Abstract
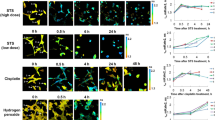
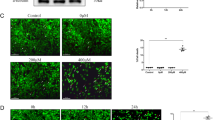
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is a neurotoxin and is commonly used to generate experimental models of Parkinson's disease (PD). In this study, we investigated the signaling molecules involved in the 6-OHDA-induced cell death using a neuronal catecholaminergic cell line (SK-N-SH cells), and the protective effect of fustin, a flavonoid from Rhus verniciflua Stokes, on 6-OHDA-induced neuronal death. 6-OHDA significantly increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i), and p38 phosphorylation. In addition, this ROS increase by 6-OHDA was reduced by pretreatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a free radical scavenger, but not by bis-(o-aminophenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N,N-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA), a Ca2+ chelator. However, the [Ca2+]i increase induced by 6-OHDA was suppressed by NAC. Moreover, pretreatment with NAC or BAPTA significantly prevented the 6-OHDA-induced increases in p38 phosphorylation, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and caspase-3 activity. Although 6-OHDA-increased phosphorylation of p38 was prevented by NAC or BAPTA, inhibition of p38 by SB203580 did not suppress ROS, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, or caspase-3 activity increases, and only partially prevented 6-OHDA-induced cell death, thus demonstrating that p38 activation is a component of a signaling pathway leading to the initiation of 6-OHDA-induced cell death, which acts in parallel with an ROS-Ca2+ -Bcl-2-caspase-3 pathway. Moreover, fustin not only suppressed 6-OHDA-induced cell death in a concentration-dependent manner but also blocked 6-OHDA-induced increases in ROS, [Ca2+]i, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, caspase-3 activity, and p38 phosphorylation. These results suggest that fustin exerts neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-induced cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, B., Lee, Y., Park, HJ. et al. Protective effects of fustin, a flavonoid from Rhus verniciflua Stokes, on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death. Exp Mol Med 39, 316–326 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.35
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.35
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RNA sequencing and de novo assembly of Solanum trilobatum leaf transcriptome to identify putative transcripts for major metabolic pathways
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Characterization of mango (Mangifera indica L.) transcriptome and chloroplast genome
Plant Molecular Biology (2014)
-
Flavonoids from the fruits of Nepalese sumac (Rhus parviflora) attenuate glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells
Food Science and Biotechnology (2013)
-
Antiviral activities of flavonoids isolated from the bark of Rhus verniciflua stokes against fish pathogenic viruses In Vitro
The Journal of Microbiology (2012)
-
Detoxified Extract of Rhus verniciflua Stokes Inhibits Rotenone-Induced Apoptosis in Human Dopaminergic Cells, SH-SY5Y
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2011)