
Costa AG, Cusano NE, Silva BC, Cremers S, Bilezikian JP . Cathepsin K: its skeletal actions and role as a therapeutic target in osteoporosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2011; 7: 447–56.
Broadhead ML, Clark JCM, Dass CR, Choong PFM, Myers DE . Therapeutic targeting of osteoclast function and pathways. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15: 169–81.
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Toyama Y, Suda T . Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage giant cells. J Bone Miner Metab 2006; 24: 355–8.
Chiu YH, Mensah KA, Schwarz EM, Ju Y, Takahata M, Feng C, et al. Regulation of human osteoclast development by dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27: 79–92.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81073119 and 81373123) to Xiao-juan LI and a Guangdong Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme to Shu-wen LIU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Xz., He, Lg., Wang, S. et al. Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1 activation and DC-STAMP expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 255–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.85
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.85
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exploring the role and mechanism of Fuzi decoction in the treatment of osteoporosis by integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2023)
-
The mechanism of dendritic cell-T cell crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Small-molecule amines: a big role in the regulation of bone homeostasis
Bone Research (2023)
-
The effects and mechanism of paeoniflorin in promoting osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2022)
-
Strontium inhibits osteoclastogenesis by enhancing LRP6 and β-catenin-mediated OPG targeted by miR-181d-5p
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)