Abstract
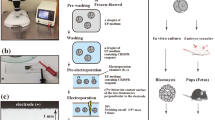
The production of transgenic swine for xenotransplantation has been proposed as an optimal option to overcome the chronic shortage of human organ donors. Generation of genetically engineered swine has been elusive due to the difficulties in gene transfer. In order to achieve effective gene delivery, a key step for the genetic modification, we applied electronic pulse delivery (EPD) technology to introduce H2Kb-DC DNA construct into swine eggs. Using the developed EPD Protocols™, we have achieved good viability of the EPD treated oocytes, satisfactory embryonic development of the EPD treated embryos, and stable DNA transfer into the swine embryos with high efficiency. Thus, application of the EPD technology promises to effectively facilitate the generation of large trangenic mammals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cozzi E, White DJ . The generation of transgenic pigs as potential organ donors for humans. Nat Med 1995; 1 (9):964–6.
Michaels MG, Simmons RL . Xenotransplant-associated zoonoses. Strategies for prevention. Transplantation 1994; 57 (1):1–7.
Ye Y, Niekrasz M, Kosanke S, et al. The pig as a potential organ donor for man. A study of potentially transferable disease from donor pig to recipient man. Transplantation 1994; 57 (5):694–703.
Michaels MG, McMichael JP . Brasky K, et al. Screening donors for xenotransplantation. The potential for xenozoonoses. Transplantation 1994; 57 (10):1462–5.
Sandrin MS, McKenzie IF . Gal alpha (1,3)Gal, the major xenoantigen(s) recognized in pigs by human natural antibodies. Immunol Rev 1994; 141:169–90.
Dalmasso AP, Vercellotti GM, Platt JL, Bach FH . Inhibition of complement-mediated endothelial cell cytotoxicity by decay-accelerating factor. Potential for prevention of xenograft hyperacute rejection. Transplantation 1991; 52 (3):530–3.
Fodor WL, Williams BL, Matis LA, et al. Expression of a functional human complement inhibitor in a transgenic pig as a model for the prevention of xenogeneic hyperacute organ rejection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91 (23):11153–7.
Ryan US . Complement inhibitory therapeutics and xenotransplantation. Nat Med 1995; 1(9):967–8.
Mullins JJ, Mullins LJ . Transgenesis in nonmurine species. Hypertension 1993; 22 (4):630–3.
Janne J, Hyttinen JM, Peura T, et al. Transgenic bioreactors. Int J Biochem 1994; 26 (7):859–70.
Wall RJ, Pursel VG, Hammer RE, Brinster RL . Development of porcine ova that were centrifuged to permit visualization of pronuclei and nuclei. Biol Reprod 1985; 32 (3):645–51.
Zhao X . EPD, a novel technology for drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery reviews 1995; 17: 257–62
Zhao X . The Appylication of Electroic Pulse Delivery in Gene Therapy: progress and perspectives. In: Felgner PL, heller M J, Lehn P, Behr JP, Szoka FC. eds. Artificial Self-Assembling Systems for gene Delivery. The American Chemical Society 1996:64–71.
Zhao X, Zhang P J, Wong TK . Application of Baekonization: A new approach to produce transgenic fish. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology 1993; 2:63–69.
Zhao X, Wong, TK . Production of transgenics by electronic pulse delivery J Cell Biology 1991; 115:83.
Langford GA, Yannoutsos N, Cozzi E, et al. Production of pigs transgenic for human decay accelerating factor. Transplant Proc 1994; 26 (3):1400–1.
Rosengard AM, Cary NR, Langford GA, Tucker AW, Wallwork J, White DJ . Tissue expression of human complement inhibitor, decay-accelerating factor, in transgenic pigs. A potential approach for preventing xenograft rejection. Transplantation 1995; 59 (9):1325–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*This publication is dedicated to Professor Lu Ji SHI's (L.C. Sze) 80th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Huang, S. & Zhao, X. High efficiency DNA delivery into swine oocytes and embryos by electronic pulse delivery (EPD). Cell Res 7, 39–49 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.1997.5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.1997.5