Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the long-term effectiveness and safety of botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) treatment in patients with blepharospasm (BEB), hemifacial spasm (HFS), and entropion (EN) and to use for the first time two modified indexes, ‘botulin toxin escalation index-U’ (BEI-U) and ‘botulin toxin escalation index percentage’ (BEI-%), in the dose-escalation evaluation.
Methods
All patients in this multicentre study were followed for at least 10 years and main outcomes were clinical efficacy, duration of relief, BEI-U and BEI-%, and frequency of adverse events.
Results
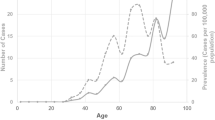
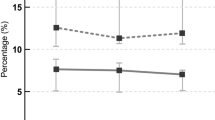
BEB, HFS, and EN patients received a mean BoNT-A dose with a significant inter-group difference (P<0.0005, respectively). The mean (±SD) effect duration was statistically different (P=0.009) among three patient groups. Regarding the BoNT-A escalation indexes, the mean (±SD) values of BEI-U and BEI-% were statistically different (P=0.035 and 0.047, respectively) among the three groups. In BEB patients, the BEI-% was significantly increased in younger compared with older patients (P=0.008). The most frequent adverse events were upper lid ptosis, diplopia, ecchymosis, and localized bruising.
Conclusions
This long-term multicentre study supports a high efficacy and good safety profile of BoNT-A for treatment of BEB, HFS, and EN. The BEI indexes indicate a significantly greater BoNT-A-dose escalation for BEB patients compared with HFS or EN patients and a significantly greater BEI-% in younger vsolder BEB patients. These results confirm a greater efficacy in the elderly and provide a framework for long-term studies with a more flexible and reliable evaluation of drug-dose escalation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jankovic J, Orman J . Blepharospasm: demographic and clinical survey of 250 patients. Ann Ophthalmol 1984; 16: 371–376.
Grandas F, Elston J, Quinn N, Marsden CD . Blepharospasm: a review of 264 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1988; 51: 767–772.
Vitek JL . Pathophysiology of dystonia: a neuronal model. Mov Disord 2002; 17: S49–S62.
Jankovic J, Havins WE, Wilkins RB . Blinking and blepharospasm. Mechanism, diagnosis, and management. JAMA 1982; 248: 3160–3164.
Reimer J, Gilg K, Karow A, Esser J, Franke GH . Health-related quality of life in blepharospasm or hemifacial spasm. Acta Neurol Scand 2005; 111: 64–70.
Epidemiological Study of Dystonia in Europe (ESDE) Collaborative Group. A prevalence study of primary dystonia in eight European countries. J Neurol 2000; 247: 787–792.
Defazio G, Livrea P . Epidemiology of primary blepharospasm. Mov Disord 2002; 17: 7–12.
Cossu G, Mereu A, Deriu M, Melis M, Molari A, Melis G et al. Prevalence of primary blepharospasm in Sardinia, Italy: a service-based survey. Mov Disord 2006; 21: 2005–2008.
Kenney C, Jankovic J . Botulinum toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neural Transm 2008; 115: 585–591.
Anderson RL, Patel BC, Holds JB, Jordan DR . Blepharospasm: past, present and future. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 1998; 14: 305–317.
Scott AB . Botulinum toxin injection into extraocular muscles as an alternative to strabismus surgery. Ophthalmology 1980; 87: 1044–1049.
FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Botulinum toxin type A (Botox), Allergan, Inc. Product approval information, licensing action, 2000a. Available at:http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/appletter/2000/botaller122100L.htm.
Porter JD, Strebeck S, Capra NF . Botulinum-induced changes in monkey eyelid muscle. Comparison with change seen in extraocular muscle. Arch Ophthalmol 1991; 109: 396–404.
Siatkowski RM, Tyutyunikov A, Biglan AW, Scalise D, Genovese C, Raikow RB et al. Serum antibody production to botulinum A toxin. Ophthalmology 1993; 100: 1861–1866.
Huang W, Foster JA, Rogachefsky AS . Pharmacology of botulinum toxin. J Am Acad Dermatol 2000; 43: 249–259.
Snir M, Weinberger D, Bourla D, Kristal-Shalit O, Dotan G, Axer-Siegel R . Quantitative changes in botulinum toxin a treatment over time in patients with essential blepharospasm and idiopathic hemifacial spasm. Am J Ophthalmol 2003; 136: 99–105.
Costa J, Espírito-Santo C, Borges A, Ferreira JJ, Coelho M, Moore P et al. Botulinum toxin type A therapy for blepharospasm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; (1): CD004900.
Mauriello JA . Blepharospasm, Meige syndrome, and hemifacial spasm: treatment with botulinum toxin. Neurology 1985; 35: 1499–1500.
Scott AB, Kennedy RA, Stubbs HA . Botulinum A toxin injection as a treatment for blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol 1985; 103: 347–350.
Cohen DA, Savino PJ, Stern MB, Hurtig HI . Botulinum injection therapy for blepharospasm: a review and report of 75 patients. Clin Neuropharmacol 1986; 9: 415–429.
Dutton JJ, Buckley EG . Botulinum toxin in the management of blepharospasm. Arch Neurol 1986; 43: 380–382.
Elston JS . Long-term results of treatment of idiopathic blepharospasm with botulinum toxin injections. Br J Ophthalmol 1987; 71: 664–668.
Engstrom PF, Arnoult JB, Mazow ML, Prager TC, Wilkins RB, Byrd WA et al. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin therapy for essential blepharospasm. Ophthalmology 1987; 17: 971–975.
Dutton JJ, Buckley EG . Long-term results and complications of botulinum A toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm. Ophthalmology 1988; 95: 1529–1534.
Taylor JD, Kraft SP, Kazdan MS, Flanders M, Cadera W, Orton RB . Treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm with botulinum A toxin: a Canadian multicentre study. Can J Ophthalmol 1991; 26: 133–138.
Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Training guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of neurologic disorders. Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment. Neurology 1994; 44: 2401–2403.
Dutton JJ . Botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of craniocervical muscle spasms: short- and long-term, local and systemic effects. Surv Ophthalmol 1996; 41: 51–65.
Calace P, Cortese G, Piscopo R, Della Volpe G, Gagliardi V, Magli A et al. Treatment of blepharospasm with botulinum neurotoxin type A: longterm results. Eur J Ophthalmol 2003; 13: 331–336.
Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, Comes G, Grafe S . for the NT 201 Blepharospasm Study Team. Efficacy and safety of a new Botulinum Toxin Type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm 2006; 113: 303–312.
Frueh BR, Musch DC . Treatment of facial spasm with botulinum toxin. An interim report. Ophthalmology 1986; 93: 917–923.
Gonnering RS . Treatment of hemifacial spasm with botulinum A toxin. Results and rationale. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 1986; 2: 143–146.
Auger RG, Whisnant JP . Hemifacial spasm in Rochester and Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1960 to 1984. Arch Neurol 1990; 47: 1233–1234.
Micheli F, Scorticati MC, Gatto E, Cersosimo G, Adi J . Familial hemifacial spasm. Mov Disord 1994; 9: 330–332.
Wang A, Jankovic J . Hemifacial spasm: clinical findings and treatment. Muscle Nerve 1998; 21: 1740–1747.
Yoshimura DM, Aminoff MJ, Tami TA, Scott AB . Treatment of hemifacial spasm with botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 1992; 15: 1045–1049.
Elston JS . The management of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neurol 1992; 239: 5–8.
Flanders M, Chin D, Boghen D . Botulinum toxin: preferred treatment for hemifacial spasm. Eur Neurol 1993; 33: 316–319.
Costa J, Espírito-Santo C, Borges A, Ferreira JJ, Coelho M, Moore P et al. Botulinum toxin type A therapy for hemifacial spasm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; (1): CD004899.
Dutton JJ, Fowler AM . Botulinum toxin in ophthalmology. Surv Ophthalmol 2007; 52: 13–31.
Mauriello JA, Leone T, Dhillon S, Pakeman B, Mostafavi R, Yepez MC . Treatment choices of 119 patients with hemifacial spasm over 11 years. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1996; 98: 213–216.
Jitpimolmard S, Tiamkao S, Laopaiboon M . Long term results of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of hemifacial spasm: a report of 175 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998; 64: 751–757.
Carruthers J, Stubbs HA . Botulinum toxin for benign essential blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm and age-related lower eyelid entropion. Can J Neurol Sci 1987; 14: 42–45.
Neetens A, Rubbens MC, Smet H . Botulinum A-toxin treatment of spasmodic entropion of the lower eyelid. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol 1987; 224: 105–109.
Clarke JR, Spalton DJ . Treatment of senile entropion with botulinum toxin. Br J Ophthalmol 1988; 72: 361–362.
Steel DH, Hoh HB, Harrad RA, Collins CR . Botulinum toxin for the temporary treatment of involutional lower lid entropion: a clinical and morphological study. Eye 1997; 11: 472–475.
Ochudlo S, Bryniarski P, Opala G . Botulinum toxin improves the quality of life and reduces the intensification of depressive symptoms in patients with blepharospasm. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2007; 13: 505–508.
Vogt T, Lüssi F, Paul A, Urban P . Long-term therapy of focal dystonia and facial hemispasm with botulinum toxin A. Nervenarzt 2008; 79: 912–917.
Dressler D, Münchau A, Bhatia KP, Quinn NP, Bigalke H . Antibody-induced botulinum toxin therapy failure: can it be overcome by increased botulinum toxin doses? Eur Neurol 2002; 47: 118–121.
Greene P, Fahn S . Development of resistance to Botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov Disord 1994; 9: 213–217.
Atassi MZ, Oshima M . Structure, activity and immune recognition of botulinum neurotoxins. Crit Rev Immunol 1999; 19: 219–260.
Pang AL, O’Day J . Use of high-dose botulinum A toxin in benign essential blepharospasm: is too high too much? Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2006; 34: 441–444.
Levy RL, Berman D, Parikh M, Miller NR . Supramaximal doses of botulinum toxin for refractory blepharospasm. Ophthalmology 2006; 113: 1665–1668.
Mercadante S, Dardanoni G, Salvaggio L, Armata MG, Agnello A . Monitoring of opioid therapy in advanced cancer pain patients. J Pain Symptom Manage 1997; 13: 204–212.
Berardelli A, Abbruzzese G, Bertolasi L, Cantarella G, Carella F, Currà A et al. Guidelines for the therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in movement disorders. Italian Study Group for Movement Disorders, Italian Society of Neurology. Ital J Neurol Sci 1997; 18: 261–269.
Helveston EM . Surgical Management of Strabismus. An Atlas of Strabismus Surgery, 4th ed. St Louis: CV Mosby, 1993, pp 345–354.
Drummond GT, Hinz BJ . Botulinum toxin for blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm: stability of duration of effect and dosage over time. Can J Ophthalmol 2001; 36: 398–403.
Ainsworth JR, Kraft SP . Long-term changes in duration of relief with botulinum toxin treatment of essential blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Ophthalmology 1995; 102: 2036–2040.
Defazio G, Abbruzzese G, Girlanda P, Vacca L, Currà A, De Salvia R et al. Botulinum toxin A treatment for primary hemifacial spasm: a 10-year multicenter study. Arch Neurol 2002; 59: 418–420.
Wabbels B, Förl M . Botulinum toxin treatment for crocodile tears, spastic entropion and for dysthyroid upper eyelid retraction. Ophthalmologe 2007; 104: 771–776.
Lowe SS, Nekolaichuk CL, Fainsinger RL, Lawlor PG . Should the rate of opioid dose escalation be included as a feature in a cancer pain classification system? J Pain Symptom Manage 2008; 35: 51–57.
Truong D, Comella C, Fernandez HH, Ondo WG . Dysport Benign Essential Blepharospasm Study Group. Efficacy and safety of purified botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) for the treatment of benign essential blepharospasm: a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2008; 14: 407–414.
Simpson DM, Blitzer A, Brashear A, Comella C, Dubinsky R, Hallett M et al. Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Assessment: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders (an evidence-based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008; 70: 1699–1706.
Hallett M, Evinger C, Jankovic J, Stacy M . BEBRF International Workshop. Update on blepharospasm: report from the BEBRF International Workshop. Neurology 2008; 71: 1275–1282.
Cetinkaya A, Brannan PA . What is new in the era of focal dystonia treatment? Botulinum injections and more. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2007; 18: 424–429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cillino, S., Raimondi, G., Guépratte, N. et al. Long-term efficacy of botulinum toxin A for treatment of blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm, and spastic entropion: a multicentre study using two drug-dose escalation indexes. Eye 24, 600–607 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2009.192
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2009.192
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How to face the hemifacial spasm: challenges and misconceptions
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2024)
-
Validation of a new hemifacial spasm grading questionnaire (HFS score) assessing clinical and quality of life parameters
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)
-
Botulinum Toxin for the Head and Neck: a Review of Common Uses and Recent Trends
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2020)
-
Treatment of blepharospasm and Meige’s syndrome with abo- and onabotulinumtoxinA: long-term safety and efficacy in daily clinical practice
Journal of Neurology (2020)