Abstract
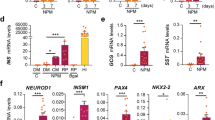
The capacity for self-renewal and differentiation of human embryonic stem (ES) cells makes them a potential source for generation of pancreatic beta cells for treating type I diabetes mellitus. Here, we report a newly developed and effective method, carried out in a serum-free system, which induced human ES cells to differentiate into insulin-producing cells. Activin A was used in the initial stage to induce definitive endoderm differentiation from human ES cells, as detected by the expression of the definitive endoderm markers Sox17 and Brachyury. Further, all-trans retinoic acid (RA) was used to promote pancreatic differentiation, as indicated by the expression of the early pancreatic transcription factors pdx1 and hlxb9. After maturation in DMEM/F12 serum-free medium with bFGF and nicotinamide, the differentiated cells expressed islet specific markers such as C-peptide, insulin, glucagon and glut2. The percentage of C-peptide-positive cells exceeded 15%. The secretion of insulin and C-peptide by these cells corresponded to the variations in glucose levels. When transplanted into renal capsules of Streptozotocin (STZ)-treated nude mice, these differentiated human ES cells survived and maintained the expression of beta cell marker genes, including C-peptide, pdx1, glucokinase, nkx6.1, IAPP, pax6 and Tcf1. Thirty percent of the transplanted nude mice exhibited apparent restoration of stable euglycemia; and the corrected phenotype was sustained for more than six weeks. Our new method provides a promising in vitro differentiation model for studying the mechanisms of human pancreas development and illustrates the potential of using human ES cells for the treatment of type I diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med 2000; 343:230–238.
Hussain MA, Theise ND . Stem-cell therapy for diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2004; 364:203–205.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998; 282:1145–1147.
Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med 2004; 350:1353–1356.
Assady S, Maor G, Amit M, et al. Insulin production by human embryonic stem cells. Diabetes 2001; 50:1691–1697.
Brolén G, Heins N, Edsbagge J, et al. Signals from the embryonic mouse pancreas induce differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing beta-cell-like cells. Diabetes 2005; 54:2867–2874.
Lumelsky N, Blondel O, Laeng P, et al. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to insulin-secreting structures similar to pancreatic islets. Science 2001; 292:1389–1394.
Segev H, Fishman B, Ziskind A, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing clusters. Stem Cells 2004; 22:265–274.
Hansson M, Tonning A, Frandsen U, et al. Artifactual insulin release from differentiated embryonic stem cells. Diabetes 2004; 53:2603–2609.
D'Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, et al. Production of pancreatic hormone–expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnol 2006; 24:1392–1401.
Shi Y, Hou L, Tang F, et al. Inducing embryonic stem cells to differentiate into pancreatic â cells by a novel three-step approach with activin A and all-trans retinoic acid. Stem Cells 2005; 23:656–662.
Johansson, BM, Wiles MV . Evidence for involvement of Activin A and bone morphogenetic protein 4 in mammalian mesoderm and hematopoietic development. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15:141–151.
Gao R, Ustinov J, Pulkkinen MA, et al. Characterization of endocrine progenitor cells and critical factors for their differentiation in human adult pancreatic cell culture. Diabetes 2003; 52:2007–2015.
Kanai-Azuma M, Kanai Y, Gad JM, et al. Depletion of definitive gut endoderm in Sox17-null mutant mice. Development 2002; 129:2367–2379.
Hardikar AA, Marcus-Samuels B, Geras-Raaka E, et al. Human pancreatic precursor cells secrete FGF2 to stimulate clustering into hormone-expressing islet-like cell aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100:7117–7122.
Otonkoski T, Beattie GM, Mally MI, et al. Nicotinamide is a potent inducer of endocrine differentiation in cultured human fetal pancreatic cells. J Clin Invest 1993; 92:1459–1466.
Lechner A, Nolan AL, Blacken RA, et al. Redifferentiation of insulin-secreting cells after in vitro expansion of adult human pancreatic islet tissue. BBRC 2005; 327:581–588.
Kubo A, Shinozaki K, Shannon JM, et al. Development of definitive endoderm from embryonic stem cells in culture. Development 2004; 131:1651–1662.
Tada S, Era T, Furusawa C, et al. Characterization of mesendoderm: a diverging point of the definitive endoderm and mesoderm in embryonic stem cell differentiation culture. Development 2005; 132:4363–4374.
D'Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, et al. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nature Biotechnol 2005; 23:1534–41.
Stafford D, Prince VE . Retinoic Acid signaling is required for a critical early step in Zebrafish pancreatic development. Current Biology 2002; 12:1215–1220.
Stafford D, White RJ, Kinkel MD . Retinoids signal directly to zebrafish endoderm to specify insulin-expressing cells. Development 2006; 133:949–956.
Martin M, Gallego-Llamas J, Ribes V, et al. Dorsal pancreas agenesis in retinoic acid-deficient Raldh2 mutant mice. Dev Biol 2005; 284:399–411.
Micallef SJ, Janes ME, Knezevic K, et al. Retinoic acid induces pdx1-positive endoderm in differentiating mouse embryonic stem cells. Diabetes 2005; 54:301–305.
Migliavacca B, Nano R, Antonioli B, et al. Identification of in vitro parameters predictive of graft function: A study in an animal model of islet transplantation. Transplant Proc 2004; 36:612–613.
Gray DW, Sutton R, McShane P, et al. Exocrine contamination impairs implantation of pancreatic islets transplanted beneath the kidney capsule. J Surg Res 1988; 45:432–442.
Mattsson G, Jansson L, Nordin A, et al. Impaired revascularization of transplanted mouse pancreatic islets is chronic and glucose-independent. Transplantation 2003; 75:736–739.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology Grant (2001CB510106), Science and Technology Plan of Beijing Municipal Government (H020220050290), National Natural Science Foundation of China Awards for Outstanding Young Scientists (30125022) and for Creative Research Groups (30421004), and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Grant (37871) to H Deng. We thank Dr C Wright for kindly providing us with the pdx1 antibody. We thank Drs Matt Stremlau, Tung-Tien Sun, Johnny He, and Hui Zhang for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank Yizhe Zhang for technical support on real-time PCR. We also thank Donghui Zhang, Xulei Sun, Yushan Guo, Zan Tong, Jun Cai, Han Qin, Chengyan Wang, Pengbo Zhang, Chunbo Teng, Jiefang You, Yan Shen, Wei Wei and other colleagues in our laboratory for technical assistance and advice during experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Shi, Y., Zhao, D. et al. In vitro derivation of functional insulin-producing cells from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res 17, 333–344 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
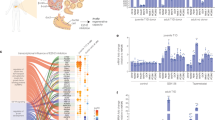
Pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in adult human islets and stem cell-derived islets
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Optimization of differentiation protocols of dental tissues stem cells to pancreatic β-cells
BMC Molecular and Cell Biology (2022)
-
Stepwise differentiation of functional pancreatic β cells from human pluripotent stem cells
Cell Regeneration (2022)
-
Stem cells differentiation into insulin-producing cells (IPCs): recent advances and current challenges
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Recent progress in pancreatic islet cell therapy
Inflammation and Regeneration (2021)