Abstract
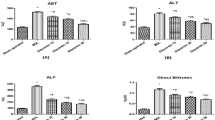
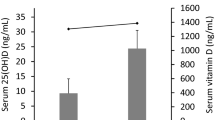
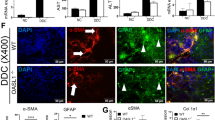
Cholestatic liver diseases are important causes of liver cirrhosis and liver transplantation, but few drugs are available for treatment. D-chiro-inositol (DCI), an isomer of inositol found in many Leguminosae plants and in animal viscera, is used clinically for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated whether DCI exerted an anti-cholestatic effect and its underlying mechanisms. A cholestatic rat model was established via bile duct ligation (BDL). After the surgery, the rats were given DCI (150 mg·kg-1·d-1) in drinking water for 2 weeks. Oral administration of DCI significantly decreased the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and attenuated bile duct proliferation, parenchymal necrosis and fibrosis in BDL rats. Furthermore, DCI treatment significantly increased the serum and bile levels of total bile acid (TBA), and decreased TBA levels in the liver. Moreover, DCI treatment significantly increased expression of the genes encoding bile acid transporters BSEP (Abcb11) and MRP2 (Abcc2) in liver tissues. DCI treatment also markedly decreased hepatic CD68 and NF-kappaB (NF-κB) levels, significantly decreased the serum and hepatic MDA levels, markedly increased superoxide dismutase activity in both serum and liver tissues. Using whole-genome oligonucleotide microarray, we revealed that DCI treatment altered the expression profiles of oxidation reduction-related genes in liver tissues. Collectively, DCI effectively attenuates BDL-induced hepatic bile acid accumulation and decreases the severity of injury and fibrosis by improving bile acid secretion, repressing inflammation and decreasing oxidative stress. The results suggest that DCI might be beneficial for patients with cholestatic disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Trauner M, Meier PJ, Boyer JL . Molecular pathogenesis of cholestasis. New Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1217–27.
Scheiman JM, Moseley RH . Cholestasis. Compr Ther 1994; 20: 28–35.
Wagner M, Trauner M . Recent advances in understanding and managing cholestasis. F1000Res 2016; 5. pii: F1000 Faculty Rev-705.
Chapman RW . High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: throwing the urso out with the bathwater? Hepatology 2009; 50: 671–3.
Gao YF, Zhang MN, Wang TX, Wu TC, Ai RD, Zhang ZS . Hypoglycemic effect of D-chiro-inositol in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2016; 433: 26–34.
Lagana AS, Barbaro L, Pizzo A . Evaluation of ovarian function and metabolic factors in women affected by polycystic ovary syndrome after treatment with D-Chiro-Inositol. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2015; 291: 1181–6.
Cianci A, Panella M, Fichera M, Falduzzi C, Bartolo M, Caruso S . d-chiro-Inositol and alpha lipoic acid treatment of metabolic and menses disorders in women with PCOS. Gynecol Endocrinol 2015; 31: 483–6.
Hada B, Yoo MR, Seong KM, Jin YW, Myeong HK, Min KJ . D-chiro-inositol and pinitol extend the life span of Drosophila melanogaster. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2013; 68: 226–34.
Hu Y, Zhao Y, Ren D, Guo J, Luo Y, Yang X . Hypoglycemic and hepatoprotective effects of D-chiro-inositol-enriched tartary buckwheat extract in high fructose-fed mice. Food Funct 2015; 6: 3760–9.
He H, Mennone A, Boyer JL, Cai SY . Combination of retinoic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates liver injury in bile duct-ligated rats and human hepatic cells. Hepatology 2011; 53: 548–57.
Zhao S, Li N, Zhen Y, Ge M, Li Y . Yu B, et al. Protective effect of gastrodin on bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2015; 86: 202–7.
Yu DK, Zhang CX, Zhao SS, Zhang SH, Zhang H . Cai SY, et al. The anti-fibrotic effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in bile duct-ligated cholestatic rats and human hepatic stellate LX-2 cells are mediated by the PI3K/Akt/Smad pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2015; 36: 473–82.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA . Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 44–57.
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D . Bryant D, et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35(Web Server issue): W169–75.
Zhen YZ, Li NR, He HW, Zhao SS, Zhang GL . Hao XF, et al. Protective effect of bicyclol against bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: 7155–64.
Zhao W, He H, Ren K, Zhang H, Chen Y, Shao RG . Myofibrillogenesis regulator-1 promotes cell adhesion and migration in human hepatoma cells. Chin Sci Bull 2013; 58: 3007–14.
O'Leary JG, Lepe R, Davis GL . Indications for liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2008; 134: 1764–76.
Heathcote EJ . Diagnosis and management of cholestatic liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 5: 776–82.
Guo J, Friedman SL . Hepatic fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis 2007; 27: 413–26.
Boyer JL . Bile formation and secretion. Compr Physiol 2013; 3: 1035–78.
Tomita K, Tamiya G, Ando S, Ohsumi K, Chiyo T . Mizutani A, et al. Tumour necrosis factor alpha signalling through activation of Kupffer cells plays an essential role in liver fibrosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Gut 2006; 55: 415–24.
Luedde T, Schwabe RF . NF-kappaB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 8: 108–18.
Jones H, Alpini G, Francis H . Bile acid signaling and biliary functions. Acta Pharm Sin B 2015; 5: 123–8.
Bataller R, Brenner DA . Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 209–18.
Kisseleva T, Brenner DA . Role of hepatic stellate cells in fibrogenesis and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 22: S73–8.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2016-I2M-2-002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81673497 and 81473249), the National Mega-project for Innovative Drugs (2014ZX09201042), and the Beijing Natural Scientific Foundation (7162130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Ss., Li, Nr., Zhao, Wl. et al. D-chiro-inositol effectively attenuates cholestasis in bile duct ligated rats by improving bile acid secretion and attenuating oxidative stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39, 213–221 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.98
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.98
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effect of Crocin on TFAM and PGC-1α expression and Catalase and Superoxide dismutase activities following cholestasis-induced neuroinflammation in the striatum of male Wistar rats
Metabolic Brain Disease (2021)
-
Sirt6 opposes glycochenodeoxycholate-induced apoptosis of biliary epithelial cells through the AMPK/PGC-1α pathway
Cell & Bioscience (2020)