Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate serum levels of YKL-40 in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEX) in comparison with those of age- and sex-matched healthy subjects.
Methods
Forty patients with PEX (PEX group) and 40 age- and sex-matched control subjects (control group) were enrolled in the study. An enzyme immunoassay method using the commercially available test MicroVue YKL-40 was used to measure serum YKL-40 concentration. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures, serum levels of high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), and triglycerides were also examined.
Results
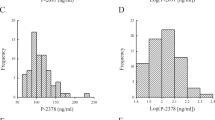
The mean age was 54.4±7.6 (ranging 41–65) years in each group. The mean serum YKL-40 level of the PEX group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.001). In addition, the mean serum HsCRP, total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides levels were significantly higher, and mean serum HDL level was significantly lower in the PEX group than in the control group (all P<0.001, excluding both P=0.002 for triglycerides and HDL levels). Further, the mean systolic and diastolic blood pressures were significantly higher in the PEX group than in the control group (P1=0.001 and P2=0.01, respectively).
Conclusion
We have shown a relationship between PEX and elevated serum levels of YKL-40. We imply that a better understanding of the role of YKL-40 in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis is necessary to develop new therapies for preventing or treating PEX. Further studies are warranted to clarify the clinical relevance of these findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Streeten BW, Li Z-Y, Wallace RN, Eagle RC, Keshgegian AA . Pseudoexfoliative fibrillopathy in visceral organs of a patient with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Arch Ophtalmol 1992; 110: 1757–1762.
Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Naumann GO . Ocular and systemic pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 2006; 141: 921–937.
Ritch R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U . Exfoliation syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol 2001; 45: 265–315.
Vesti E, Kivela T . Exfoliation syndrome and exfoliation glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res 2000; 19: 345–368.
Ritch R . Exfoliation syndrome-the most common identifiable cause of open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma 1994; 3: 176–177.
Hietanen J, Soisalon-Soininen S, Kivela T, Tarkkanen A . Evaluation of the clinical association between exfoliation syndrome and abdominal aortic aneurysm. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2002; 80: 617–619.
Schumacher S, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Martus P, Lang W, Naumann GO . Pseudoexfoliation syndrome and aneurysms of the abdominal aorta. Lancet 2001; 357: 359–360.
Rathcke CN, Vestergaard H . YKL-40, a new inflammatory marker with relation to insulin resistance and with a role in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Inflamm Res 2006; 55: 221–227.
Rathcke CN, Raymond I, Kistorp C, Hildebrandt P, Faber J, Vestergaard H . Low grade inflammation as measured by levels of YKL-40: association with an increased overall and cardiovascular mortality rate in an elderly population. Int J Cardiol 2010; 143: 35–42.
Kastrup J, Johansen JS, Winkel P, Hansen JF, Hildebrandt P, Jensen GB et al. High serum YKL-40 concentration is associated with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J 2009; 30: 1066–1072.
Boot RG, van Achterberg TA, van Aken BE . Strong induction of members of the chitinase family of proteins in atherosclerosis: chitotriosidase and human cartilage gp-39 expressed in lesion macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19: 687–694.
Johansen JS . Studies on serum YKL-40 as a biomarker in diseases with inflammation, tissue remodelling, fibroses and cancer. Dan Med Bull 2006; 53: 172–209.
Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD . Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 25803–25810.
Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ . Identification of a 38-kDa heparin-binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 13076–13083.
Rehli M, Krause SW, Andreesen R . Molecular characterization of the gene for human cartilage gp-39(CHI3L1), a member of the chitinase protein family and marker for late stages of macrophage differentiation. Genomics 1997; 43: 221–225.
Renkema GH, Boot RG, Au FL, Donker-Koopman WE, Strijland A, Muijsers AO et al. Chitotriosidase, a chitinase, and the 39-kDa human cartilage glycoprotein, a chitin-binding lectin, are homologues of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases secreted by human macrophages. Eur J Biochem 1998; 251: 504–509.
Boot RG, Renkema GH, Strijland A, van Zonneveld AJ, Aerts JM . Cloning of a cDNA encoding chitotriosidase, a human chitinase produced by macrophages. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 26252–26256.
de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Gibson CM, Antman EM et al. Association between plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and long-term clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2003; 107: 690–695.
Malinda KM, Ponce L, Kleinman HK, Shackelton LM, Millis AJ . Gp38k, a protein synthesized by vascular smooth muscle cells, stimulates directional migration of human umbilical veinendothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 1999; 250: 168–173.
Wang Y, Ripa RS, Johansen JS, Gabrielsen A, Steinbruchel DA, Friis T et al. YKL-40 a new biomarker in patients with acute coronary syndrome or stable coronary artery disease. Scand Cardiovasc J 2008; 42: 295–302.
Nojgaard C, Host NB, Christensen IJ, Poulsen SH, Egstrup K, Price PA et al. Serum levels of YKL-40 increases in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis 2008; 19: 257–263.
Repo LP, Teräsvirta ME, Koivisto KJ . Generalized transluminance of the iris and the frequency of the pseudoexfoliation syndrome in the eyes of transient ischemic attack patients. Ophthalmology 1993; 100: 352–355.
Mitchell P, Wang JJ, Smith W . Association of pseudoexfoliation syndrome with increased vascular risk. Am J Ophthalmol 1997; 124: 685–687.
Bojic L, Ermacora R, Polic S, Ivanisevic M, Mandic Z, Rogosic V et al. Pseudoexfoliation syndrome and asymptomatic myocardial dysfunction. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2005; 243: 446–449.
Andrikopoulos GK, Mela EK, Georgakopoulos CD, Papadopoulos GE, Damelou AN, Alexopoulos DK et al. Pseudoexfoliation syndrome prevalence in Greek patients with cataract and its association to glaucoma and coronary artery disease. Eye 2009; 23: 442–447.
Yüksel N, Pirhan D, Altintaş O, Cağlar Y . Systemic high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. J Glaucoma 2010; 19: 373–376.
Miyazaki M, Kubota T, Kubo M, Kiyohara Y, Iida M, Nose Y et al. The prevalence of pseudoexfoliation syndrome in a Japanese population: the Hisayama study. J Glaucoma 2005; 14: 482–484.
Damji KF, Bains HS, Stefansson E, Loftsdottir M, Sverrisson T, Thorgeirsson E et al. Is pseudoexfoliation syndrome inherited? A review of genetic and nongenetic factors and a new observation. Ophthalmic Genet 1998; 19: 175–185.
Janciauskiene S, Krakau T . Alzheimer’s peptide and serine proteinase inhibitors in glaucoma and exfoliation syndrome. Doc Ophthalmol 2003; 106: 215–223.
Cumurcu T, Ozyurt H, Demir HD, Yardim H . Serum alpha-1-antitriypsin levels in patients with pseudoexfolative syndrome. Curr Eye Res 2008; 33: 159–162.
Fiore PM, Melamed S, Epstein DL . Trabecular precipitates and elevated intraocular pressure following argon laser trabeculoplasty. Ophthalmic Surg 1989; 20: 697–701.
Cumurcu T, Sahin S, Aydin E . Serum homocysteine, vitamin B12 and folic acid levels in different types of glaucoma. BMC Ophthalmol 2006; 6: 6.
Puustjarvi T, Blomster H, Kontkanae M, Punnonen K, Terasvirta M . Plasma and aqueous humour levels of homocysteine in exfoliation syndrome. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004; 242: 749–754.
Yxfeldt A, Wallberg-Jonsson S, Hultdin J, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S . Homocysteine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in relation to inflammation and B-vitamin treatment. Scand J Rheumatol 2003; 32: 205–210.
Su SJ, Huang LW, Pai LS, Liu HW, Chang KL . Homocysteine at pathophysiologic concentrations activates human monocyte and induces cytokine expression and inhibits macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression. Nutrition 2005; 21: 994–1002.
Holven KB, Aukrust P, Retterstol K, Hangve TA, Morkid L, Ose L et al Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2006; 66: 45–54.
Tso TK, Huang WN, Huang HY, Chang CK . Relationship of plasma interleukin-18 concentrations to traditional and non-traditional cardiovascular risk factors in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2006; 45: 1148–1153.
Vasavada RM, Ritch R, Liebmann JM, Jole M . Plasma homocysteine is elevated in patients with exfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 2003; 136: 41–46.
Tranchina L, Centofanti M, Oddone F, Tanga L, Roberti G, Liberatoscioli L et al. Levels of plasma homocysteine in pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2011; 249: 443–448.
Bojesen SE, Johansen JS, Nordestgaard BG . Plasma YKL-40 levels in healthy subjects from the general population. Clin Chim Acta 2011; 412: 709–712.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Türkyılmaz, K., Öner, V., Kırbas, A. et al. Serum YKL-40 levels as a novel marker of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Eye 27, 854–859 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.92
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.92
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of genetically determined gene expression suggests role of inflammatory processes in exfoliation syndrome
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of perioperative complications in patients with PEX Syndrome during cataract surgery
International Ophthalmology (2022)
-
YKL-40 is a local marker for inflammation in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome
Eye (2019)
-
Atherogenic indices in pseudoexfoliation syndrome
Eye (2019)
-
Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pseudoexfoliation syndrome
Eye (2016)