Abstract
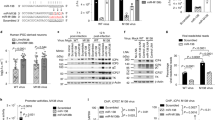
BX-795 is an inhibitor of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), but also a potent inhibitor of the IKK-related kinase, TANKbinding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IKKɛ. In this study we attempted to elucidate the molecular mechanism(s) underlying the inhibition of BX-795 on Herpes simplex virus (HSV) replication. HEC-1-A or Vero cells were treated with BX-795 and infected with HSV-1 or HSV-2 for different periods. BX-795 (3.125-25 μmol/L) dose-dependently suppressed HSV-2 replication, and displayed a low cytotoxicity to the host cells. BX-795 treatment dose-dependently suppressed the expression of two HSV immediate-early (IE) genes (ICP0 and ICP27) and the late gene (gD) at 12 h postinfection. HSV-2 infection resulted in the activation of PI3K and Akt in the host cells, and BX-795 treatment inhibited HSV-2-induced Akt phosphorylation and activation. However, the blockage of PI3K/Akt/mTOR with LY294002 and rapamycin did not affect HSV-2 replication. HSV-2 infection increased the phosphorylation of JNK and p38, and reduced ERK phosphorylation at 8 h postinfection in the host cells; BX-795 treatment inhibited HSV-2-induced activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinase as well as the phosphorylation of c-Jun and ATF-2, the downstream targets of JNK and p38 MAP kinase. Furthermore, SB203580 (a p38 inhibitor) or SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor) dose-dependently inhibited the viral replication in the host cells, whereas PD98059 (an ERK inhibitor) was not effective. Moreover, BX-795 blocked PMA-stimulated c-Jun activation as well as HSV-2-mediated c-Jun nuclear translocation. BX-795 dose-dependently inhibited HSV-2, PMA, TNF-α-stimulated AP-1 activation, but not HSV-induced NF-κB activation. Overexpression of p38/JNK attenuated the inhibitory effect of BX-795 on HSV replication. BX-795 completely blocked HSV-2-induced MKK4 phosphorylation, suggesting that BX-795 acting upstream of JNK and p38 MAP kinase. In conclusion, this study identifies the anti-HSV activity of BX-795 and its targeting of the JNK/p38 MAP kinase pathways in host cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Freeman EE, Weiss HA, Glynn JR, Cross PL, Whitworth JA, Hayes RJ . Herpes simplex virus 2 infection increases HIV acquisition in men and women: systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. AIDS 2006; 20: 73.
Bacon TH, Levin MJ, Leary JJ, Sarisky RT, Sutton D . Herpes simplex virus resistance to acyclovir and penciclovir after two decades of antiviral therapy. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003; 16: 114–28.
Morfin F, Thouvenot D . Herpes simplex virus resistance to antiviral drugs. J Clin Virol 2003; 26: 29–37.
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J . Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 2001; 81: 807–69.
Shaulian E, Karin M . AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: E131–6.
Holloway G, Coulson BS . Rotavirus activates JNK and p38 signaling pathways in intestinal cells, leading to AP-1-driven transcriptional responses and enhanced virus replication. J Virol 2006; 80: 10624–33.
Rahaus M, Desloges N, Wolff MH . Replication of varicella-zoster virus is influenced by the levels of JNK/SAPK and p38/MAPK activation. J Gen Virol 2004; 85: 3529–40.
Zapata HJ, Nakatsugawa M, Moffat JF . Varicella-zoster virus infection of human fibroblast cells activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J Virol 2007; 81: 977–90.
Kumar A, Manna SK, Dhawan S, Aggarwal BB . HIV-Tat protein activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase and activator protein-1. J Immunol 1998; 161: 776–81.
McLean T, Bachenheimer S . Activation of c-JUN N-terminal kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1 enhances viral replication. J Virol 1999; 73: 8415–26.
Karaca G, Hargett D, McLean TI, Aguilar J, Ghazal P, Wagner EK, et al. Inhibition of the stress-activated kinase, p38, does not affect the virus transcriptional program of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology 2004; 329: 142–56.
Kim SM, Park JH, Chung SK, Kim JY, Hwang HY, Chung KC, et al. Coxsackievirus B3 infection induces cyr61 activation via JNK to mediate cell death. J Virol 2004; 78: 13479–88.
Adamson AL, Darr D, Holley-Guthrie E, Johnson RA, Mauser A, Swenson J, et al. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early proteins BZLF1 and BRLF1 activate the ATF2 transcription factor by increasing the levels of phosphorylated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinases. J Virol 2000; 74: 1224–33.
Kopecky-Bromberg SA, Martinez-Sobrido L, Palese P . 7a protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus inhibits cellular protein synthesis and activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Virol 2006; 80: 785–93.
Benn J, Su F, Doria M, Schneider RJ . Hepatitis B virus HBx protein induces transcription factor AP-1 by activation of extracellular signal-regulated and c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Virol 1996; 70: 4978–85.
Hassan M, Ghozlan H, Abdel-Kader O . Activation of c-Jun NH 2-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway is essential for the stimulation of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 3 (NS3)-mediated cell growth. Virology 2005; 333: 324–36.
Zachos G, Clements B, Conner J . Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection stimulates p38/c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and activates transcription factor AP-1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 5097–103.
Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M, Shpiro N, Hastie CJ, Mclauchlan H, et al. The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J 2007; 408: 297.
Clark K, Plater L, Peggie M, Cohen P . Use of the pharmacological inhibitor BX795 to study the regulation and physiological roles of TBK1 and IκB kinase ɛ. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 14136–46.
McLean C, Erturk M, Jennings R, Ni Challanain D, Minson A, Duncan I, et al. Protective vaccination against primary and recurrent disease caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2 using a genetically disabled HSV-1. J Infect Dis 1994; 170: 1100–9.
Qiu M, Chen Y, Song S, Song H, Chu Y, Yuan Z, et al. Poly (4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) is an entry inhibitor against both HIV-1 and HSV infections-potential as a dual functional microbicide. Antiviral Res 2012; 96: 138–47.
Feldman RI, Wu JM, Polokoff MA, Kochanny MJ, Dinter H, Zhu D, et al. Novel small molecule inhibitors of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 19867–74.
Honess RW, Roizman B . Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol 1974; 14: 8–19.
Barklie Clements J, Watson RJ, Wilkie NM . Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell 1977; 12: 275–85.
Post LE, Mackem S, Roizman B . Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell 2006; 24: 555–65.
Huttunen P, Hyypiä T, Vihinen P, Nissinen L, Heino J . Echovirus 1 infection induces both stress-and growth-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and regulates the transcription of cellular immediate-early genes. Virology 1998; 250: 85–93.
Wei L, Zhu Z, Wang J, Liu J . JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways contribute to porcine circovirus type 2 infection. J Virol 2009; 83: 6039–47.
Ceballos-Olvera I, Chávez-Salinas S, Medina F, Ludert JE, Del Angel RM . JNK phosphorylation, induced during dengue virus infection, is important for viral infection and requires the presence of cholesterol. Virology 2010; 396: 30–6.
Kolchinsky P, Mirzabekov T, Farzan M, Kiprilov E, Cayabyab M, Mooney LJ, et al. Adaptation of a CCR5-using, primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate for CD4-independent replication. J Virol 1999; 73: 8120.
Iordanov MS, Paranjape JM, Zhou A, Wong J, Williams BRG, Meurs EF, et al. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase by double-stranded RNA and encephalomyocarditis virus: involvement of RNase L, protein kinase R, and alternative pathways. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 617–27.
Hu W, Hofstetter W, Guo W, Li H, Pataer A, Peng HH, et al. JNK-deficiency enhanced oncolytic vaccinia virus replication and blocked activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Cancer Gene Ther 2008; 15: 616–24.
Livingstone C, Patel G, Jones N . ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J 1995; 14: 1785–97.
Van Dam H, Wilhelm D, Herr I, Steffen A, Herrlich P, Angel P . ATF-2 is preferentially activated by stress-activated protein kinases to mediate c-jun induction in response to genotoxic agents. EMBO J 1995; 14: 1798–811.
Gupta S, Campbell D, Derijard B, Davis RJ . Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science 1995; 267: 389–93.
Lin A, Minden A, Martinetto H, Claret FX, Lange-Carter C, Mercurio F, et al. Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science 1995; 268: 286–90.
Everett RD . ICP 0, a regulator of herpes simplex virus during lytic and latent infection. Bioessays 2000; 22: 761–70.
Diao L, Zhang B, Xuan C, Sun S, Yang K, Tang Y, et al. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by HSV-1 immediate early protein ICP0. Exp Cell Res 2005; 308: 196–210.
Diao L, Zhang B, Fan J, Gao X, Sun S, Yang K, et al. Herpes virus proteins ICP0 and BICP0 can activate NF-κB by catalyzing IκBα ubiquitination. Cell Signal 2005; 17: 217–29.
Patel A, Hanson J, McLean TI, Olgiate J, Hilton M, Miller WE, et al. Herpes simplex virus type 1 induction of persistent NF-kappa B nuclear translocation increases the efficiency of virus replication. Virology 1998; 247: 212–22.
Gregory D, Hargett D, Holmes D, Money E, Bachenheimer S . Efficient replication by herpes simplex virus type 1 involves activation of the IκB kinase-IκB-p65 pathway. J Virol 2004; 78: 13582–90.
Belham C, Wu S, Avruch J . Intracellular signalling: PDK1-a kinase at the hub of things. Curr Biol 1999; 9: R93–6.
Regulator AK . Cellular signaling: pivoting minireview around PDK-1. Cell 2000; 103: 185–8.
Hsu MJ, Wu CY, Chiang HH, Lai YL, Hung SL . PI3K/Akt signaling mediated apoptosis blockage and viral gene expression in oral epithelial cells during herpes simplex virus infection. Virus Res 2010; 153: 36–43.
Hess J, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M . AP-1 subunits: quarrel and harmony among siblings. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 5965–73.
Davis RJ . Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 2000; 13: 239–52.
Hargett D, McLean T, Bachenheimer SL . Herpes simplex virus ICP27 activation of stress kinases JNK and p38. J Virol 2005; 79: 8348–60.
Tojima Y, Fujimoto A, Delhase M, Chen Y, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K, et al. NAK is an IκB kinase-activating kinase. Nature 2000; 404: 778–82.
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT, et al. IKKsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 491–6.
Hiscott J, Pitha P, Genin P, Nguyen H, Heylbroeck C, Mamane Y, et al. Triggering the interferon response: the role of IRF-3 transcription factor. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19: 1–13.
Domke-Opitz I, Straub P, Kirchner H . Effect of interferon on replication of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in human macrophages. J Virol 1986; 60: 37–42.
Ma Y, Jin H, Valyi-Nagy T, Cao Y, Yan Z, He B . Inhibition of TANK binding kinase 1 by herpes simplex virus 1 facilitates productive infection. J Virol 2012; 86: 2188–96.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Qi-han LI at the Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences for HSV-1 (HF), Dr Er-guang LI at the School of Medicine, Nanjing University, China for HSV-2 (G) and Dr Claus-Henning NAGEL at the Heinrich Pette Institute-Leibniz Institute for Experimental Virology, Germany for pcDNA3-ICP0-1/2-GFP.
This study was supported by the Major Research and Development Project from the Ministry of Health (Grant No 2013ZX10001005-003 and 2016ZX10001005003), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No 2016YFC1201000), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (Grant No BK20130591), MOE Doctoral Base Foundation (Grant No 20130091120022), State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science (Grant No 5431ZZXM1615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Ar., Qiu, M., Li, Yl. et al. BX-795 inhibits HSV-1 and HSV-2 replication by blocking the JNK/p38 pathways without interfering with PDK1 activity in host cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 402–414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.160
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.160
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Gasdermin D aggravates a mouse model of radiation-induced liver disease by promoting chemokine secretion and neutrophil recruitment
Nature Communications (2025)
-
p38-MAPK is prerequisite for the synthesis of SARS-CoV-2 protein
VirusDisease (2024)
-
High content screening and proteomic analysis identify a kinase inhibitor that rescues pathological phenotypes in a patient-derived model of Parkinson’s disease
npj Parkinson's Disease (2022)
-
The roles of signaling pathways in SARS-CoV-2 infection; lessons learned from SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV
Archives of Virology (2021)
-
Toll-like receptor-mediated innate immunity against herpesviridae infection: a current perspective on viral infection signaling pathways
Virology Journal (2020)