Abstract
Purpose
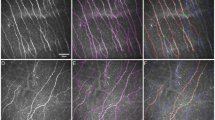
This study was designed to compare and contrast quantitative data of the human corneal sub-basal nerve plexus (SBP) evaluated by two different methods: in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM), and immunohistochemical staining of ex vivo donor corneas.
Methods
Seven parameters of the SBP in large-scale IVCM mosaicking images from healthy subjects were compared with the identical parameters in ex vivo donor corneas stained by β-III-tubulin immunohistochemistry. Corneal nerve fiber length (CNFL), corneal nerve fiber density (CNFD), corneal nerve branch density (CNBD), average weighted corneal nerve fiber tortuosity (CNFTo), corneal nerve connection points (CNCP), average corneal nerve single-fiber length (CNSFL), and average weighted corneal nerve fiber thickness (CNFTh) were calculated using a dedicated, published algorithm and compared.
Results
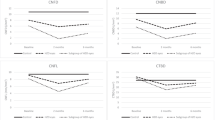
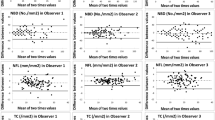
Our experiments showed significantly higher values for CNFL (50.2 vs 21.4 mm/mm2), CNFD (1358.8 vs 277.3 nerve fibers/mm2), CNBD (847.6 vs 163.5 branches/mm2), CNFTo (0.095 vs 0.081 μm−1), and CNCP (49.4 vs 21.6 connections/mm2) in histologically staining specimens compared with IVCM images. In contrast, CNSFL values were higher in IVCM images than in histological specimens (32.1 vs 74.1 μm). No significant difference was observed in CNFTh (2.22 vs 2.20 μm) between the two groups.
Conclusions
The results of this study have shown that IVCM has an inherently lower resolution compared with ex vivo immunohistochemical staining of the corneal SBP and that this limitation leads to a systematic underestimation of several SBP parameters. Despite this shortcoming, IVCM is a vital clinical tool for in vivo characterization, quantitative clinical imaging, and evaluation of the human corneal SBP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Tavakoli M, Quattrini C, Abbott C, Kallinikos P, Marshall A, Finnigan J et al. Corneal confocal microscopy: a novel noninvasive test to diagnose and stratify the severity of human diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2010; 33 (8): 1792–1797.
Shtein RM, Callaghan BC . Corneal confocal microscopy as a measure of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2013; 62 (1): 25–26.
Ziegler D, Papanas N, Zhivov A, Allgeier S, Winter K, Ziegler I et al. Early detection of nerve fiber loss by corneal confocal microscopy and skin biopsy in recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2014; 63: 2454–2463.
Tavakoli M, Ferdousi M, Petropoulos IN, Morris J, Pritchard N, Zhivov A et al. Normative values for corneal nerve morphology assessed using corneal confocal microscopy: a multinational normative data set. Diabetes Care 2015; 38 (5): 838–843.
Winter K, Scheibe P, Köhler B, Allgeier S, Guthoff RF, Stachs O . Local variability of parameters for characterization of the corneal subbasal nerve plexus. Curr Eye Res 2016; 41 (2): 186–198.
Turuwhenua JT, Patel DV, McGhee CN . Fully automated montaging of laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy images of the human corneal subbasal nerve plexus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53 (4): 2235–2242.
Edwards K, Pritchard N, Gosschalk K, Sampson GP, Russell A, Malik RA et al. Wide-field assessment of the human corneal subbasal nerve plexus in diabetic neuropathy using a novel mapping technique. Cornea 2012; 31 (9): 1078–1082.
Allgeier S, Maier S, Mikut R, Peschel S, Reichert KM, Stachs O et al. Mosaicking the subbasal nerve plexus by guided eye movements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55 (9): 6082–6089.
Zhivov A, Winter K, Hovakimyan M, Peschel S, Harder V, Schober HC et al. Imaging and quantification of subbasal nerve plexus in healthy volunteers and diabetic patients with or without retinopathy. PLoS One 2013; 8 (1): e52157.
Winter K, Allgeier S, Eberle F, Köhler B, Maier S, Stachs O et al. Software-based imaging and segmentation of corneal nerve fibres. Biomed Tech (Berl) 2013; 58 (suppl 1); doi:10.1515/bmt-2013-4293.
Petropoulos IN, Alam U, Fadavi H, Marshall A, Asghar O, Dabbah MA et al. Rapid automated diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with in vivo corneal confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55 (4): 2071–2078.
Dehghani C, Pritchard N, Edwards K, Russell AW, Malik RA, Efron N . Fully automated, semiautomated, and manual morphometric analysis of corneal subbasal nerve plexus in individuals with and without diabetes. Cornea 2014; 33 (7): 696–702.
Sindt CW, Lay B, Bouchard H, Kern JR . Rapid image evaluation system for corneal in vivo confocal microscopy. Cornea 2013; 32 (4): 460–465.
Coleman R . The impact of histochemistry—a historical perspective. Acta Histochem 2000; 102 (1): 5–14.
Matos LL, Trufelli DC, de Matos MG, da Silva Pinhal MA . Immunohistochemistry as an important tool in biomarkers detection and clinical practice. Biomark Insights 2010; 5: 9–20.
Teruya-Feldstein J . The immunohistochemistry laboratory: looking at molecules and preparing for tomorrow. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010; 134 (11): 1659–1665.
Marfurt CF, Cox J, Deek S, Dvorscak L . Anatomy of the human corneal innervation. Exp Eye Res 2010; 90 (4): 478–492.
Al-Aqaba MA, Fares U, Suleman H, Lowe J, Dua HS . Architecture and distribution of human corneal nerves. Br J Ophthalmol 2010; 94 (6): 784–789.
He J, Bazan NG, Bazan HE . Mapping the entire human corneal nerve architecture. Exp Eye Res 2010; 91 (4): 513–523.
Kheirkhah A, Muller R, Mikolajczak J, Ren A, Kadas EM, Zimmermann H et al. Comparison of standard versus wide-field composite images of the corneal subbasal layer by in vivo confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015; 56 (10): 5801–5807.
Köhler B, Allgeier S, Stachs O, Winter K, Bretthauer G . Software-based imaging and quantitative analysis of the corneal sub-basal nerve plexus. Nova Acta Leopold 2014; 119 (401): 127–142.
Allgeier S, Zhivov A, Eberle F, Köhler B, Maier S, Bretthauer G et al. Image reconstruction of the subbasal nerve plexus with in vivo confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52: 5022–5028.
Jiang MS, Yuan Y, Gu ZX, Zhuang SL . Corneal confocal microscopy for assessment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol 2015; 100: 9–14.
Parissi M, Karanis G, Randjelovic S, Germundsson J, Poletti E, Ruggeri A et al. Standardized baseline human corneal subbasal nerve density for clinical investigations with laser-scanning in vivo confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54 (10): 7091–7102.
Niederer RL, Perumal D, Sherwin T, McGhee CN . Corneal innervation and cellular changes after corneal transplantation: an in vivo confocal microscopy study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (2): 621–626.
Patel DV, Ku JY, Johnson R, McGhee CN . Laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy and quantitative aesthesiometry reveal decreased corneal innervation and sensation in keratoconus. Eye (Lond) 2009; 23 (3): 586–592.
Jalbert I, Stapleton F, Papas E, Sweeney DF, Coroneo M . In vivo confocal microscopy of the human cornea. Br J Ophthalmol 2003; 87 (2): 225–236.
Dehghani C, Pritchard N, Edwards K, Vagenas D, Russell AW, Malik RA et al. Morphometric stability of the corneal subbasal nerve plexus in healthy individuals: a 3-year longitudinal study using corneal confocal microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55 (5): 3195–3199.
Erie JC, McLaren JW, Hodge DO, Bourne WM . The effect of age on the corneal subbasal nerve plexus. Cornea 2005; 24 (6): 705–709.
Tervo T, Holopainen J, Belmonte C . Confocal microscopy of corneal nerves-a limited but still useful technique to evaluate peripheral neuropathies. JAMA Ophthalmol 2016; 134 (9): 990–991.
Müller LJ, Marfurt CF, Kruse F, Tervo TM . Corneal nerves: structure, contents and function. Exp Eye Res 2003; 76 (5): 521–542.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by DFG (KO-4979/1-1) and BMBF (RESPONSE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kowtharapu, B., Winter, K., Marfurt, C. et al. Comparative quantitative assessment of the human corneal sub-basal nerve plexus by in vivo confocal microscopy and histological staining. Eye 31, 481–490 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.220
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.220
This article is cited by
-
En Face and Cross-sectional Corneal Tomograms Using Sub-micron spatial resolution Optical Coherence Tomography
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Morphometrische Charakterisierung des subbasalen Nervenplexus
Der Ophthalmologe (2017)