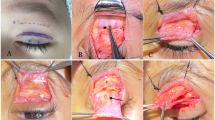
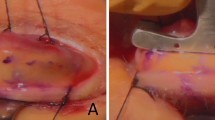
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the surgical outcome of levator resection with suspensory ligament of the superior fornix (SLSF) suspension in severe congenital ptosis with poor levator function (LF).
Patients and methods
The medical records of 25 patients who underwent levator resection with SLSF suspension between March 2011 and January 2013 were retrospectively reviewed. All of the patients had severe congenital ptosis (>4 mm) and poor LF (<4 mm). The follow-up time ranged from 12 to 18 months (median, 15 months). Data regarding eyelid position, cosmetic outcomes, and postoperative complications were evaluated.
Results
The average preoperative margin reflex distance-1 (MRD1) measured −0.30±0.11 mm. The average postoperative MRD1 measured 3.1±1.25 mm at the last follow-up visit. There was a statistically significant difference between preoperative and postoperative MRD1 values (P<0.001). Excellent cosmetic results occurred in 14 patients, good cosmetic results occurred in eight patients and poor cosmetic results did not occur. Three patients (12%) underwent reoperation for residual ptosis. No serious postoperative complications occurred.
Conclusion
Levator resection with SLSF suspension is very effective in the treatment of severe congenital ptosis with poor LF. This surgery technique results in high functional and cosmetic successes in the long term.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
SooHoo JR, Davies BW, Allard FD, Durairaj VD . Congenital ptosis. Surv Ophthalmol 2014; 59 (5): 483–492.
Lee SY, Yonn JS . Long-term functional and cosmetic outcomes after frontalis suspension using autogenous fascia lata for pediatric congenital ptosis. Ophthalmology 2009; 116: 1405–1414.
Epstein GA, Putterman AM . Super-maximum levator resection for severe unilateral congenital blepharoptosis. Ophthalmic Surg 1984; 15: 971–979.
Putterman AM, Shields M, Pak J . Superior tarsectomy augment super-maximum levator resection in correction of severe blepharoptosis with poor levator function. Ophthalmology 2006; 113: 1201–1208.
Holmström H, Santanelis F . Suspension of the eyelid on the check ligament of the superior for congenital blepharoptosis. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 2002; 36: 149–156.
Holmström H, Bernström-Lundberg C, Oldfors A . Anatomical study of the structures at the roof of the orbit with the special reference to the check ligament of the superior fornix. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 2002; 36: 157–159.
Santanelli F, Paolini G, Renzi LF, Longo B, Pagnoni M, Holmström H . Correction of myopathic blepharoptosis by check ligamentsuspension: Clinical evaluation of 89 eyelids. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 2011; 45: 194–199.
Pan E, Zhang Y, Li L, Shen SY, Wang XY, Wang HY et al. [Check ligament suspension for correction of congenital severe blepharoptosis]. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2011; 27: 253–256.
Simon B, Macedo AA, Schwacz RM, Wang DY, McCann JD, Goldberg RA . Frontalis suspension for upper eyelid ptosis: evaluation of different surgical designs and suture material. Am J Ophthalmol 2005; 140: 877–885.
Edmunds B, Manners RM, Weller PO, Steart P, Collin JR . Levator palpebrae superioris fibre size in normal and patients with congenital ptosis. Eye 1998; 12: 47–50.
Baldwin HC, Manners RM . Congenital blepharoptosis: a literature review of the histology of levator palpebrae superioris muscle. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2002; 18: 301–307.
Baik BS, Ha W, Lee JW, Ji SY, Yang WS, Park D et al. Adjunctive techniques to traditional advancement procedures for treatement severe blepharoptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014; 133: 887–896.
Pak DH, Choi WS, Yoon SH, Shim JS . Comparison of levator resection and frontalis muscle transfer in the treatment of severe blepharoptosis. Ann Plast Surg 2007; 59: 388–392.
Göncü T, Cakmak S, Akal A, Karaismailoğlu E . Improvement in levator function after anterior levator resection for the treatment of congenital ptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2015; 31: 197–201.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC no 81470660), the Xiamen Science and Technology Plan Projects (no 3502Z20131017 and no 3502Z20159017) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (no 2015-ZQN-ZD-34 and 2016D13). The research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not for profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Liu, Z., Tian, Q. et al. Levator resection with suspensory ligament of the superior fornix suspension for correction of pediatric congenital ptosis with poor levator function. Eye 30, 1490–1495 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.165
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.165