Abstract
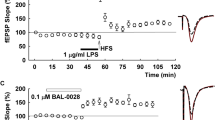
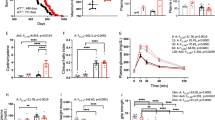
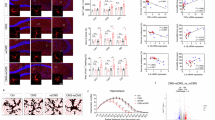
Evidence suggests that neuroinflammation is involved in depression and that the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLT1R) plays a potential pathophysiological role in several types of CNS disorders. Our previous study has shown that knockdown of hippocampal CysLT1R in mice prevents the depressive-like phenotype and neuroinflammation induced by chronic mild stress (CMS). Here, we examined the effects of hippocampal CysLT1R knockdown and CysLT1R blockade on LPS-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. We found that injection of LPS (0.5 mg/kg, ip) caused marked increase in hippocampal CysLT1R expression, which was reversed by pretreatment with fluoxetine (20 mg·kg−1·d−1 for 7 d, ig). Knockdown of hippocampal CysLT1R or blockade of CysLT1R by pretreatment with pranlukast (0.5 mg/kg, ip) significantly suppressed LPS-induced depressive behaviors, as evidenced by decreases in mouse immobility time in the forced swimming test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) and latency to feed in the novelty-suppressed feeding (NSF) test. Moreover, both CysLT1R knockdown and CysLT1R blockade markedly prevented LPS-induced neuroinflammation, as shown by the suppressed activation of microglia and NF-κB signaling as well as the hippocampal levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in mice. Our results suggest that CysLT1R may be involved in LPS-induced depressive-like behaviors and neuroinflammation, and that downregulation of CysLT1R could be a novel and potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of depression, at least partially due to its role in neuroinflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Wong ML, Licinio J . Research and treatment approaches to depression. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 343–51.
Shelton RC, Osuntokun O, Heinloth AN, Corya SA . Therapeutic options for treatment-resistant depression. CNS Drugs 2010; 24: 131–61.
Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager WL, Reim EK, Lanctôt KL . Efficacy and tolerability of antidepressants for treatment of depression in coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Can J Psychiatry 2010; 55: 91–9.
Babcock TA, Carlin JM . Transcriptional activation of indoleamine dioxygenase by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in interferon-treated epithelial cells. Cytokine 2000; 12: 588–94.
Hannestad J, Dellagioia N, Bloch M . The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011; 36: 2452–9.
Capuron L, Ravaud A, Miller AH, Dantzer R . Baseline mood and psychosocial characteristics of patients developing depressive symptoms during interleukin-2 and/or interferon-alpha cancer therapy. Brain Behav Immun 2004; 18: 205–13.
Kaster MP, Gadotti VM, Calixto JB, Santos AR, Rodrigues AL . Depressive-like behavior induced by tumor necrosis factor-α in mice. Neuropharmacology 2012; 62: 419–26.
Mello BS, Monte AS, Mcintyre RS, Soczynska JK, Custódio CS, Cordeiro RC, et al. Effects of doxycycline on depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration. J Psychiatr Res 2013; 47: 1521–9.
De Paiva VN, Lima SN, Fernandes MM, Soncini R, Andrade CA, Giusti-Paiva A . Prostaglandins mediate depressive-like behaviour induced by endotoxin in mice. Behav Brain Res 2010; 215: 146–51.
Singh RK, Gupta S, Dastidar S, Ray A . Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: molecular and functional characteristics. Pharmacology 2010; 85: 336–49.
Nishio H, Hayashi Y, Terashima S, Takeuchi K . Protective effect of pranlukast, a cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 1 antagonist, on indomethacin-induced small intestinal damage in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2008; 15: 266–72.
Rao NL, Dunford PJ, Xue X, Jiang X, Lundeen KA, Coles F, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of a potent, selective leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor in comparison with the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007; 321: 1154–60.
Schelfhout V, Van De Velde V, Pauwels R, Joos G . The effect of the leukotriene receptor antagonist zafirlukast on neurokinin A-induced bronchoconstriction in patients with asthma — A comparison with leukotriene D4 induced broncoconstriction. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2008; 21: 276–84.
Tang SS, Ji MJ, Chen L, Hu M, Long Y, Li YQ, et al. Protective effect of pranlukast on Aβ1-42-induced cognitive deficits associated with downregulation of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2014; 17: 581–92.
Zhang YJ, Zhang L, Ye YL, Fang SH, Zhou Y, Zhang WP, et al. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptors CysLT1 and CysLT2 are upregulated in acute neuronal injury after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2006; 27: 1553–60.
Zhang WP, Hu H, Zhang L, Ding W, Yao HT, Chen KD, et al. Expression of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 in human traumatic brain injury and brain tumors. Neurosci Lett 2004; 363: 247–51.
Wang L, Du C, Lv J, Wei W, Cui Y, Xie X . Antiasthmatic drugs targeting the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 alleviate central nervous system inflammatory cell infiltration and pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2011; 187: 2336–45.
Yu XB, Dong RR, Wang H, Lin JR, An YQ, Du Y, et al. Knockdown of hippocampal cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 prevents depressive behavior and neuroinflammation induced by chronic mild stress in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2016; 233: 1739–49.
Kheirbek MA, Drew LJ, Burqhardt NS, Costantini DO, Tannenholz L, Ahmari SE, et al. Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsalventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Neuron 2013; 77: 955–68.
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Stephanie D, et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003; 301: 805–9.
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M . Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1977; 229: 327–36.
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A . The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: Review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2005; 29: 571–625.
Hashimoto K, Ichiyama T, Hasegawa M, Hasegawa S, Matsubara T, Furukawa S . Cysteinyl leukotrienes induce monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human monocyte/macrophages via mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB pathways. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2009; 149: 275–82.
O'Connor JC, Lawson MA, André C, Moreau M, Lestage J, Castanon N, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 511–22.
Wang XY, Tang SS, Hu M, Long Y, Li YQ, Liao MX, et al. Leukotriene D4 induces amyloid-β generation via CysLT(1)R-mediated NF-κB pathways in primary neurons. Neurochem Int 2013, 62: 340–7.
Kawano T, Matsuse H, Kondo Y, Machida I, Saeki S, Tomari S, et al. Cysteinyl leukotrienes induce nuclear factor kappaB activation and rantes production in a murine model of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 112: 369–74.
Santa-Cecília FV, Socias B, Ouidja MO, Sepulveda-Diaz JE, Acuña L, Silva RL, et al. Doxycycline suppresses microglial activation by inhibiting the p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Neurotox Res 2016; 29: 447–59.
Graeber MB, Streit WJ . Microglia: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 2010; 119: 89–105.
Krishnadas R, Cavanagh J . Depression: an inflammatory illness? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012; 83: 495–502.
Collins PY, Patel V, Joestl SS, March D, Insel TR, Daar AS, et al. Grand challenges in global mental health. Nature 2011; 475: 27–30.
Ghosh A, Chen F, Thakur A, Hong H . Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: emerging therapeutic targets in central nervous system disorders. CNS Neurosci Ther 2016. doi:10.1111/cns.12596.
Zhang JQ, Wu XH, Feng Y, Xie XF, Fan YH, Yan S, et al. Salvianolic acid B ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in chronic mild stress-treated mice: involvement of the neuroinflammatory pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2016; 37: 1141–53.
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW . From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 46–56.
Hart BL . Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1988; 12: 123–37.
Dunn AJ, Swiergiel AH . Effects of interleukin-1 and endotoxin in the forced swim and tail suspension tests in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005; 81: 688–93.
Henry CJ, Huang Y, Wynne A, Hanke M, Himler J, Bailey MT, et al. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J Neuroinflammation 2008; 5: 15.
Zhang JC, Wu J, Fujita Y, Yao W, Ren Q, Yang C, et al. Antidepressant effects of TrkB ligands on depression-like behavior and dendritic changes in mice after inflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2014; 18. pii: pyu077. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyu077.
Tomaz VS, Cordeiro RC, Costa AM, de Lucena DF, Nobre Júnior HV, de Sousa FC, et al. Antidepressant-like effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and sildenafil against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Neuroscience 2014; 268: 236–46.
Eller T, Vasar V, Shlik J, Maron E . Effects of bupropion augmentation on pro-inflammatory cytokines in escitalopram-resistant patients with major depressive disorder. J Psychopharmacol 2008; 23: 854–8.
Liu Y, Ho CM, Mak A . Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Affect Disord 2012; 139: 230–9.
Sethi G, Sung B, Aggarwal BB . Nuclear factor-kappaB activation: from bench to bedside. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2008; 233: 21–31.
Qiao L, Zhao TJ, Wang FZ, Shan CL, Ye LH, Zhang XD . NF-kappaB downregulation may be involved in the depression of tumor cell proliferation mediated by human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 333–40.
Suzuki S, Takeuchi K, Ishinaga H, Basbaum C, Majima Y . Leukotriene D4 upregulates MUC2 gene transcription in human epithelial cells. Pharmacology 2008; 81: 221–8.
Thompson C, Cloutier A, Bossé Y, Thivierge M, Gouill CL, Larivée P, et al. CysLT1 receptor engagement induces activator protein-1- and NF-kappaB-dependent IL-8 expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006; 35: 697–704.
Qin L, Wu X, Block ML, Liu Y, Breese GR, Hong JS, et al. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007; 55: 453–62.
Marschallinger J, Schäffner I, Klein B, Gelfert R, Rivera FJ, Illes S, et al. Structural and functional rejuvenation of the aged brain by an approved anti-asthmatic drug. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 8466.
Song Y, Chen X, Wang LY, Gao W, Zhu MJ . Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil protects against β-amyloid-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 2013; 19: 603–10.
Ye SM, Johnson RW . Regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in brain of aged mice by nuclear factor kappaB. J Neuroimmunol 2001; 117: 87–96.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81273497; 81573413), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No IRT1193), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Jr., Fang, Sc., Tang, Ss. et al. Hippocampal CysLT1R knockdown or blockade represses LPS-induced depressive behaviors and neuroinflammatory response in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 477–487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.145
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.145
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Early-life exposure to polypropylene nanoplastics induces neurodevelopmental toxicity in mice and human iPSC-derived cerebral organoids
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2025)
-
Atorvastatin ameliorates depressive behaviors and neuroinflammatory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
Psychopharmacology (2020)
-
Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBα represses LPS-induced microglial activation through the NF-κB pathway
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2019)
-
Protective Effects of 1-Methylnicotinamide on Aβ1–42-Induced Cognitive Deficits, Neuroinflammation and Apoptosis in Mice
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2019)
-
Hippocampal CA1 βCaMKII mediates neuroinflammatory responses via COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathways in depression
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2018)