Abstract
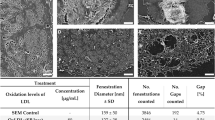
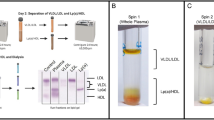
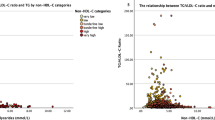
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) induces a wide range of cellular responses to produce atherosclerotic lesion, but key factors determining the response are not understood. In this study, purified LDL was oxidized with copper sulfate, and its physical properties and the related biological responses were investigated. The average hydrodynamic diameter of the lightly oxidized LDL was approximately 25 nm and its Rf value relative to nLDL on agarose gel was between 1.0 and 1.25. The diameter of the extensively oxidized LDL was over 30 nm, the Rf value was over 2.0. A 24 h-exposure of resting RAW264.7 macrophage cells to 100 µg/ml of the lightly oxidized LDL induced proliferation and macrophage activation whereas the extensively oxidized LDL induced cell death at the same concentration. In contrast, 200 µg/ml of oxLDL caused cell death regardless of oxidation degree. Short incubation (4-6 h) of the highly oxidized LDL (100 µg/ml) also resulted in cell proliferation. OxLDL-induced cell death showed mixed characteristics of apoptosis and/or necrosis depending on the strength and duration of the insult. These results suggest that cellular responses induced by oxLDL be dependent on the oxidation degree, the duration of exposure, and the concentration of oxLDL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, CY., Kim Pak, Y. Oxidation-dependent effects of oxidized LDL: proliferation or cell death. Exp Mol Med 31, 165–173 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1999.27
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1999.27
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel murine model for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis developed by combination of a high-fat diet and oxidized low-density lipoprotein
Laboratory Investigation (2012)
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of macrophage survival in atherosclerosis
Basic Research in Cardiology (2012)
-
In Vitro Evidence for the Protective role of Sida rhomboidea. Roxb Extract Against LDL Oxidation and Oxidized LDL-Induced Apoptosis in Human Monocyte–Derived Macrophages
Cardiovascular Toxicology (2011)
-
Berberine promotes the development of atherosclerosis and foam cell formation by inducing scavenger receptor A expression in macrophage
Cell Research (2009)
-
Role of macrophage and smooth muscle cell apoptosis in association with oxidized low-density lipoprotein in the atherosclerotic development
Modern Pathology (2005)