Abstract
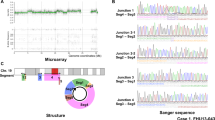
We studied a family in which the same 10 Mb inverted duplication of 2p25.3–p25.1 segregates in two children and their father, all showing a trisomy phenotype. As FISH analysis demonstrated that the duplication was inverted, we suspected that a contiguous terminal deletion was also present, according to the classical inv dup del type of rearrangements. Although FISH with 2p and 2q subtelomeric probes gave normal results, 100 kb resolution array-CGH (aCGH) showed that, beside the duplication, a 273 kb deletion was also present. The presence of a single-copy region between the deleted and duplicated regions was further suspected through high-resolution aCGH analysis (∼20 kb), although only one informative spot having a normal log ratio was detected. The precise structure of the rearrangement was re-defined by real-time PCR and breakpoint cloning, demonstrating the presence of a 2680 bp single-copy sequence between deleted and duplicated regions and the involvement of a simple repeat with the potential for forming a non-B DNA structure. The rearrangement was not mediated by segmental duplications or short inverted repeats, and the double-strand break might have been repaired by non-homologous end joining or microhomology-mediated intrastrand repair. These data highlight the fact that concomitant deletions associated with inverted duplications are very likely to be more frequent than classical cytogenetic methods alone have been able to demonstrate. The phenotypic effects of the trisomy and of the terminal 2p deletion are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jacobs PA, Browne C, Gregson N, Joyce C, White H : Estimates of the frequency of chromosome abnormalities detectable in unselected newborns using moderate levels of banding. J Med Genet 1992; 29: 103–108.
Phelan MC, Crawford EC, Bealer DM : Mental retardation in South Carolina III. Chromosome aberrations. Proc Greenwood Genet Center 1996; 15: 45–60.
Shaffer LG, Lupski JR : Molecular mechanisms for constitutional chromosomal rearrangements in humans. Annu Rev Genet 2000; 34: 297–329.
Van Dyke DL, Miller MJ, Weiss L : The origin of inverted tandem duplications, and phenotypic effects of tandem duplication of the X chromosome long arm. Am J Med Genet 1983; 15: 441–450.
Shaw CJ, Lupski JR : Implications of human genome architecture for rearrangement-based disorders: the genomic basis of disease. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: R57–R64.
Floridia G, Piantanida M, Minelli A et al: The same molecular mechanism at the maternal meiosis I produces mono and dicentric 8p duplications. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 785–796.
Giglio S, Broman KW, Matsumoto N et al: Olfactory receptor-gene clusters, genomic-inversion polymorphisms, and common chromosome rearrangements. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 874–883.
Vissers LE, de Vries BB, Osoegawa K et al: Array-based comparative genomic hybridization for the genomewide detection of submicroscopic chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 1261–1270.
De Gregori M, Ciccone R, Magini P et al: Cryptic deletions are a common finding in ‘balanced’ reciprocal and complex chromosome rearrangements: a study of 59 patients. J Med Genet 2007; 44: 750–762.
Jenderny J, Poetsch M, Hoeltzenbein M, Friedrich U, Jauch A : Detection of a concomitant distal deletion in an inverted duplication of chromosome 3. Is there an overall mechanism for the origin of such duplications/deficiencies? Eur J Hum Genet 1998; 6: 439–444.
Bonaglia MC, Giorda R, Poggi G et al: Inverted duplications are recurrent rearrangements always associated with a distal deletion: description of a new case involving 2q. Eur J Hum Genet 2000; 8: 597–603.
Macina RA, Morii K, Hu XL et al: Molecular cloning and RARE cleavage mapping of human 2p, 6q, 8q, 12q, and 18q telomeres. Genome Res 1995; 5: 225–232.
de Smith AJ, Tsalenko A, Sampas N et al: Array CGH analysis of copy number variation identifies 1284 new genes variant in healthy white males: implications for association studies of complex diseases. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: 2783–2794.
Narayanan V, Lobachev KS : Intrachromosomal gene amplification triggered by hairpin-capped breaks requires homologous recombination and is independent of nonhomologous end-joining. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 1814–1818.
Okuno Y, Hahn PJ, Gilbert DM : Structure of a palindromic amplicon junction implicates microhomology-mediated end joining as a mechanism of sister chromatid fusion during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: 749–756.
Tanaka H, Cao Y, Bergstrom DA, Kooperberg C, Tapscott SJ, Yao MC : Intrastrand annealing leads to the formation of a large DNA palindrome and determines the boundaries of genomic amplification in human cancer. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 1993–2002.
Woodford KJ, Howell RM, Usdin K : A novel K(+)-dependent DNA synthesis arrest site in a commonly occurring sequence motif in eukaryotes. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 27029–27035.
Aviram-Goldring A, Fritz B, Bartsch C et al: Molecular cytogenetic studies in three patients with partial trisomy 2p, including CGH from paraffin-embedded tissue. Am J Med Genet 2000; 91: 74–82.
Thangavelu M, Frolich G, Rogers D : Partial duplication 2p as the sole abnormality in two cases with anencephaly. Am J Med Genet Part A 2004; 124A: 170–172.
Gruchy N, Jacquemont ML, Lyonnet S et al: Recurrent inverted duplication of 2p with terminal deletion in a patient with the classical phenotype of trisomy 2p23-pter. Am J Med Genet 2007; 143: 2417–2422.
Kochilas LK, Abuelo DN, Tantravahi U : Bilateral semilunar valve dysplasia in a patient with inverted duplication 2p25-22. Pediatr Cardiol 2008; 29: 172–175.
Ravnan JB, Tepperberg JH, Papenhausen P et al: Subtelomere FISH analysis of 11 688 cases: an evaluation of the frequency and pattern of subtelomere rearrangements in individuals with developmental disabilities. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 478–489.
Zou YS, Van Dyke DL, Ellison JW : Microarray comparative genomic hybridization and FISH studies of an unbalanced cryptic telomeric 2p deletion/16q duplication in a patient with mental retardation and behavioral problems. Am J Med Genet A 2007; 143: 746–751.
Bakker B, Bikker H, Vulsma T, De Randamie JSE, Wiedijk BM, De Vijlder JJM : Two decades of screening for congenital hypothyroidism in the Netherlands: TPO gene mutations in total iodide organification defects (an update). J Clin Endocr Metab 2000; 85: 3708–3712.
Kim JG, Hudson LD : Novel member of the zinc finger superfamily: a C(2)-HC finger that recognizes a glia-specific gene. Molec Cell Biol 1992; 12: 5632–5639.
Azuma T, Ao S, Saito Y et al: Human SOX11, an upregulated gene during the neural differentiation, has a long 30 untranslated region. DNA Res 1999; 6: 357–360.
Sock E, Rettig SD, Enderich J, Bosl MR, Tamm ER, Wegner M : Gene targeting reveals a widespread role for the highmobility- group transcription factor Sox11 in tissue remodeling. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6635–6644.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Telethon Grant GGP06208A to MCB and RG, PRIN 2005 and 2006 to OZ and ER and Fondazione Mariani and Fondazione CARIPLO (all to OZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonaglia, M., Giorda, R., Massagli, A. et al. A familial inverted duplication/deletion of 2p25.1–25.3 provides new clues on the genesis of inverted duplications. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 179–186 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.160
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of small-sized intrachromosomal segments at the ends of INV–DUP–DEL patterns
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
The involvement of U-type dicentric chromosomes in the formation of terminal deletions with or without adjacent inverted duplications
Human Genetics (2020)
-
De novo unbalanced translocations have a complex history/aetiology
Human Genetics (2018)
-
Severe growth hormone deficiency and pituitary malformation in a patient with chromosome 2p25 duplication and 2q37 deletion
Molecular Cytogenetics (2014)
-
A new patient with a terminal de novo 2p25.3 deletion of 1.9 Mb associated with early-onset of obesity, intellectual disabilities and hyperkinetic disorder
Molecular Cytogenetics (2014)