Abstract
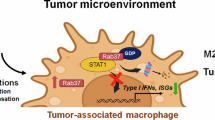
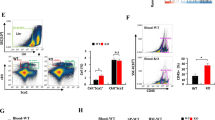
M2-like polarized tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play a pivotal role in promoting cancer cell growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. The identification of M2-like TAMs during tumor progression is an attractive approach for cancer therapy. In this study, we investigated the relevance of macrophage polarization and the antitumor effect of gefitinib in Lewis Lung cancer (LLC) in vitro and in vivo. Gefitinib at a concentration below 2.5 μmol/L did not cause significant growth inhibition on LLC and RAW 264.7 cell lines and bone marrow-derived macrophage (BMDMs). However, a small concentration of gefitinib (0.62 μmol/L) significantly inhibited IL-13-induced M2-like polarization of macrophages, evidenced by the decreased expression of the M2 surface markers CD206 and CD163, down-regulation of specific M2-marker genes (Mrc1, Ym1, Fizz1, Arg1, IL-10 and CCL2) as well as inhibition of M2-like macrophage-mediated invasion and migration of LLC cells. In RAW 264.7 cells, gefitinib inhibits IL-13-induced phosphorylation of STAT6, which was a crucial signaling pathway in macrophage M2-like polarization. In LLC mice metastasis model, oral administration of gefitinib (75 mg·kg−1·d−1, for 21 d) significantly reduced the number of lung metastasis nodules, down-regulated the expression of M2 marker genes and the percentages CD206+ and CD68+ macrophages in tumor tissues. These results demonstrated that gefitinib effectively inhibits M2-like polarization both in vitro and in vivo, revealing a novel potential mechanism for the chemopreventative effect of gefitinib.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ding L, Liang G, Yao Z, Zhang J, Liu R, Chen H, et al. Metformin prevents cancer metastasis by inhibiting M2-like polarization of tumor associated macrophages. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 36441–55.
Sica A, Mantovani A . Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 787–95.
Wang W, Wang J, Dong SF, Liu CH, Italiani P, Sun SH, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of andrographolide on macrophage activation and specific antibody response. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2010; 31: 191–201.
Shi Y, Ping YF, Zhang X, Bian XW . Hostile takeover: glioma stem cells recruit TAMs to support tumor progression. Cell Stem Cell 2015; 16: 219–20.
Fan QM, Jing YY, Yu GF, Kou XR, Ye F, Gao L, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote cancer stem cell-like properties via transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2014; 352: 160–8.
Germano G, Frapolli R, Belgiovine C, Anselmo A, Pesce S, Liguori M, et al. Role of macrophage targeting in the antitumor activity of trabectedin. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 249–62.
Qian BZ, Pollard JW . Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 2010; 141: 39–51.
Weagel E, Smith C, Liu PG, Robison R, O'Neill K . Macrophage polarization and its role in cancer. J Clin Cell Immunol 2015. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000338.
Dong R, Gong Y, Meng W, Yuan M, Zhu H, Ying M, et al. The involvement of M2 macrophage polarization inhibition in fenretinide-mediated chemopreventive effects on colon cancer. Cancer Lett 2017; 388: 43–53.
Jiménez-Garcia L, Herránz S, Luque A, Hortelano S . Critical role of p38 MAPK in IL-4-induced alternative activation of peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Immunol 2015; 45: 273–86.
Tugal D, Liao X, Jain MK . Transcriptional control of macrophage polarization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013; 33: 1135–44.
Zhu L, Yang T, Li L, Sun L, Hou Y, Hu X, et al. TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disease. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 4696.
Paulson JC . Innate immune response triggers lupus-like autoimmune disease. Cell 2007; 130: 589–91.
Lin CY, Lin CJ, Chen KH, Wu JC, Huang SH, Wang SM . Macrophage activation increases the invasive properties of hepatoma cells by destabilization of the adherens junction. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 3042–50.
Normanno N, Maiello MR, De Luca A . Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs): Simple drugs with a complex mechanism of action? J Cell Physiol 2003; 194: 13–9.
Zhang SR, Zhu LC, Jiang YP, Zhang J, Xu RJ, Xu YS, et al. Efficacy of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, in the treatment of intracerebral metastases of non-small cell lung cancer in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2017; 38: 233–40.
Ranson M, Wardell S . Gefitinib, a novel, orally administered agent for the treatment of cancer. J Clin Pharm Ther 2004; 29: 95–103.
Marim FM, Silveira TN . Lima DS Jr, Zamboni DS . A method for generation of bone marrow-derived macrophages from cryopreserved mouse bone marrow cells. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15263.
Ding L, Ma W, Littmann T, Camp R, Shen J . The P2Y2 nucleotide receptor mediates tissue factor expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 27027–38.
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A . Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 2002; 23: 549–55.
Rőszer T . Understanding the mysterious M2 macrophage through activation markers and effector mechanisms. Mediators Inflamm 2015; 2015: 816460.
Choi HJ, Choi HJ, Chung TW, Ha KT . Luteolin inhibits recruitment of monocytes and migration of Lewis lung carcinoma cells by suppressing chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 2 expression in tumor-associated macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016; 470: 101–6.
Wang C, Yu X, Cao Q, Wang Y, Zheng G, Tan TK, et al. Characterization of murine macrophages from bone marrow, spleen and peritoneum. BMC Immunol 2013; 14: 6.
Chanmee T, Ontong P, Konno K, Itano N . Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2014; 6: 1670–90.
Martinez FO, Helming L, Gordon S . Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 451–83.
Pauleau AL, Rutschman R, Lang R, Pernis A, Watowich SS, Murray PJ . Enhancer-mediated control of macrophage-specific arginase I expression. J Immunol 2004; 172: 7565–73.
Gensel JC, Zhang B . Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res 2015; 1619: 1–11.
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE . The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 618–31.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F . Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008; 454: 436–44.
Song J, Zhu J, Zhao Q, Tian B . Gefitinib causes growth arrest and inhibition of metastasis in human chondrosarcoma cells. J BUON 2015; 20: 894–901.
Pan Y, Li X, Duan J, Yuan L, Fan S, Fan J, et al. Enoxaparin sensitizes human non-small-cell lung carcinomas to gefitinib by inhibiting DOCK1 expression, vimentin phosphorylation, and Akt activation. Mol Pharmacol 2015; 87: 378–90.
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, Athar M, Ghazizadeh S, Simon M, et al. Soluble E-cadherin: a critical oncogene modulating receptor tyrosine kinases, MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Oncogene 2014; 33: 225–35.
Dai F, Liu L, Che G, Yu N, Pu Q, Zhang S, et al. The number and microlocalization of tumor-associated immune cells are associated with patient's survival time in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 220.
Ruffell B, Affara NI, Coussens LM . Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol 2012; 33: 119–26.
Hardbower DM, Singh K, Asim M, Verriere TG, Olivares-Villagómez D, Barry DP, et al. EGFR regulates macrophage activation and function in bacterial infection. J Clin Inves 2016; 126: 3296–312.
David M, Ford D, Bertoglio J, Maizel AL, Pierre J . Induction of the IL-13 receptor α2-chain by IL-4 and IL-13 in human keratinocytes: involvement of STAT6, ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Oncogene 2001; 20: 6660–8.
Yang M, Hogan SP, Henry PJ, Matthaei KI, McKenzie AN, Young IG, et al. Interleukin-13 mediates airways hyperreactivity through the IL-4 receptor-alpha chain and STAT-6 independently of IL-5 and eotaxin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001; 25: 522–30.
Stütz AM, Pickart LA, Trifilieff A, Baumruker T, Prieschl-Strassmayr E, Woisetschläger M . The Th2 cell cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 regulate found in inflammatory zone 1/resistin-like molecule α gene expression by a STAT6 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 2003; 170: 1789–96.
Jia X, Yu F, Wang J, Iwanowycz S, Saaoud F, Wang Y, et al. Emodin suppresses pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer accompanied with decreased macrophage recruitment and M2 polarization in the lungs. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2014; 148: 291–302.
Yu F, Jia X, Du F, Wang J, Wang Y, Ai W, et al. miR-155-deficient bone marrow promotes tumor metastasis. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 923–36.
Liu Y, Chen K, Wang C, Gong W, Yoshimura T, Liu M, et al. Cell surface receptor FPR2 promotes antitumor host defense by limiting M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 550–60.
Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post MJ, De Winther MP, Donners MM . Anti-inflammatory M2, but not pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo. Angiogenesis 2014; 17: 109–18.
Acknowledgements
We also acknowledge Zhejiang University for providing a scholarship for PhD studies to Mr Muhammad TARIQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tariq, M., Zhang, Jq., Liang, Gk. et al. Gefitinib inhibits M2-like polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in Lewis lung cancer by targeting the STAT6 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 1501–1511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.124
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Antibody-lectin chimeras for glyco-immune checkpoint blockade
Nature Biotechnology (2025)
-
Unravelling immune microenvironment features underlying tumor progression in the single-cell era
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-26b-5p regulates macrophage polarization and chondrocyte hypertrophy by targeting TLR3 and COL10A1 to alleviate osteoarthritis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2024)
-
Targeting Macrophage Phenotypes and Metabolism as Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Atherosclerosis and Related Cardiovascular Diseases
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2024)
-
Crosstalk between macrophages and cardiac cells after myocardial infarction
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)