Abstract
Aims
To determine the efficacy and safety of intravitreal ranibizumab in the treatment of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) secondary to pathologic myopia (PM).
Methods
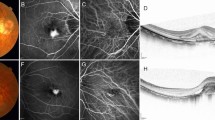
Prospective, consecutive, non-randomized, interventional case series of 23 eyes of 23 patients with CNV secondary to PM treated with intravitreal ranibizumab as needed, after the first injection (PRN: Pro Re Nata). Patients were followed-up monthly with best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), biomicroscopy, fluorescein angiography, and optical coherence tomography.
Results
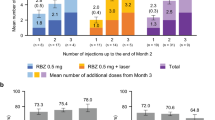
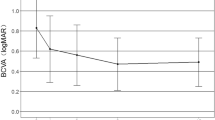
There were 23 eyes of 23 patients, and the mean age was 51.08 (SD=17.40) years. One patient was lost during the follow-up. At the 12-month follow-up, the mean VA improved by 9.53 letters (P<0.05). In all, 69% of patients increased at least one line, and 34.7% increased three or more lines. There were no cases of moderate vision loss (>3 lines) or severe vision loss (>6 lines). Favourable outcomes were obtained in all subgroups. Patients received an average of 1.52 injections. No serious ocular complications were noted.
Conclusions
The 12-month results of this consecutive series of 23 patients suggests that a small number of injections of intravitreal ranibizumab may be safe and effective for both preventing and restoring visual loss in patients with CNV secondary to PM. Further studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy are justified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ghafour IM, Allan D, Foulds WS . Common causes of blindness and visual handicap in the west of Scotland. Br J Ophthalmol 1983; 67: 209–213.
Avila MP, Weiter JJ, Jalkh AE, Trempe CL, Pruett RC, Schepens CL . Natural history of choroidal neovascularization in degenerative myopia. Ophthalmology 1984; 91: 1573–1581.
Verteporfin in Photodynamic Therapy Study Group. Photodynamic therapy of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in pathologic myopia with verteporfin. 1-year results of a randomized clinical trial—VIP report no. 1. Ophthalmology 2001; 108: 841–852.
Nguyen QD, Shah S, Tatlipinar S, Do DV, Anden EV, Campochiaro PA . Bevacizumab suppresses choroidal neovascularisation caused by pathological myopia. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89: 1368–1370.
Yamamoto I, Rogers HA, Reichel E, Yates P, Ducker J Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) as treatment for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to pathologic myopia. Br J Ophthalmol 2007; 91: 157–160.
Sakaguchi H, Ikuno Y, Gomi F, Kamei M, Sawa M, Tsujikawa M et al. Intravitreal injection of bevacizumab for choroidal neovascularisation associated with pathological myopia. Br J Ophthalmol 2007; 91: 161–165.
Tong JP, Chan WM, Liu DT, Lai TY, Choy KW, Pang CP et al. Aqueous humor levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelium-derived factor in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and choroidal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 2006; 141: 456–462.
Nishijima K, Ng YS, Zhong L, Bradley J, Schubert W, Jo N et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is a survival factor for retinal neurons and a critical neuroprotectant during the adaptative response to ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 2007; 171 (1): 53–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Some of the content of this paper was presented at the ISOPT Meeting, Budapest February 2008
Proprietary interest: None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monés, J., Amselem, L., Serrano, A. et al. Intravitreal ranibizumab for choroidal neovascularization secondary to pathologic myopia: 12-month results. Eye 23, 1275–1281 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2009.88
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2009.88
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of anatomical and functional outcomes of treating myopic choroidal neovascularization with bevacizumab or ranibizumab
International Ophthalmology (2023)
-
The efficacy of different anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents and prognostic biomarkers in monitoring of the treatment for myopic choroidal neovascularization
International Ophthalmology (2022)
-
Baseline characteristics of myopic choroidal neovascularization in patients above 50 years old and prognostic factors after intravitreal conbercept treatment
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Long-term outcomes of the intravitreal injection of ranibizumab for the treatment of choroidal neovascularization secondary to pathologic myopia
International Ophthalmology (2020)
-
Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization: Diagnosis and Treatment Update
Current Ophthalmology Reports (2019)